Binary Search
- [专题1.二分查找](#001.Binary Search)
- [有序中查找两个元素](# search for a range)
001.Binary Search
// template 1
// end the loop ,the left==right
int binarySearch(vector<int>& nums, int target){
if(nums.size() == 0)
return -1;
int left = 0, right = nums.size();
while(left < right){
// Prevent (left + right) overflow
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target)
{ return mid; }
else if(nums[mid] < target)
{ left = mid + 1; }
else
{ right = mid; }
}
// Post-processing:
// End Condition: left == right
if(left != nums.size() && nums[left] == target)
return left;
return -1;
}
// template 2
// left+1==right
// 这种方法应用到题目中就是不知道该怎么停止,确定就直接找到两个重复元素
// 就是直接指针
int binarySearch(vector<int>& nums, int target){
if (nums.size() == 0)
return -1;
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left + 1 < right){
// Prevent (left + right) overflow
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
// Post-processing:
// End Condition: left + 1 == right
if(nums[left] == target) return left;
if(nums[right] == target) return right;
return -1;
}
search for a range
// 我感觉题目有问题
// 而且,这个代码还是不是理解的很透彻
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int> res(2,-1);
if(nums.size()<=0)
return res;
int start=0;
int end=nums.size()-1;
while(start+1<end){
int mid=start+(end-start)/2;
if(nums[mid]<target)
start=mid+1;
else
end=mid;
}
if(nums[start]==target && nums[end]==target)
{
res[0]=start;
res[1]=end;
}
return res;
}
};
三种模版之间的比较
Note: The templates and their differences have been colored coded below.
Some problems can be implemented using multiple templates, but as you practice more, you will notice that some templates are more suited for certain problems than others.
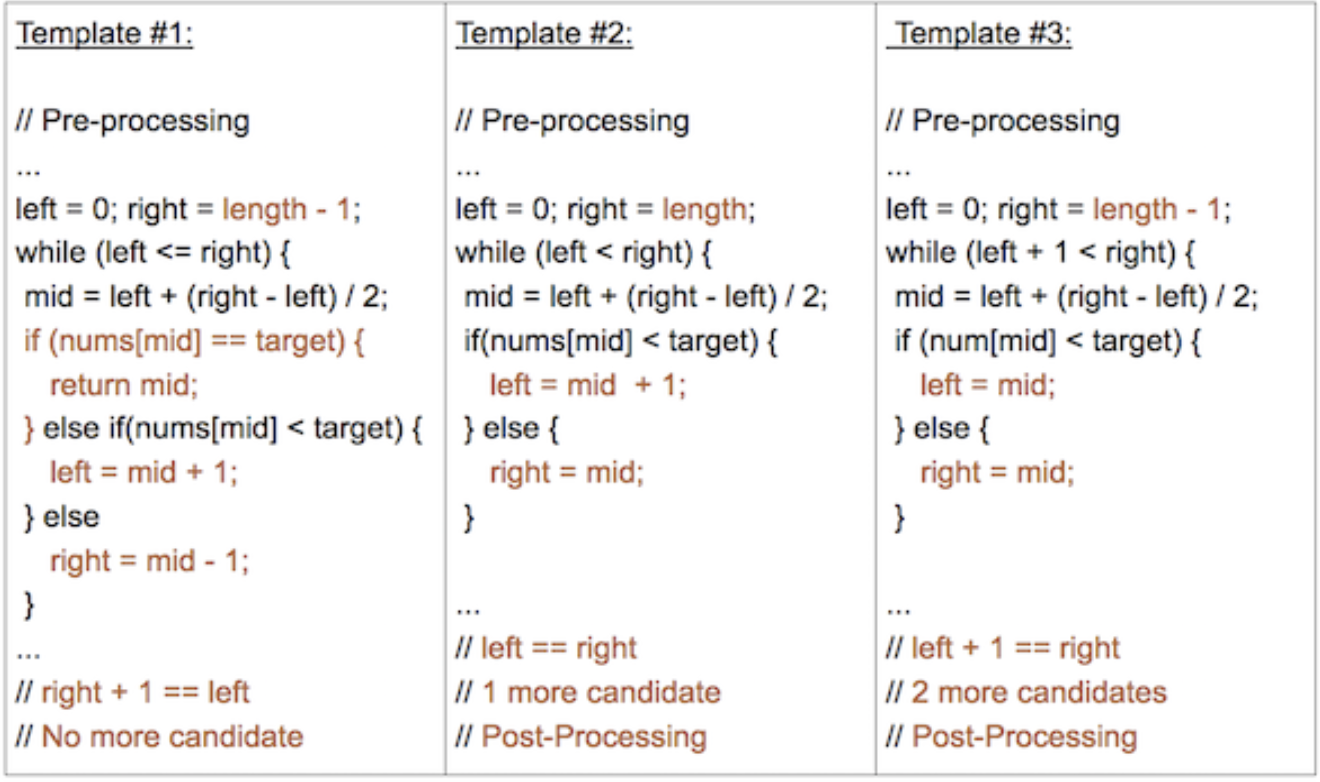
These 3 templates differ by their:
- left, mid, right index assignments
- loop or recursive termination condition
- necessity of post-processing
