1290.二进制链表转整数
[1290.二进制链表转整数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/Convert-Binary-Number-in-a-Linked-List-to Integer)
给你一个单链表的引用结点 head。链表中每个结点的值不是 0 就是 1。已知此链表是一个整数数字的二进制表示形式。
请你返回该链表所表示数字的 十进制值 。
样例输入与样例输出 Sample Input and Sample Output
示例 1:
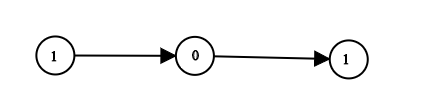
**输入:** head = [1,0,1]
**输出:** 5
**解释:** 二进制数 (101) 转化为十进制数 (5)
示例 2:
**输入:** head = [0]
**输出:** 0
示例 3:
**输入:** head = [1]
**输出:** 1
示例 4:
**输入:** head = [1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
**输出:** 18880
示例 5:
**输入:** head = [0,0]
**输出:** 0
提示 Hint
提示:
- 链表不为空。
- 链表的结点总数不超过
30。 - 每个结点的值不是
0就是1。
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int getDecimalValue(ListNode* head) {
int ans(0);
ListNode *p = head;
while(p != nullptr) {
ans = ans * 2 + (p->val);
p = p->next;
}
return ans;
}
};
1291.顺次数
我们定义「顺次数」为:每一位上的数字都比前一位上的数字大 1 的整数。
请你返回由 [low, high] 范围内所有顺次数组成的 有序 列表(从小到大排序)。
样例输入与样例输出 Sample Input and Sample Output
示例 1:
**输出:** low = 100, high = 300
**输出:** [123,234]
示例 2:
**输出:** low = 1000, high = 13000
**输出:** [1234,2345,3456,4567,5678,6789,12345]
提示 Hint
提示:
10 <= low <= high <= 10^9
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sequentialDigits(int low, int high) {
vector<int>ans = {12,23,34,45,56,67,78,89,123,234,345,456,567,678,789,1234,2345,3456,4567,5678,6789,12345,23456,34567,45678,56789,123456,234567,345678,456789,1234567,2345678,3456789,12345678,23456789,123456789};
vector<int>ret;
int p = lower_bound(ans.begin(),ans.end(),low)-ans.begin();
int n = ans.size();
while(p < n && ans[p] <= high) ret.push_back(ans[p++]);
return ret;
}
};
1292.元素和小于等于阈值的正方形的最大边长
给你一个大小为 m x n 的矩阵 mat 和一个整数阈值 threshold。
请你返回元素总和小于或等于阈值的正方形区域的最大边长;如果没有这样的正方形区域,则返回 0。
样例输入与样例输出 Sample Input and Sample Output
示例 1:
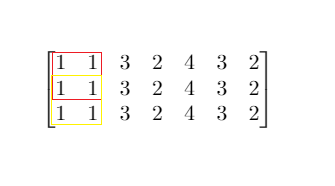
**输入:** mat = [[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2],[1,1,3,2,4,3,2]], threshold = 4
**输出:** 2
**解释:** 总和小于 4 的正方形的最大边长为 2,如图所示。
示例 2:
**输入:** mat = [[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2],[2,2,2,2,2]], threshold = 1
**输出:** 0
示例 3:
**输入:** mat = [[1,1,1,1],[1,0,0,0],[1,0,0,0],[1,0,0,0]], threshold = 6
**输出:** 3
示例 4:
**输入:** mat = [[18,70],[61,1],[25,85],[14,40],[11,96],[97,96],[63,45]], threshold = 40184
**输出:** 2
提示 Hint
提示:
1 <= m, n <= 300m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length0 <= mat[i][j] <= 100000 <= threshold <= 10^5
代码
class Solution {
public:
int s[300][300];
int n, m;
int maxSideLength(vector<vector<int>>& mat, int threshold) {
this->n = mat.size(), this->m = mat[0].size();
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
s[i][j] = mat[i][j];
if(i)
s[i][j] += s[i - 1][j];
if(j)
s[i][j] += s[i][j - 1];
if(i && j)
s[i][j] -= s[i - 1][j - 1];
}
int first = 0, middle, half, len = min(n, m);
const int key = threshold;
while(len > 0) {
half = len >> 1;
middle = first + half;
//cout << middle << "
";
if(cal(middle) > key)
len = half;
else {
first = middle + 1;
len = len - half - 1;
}
}
//cout << "first " << first << "
";
return cal(first)>key ? first - 1 : first;
}
private :
int getSum(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
int ans = s[x2][y2];
if(x1 && y1)
ans += s[x1 - 1][y1 - 1];
if(x1)
ans -= s[x1 - 1][y2];
if(y1)
ans -= s[x2][y1 - 1];
//cout << x1 << " " << y1 << " " << x2 << " " << y2 << ":" << ans << "
";
return ans;
}
int cal(int x) {
if(x == 0) return 0;
int ans = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i = x - 1; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = x - 1; j < m; ++j) {
int t = getSum(i - x + 1, j - x + 1, i, j);
ans = min(ans, t);
}
//cout << "len " << x << ":" << ans << endl;
return ans;
}
};
1293.网格中的最短路径
[1293.网格中的最短路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination)
给你一个 m * n 的网格,其中每个单元格不是 0(空)就是 1(障碍物)。每一步,您都可以在空白单元格中上、下、左、右移动。
如果您 最多 可以消除 k 个障碍物,请找出从左上角 (0, 0) 到右下角 (m-1, n-1)
的最短路径,并返回通过该路径所需的步数。如果找不到这样的路径,则返回 -1。
样例输入与样例输出 Sample Input and Sample Output
示例 1:
**输入:**
grid =
[[0,0,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,0],
[0,1,1],
[0,0,0]],
k = 1
**输出:** 6
**解释:** 不消除任何障碍的最短路径是 10。
消除位置 (3,2) 处的障碍后,最短路径是 6 。该路径是 (0,0) -> (0,1) -> (0,2) -> (1,2) -> (2,2) -> **(3,2)** -> (4,2).
示例 2:
**输入:**
grid =
[[0,1,1],
[1,1,1],
[1,0,0]],
k = 1
**输出:** -1
**解释:** 我们至少需要消除两个障碍才能找到这样的路径。
提示 Hint
提示:
grid.length == mgrid[0].length == n1 <= m, n <= 401 <= k <= m*ngrid[i][j] == 0 **or** 1grid[0][0] == grid[m-1][n-1] == 0
代码
class Solution {
public:
int shortestPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int k) {
queue<node>que;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int ans = inf;
n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
que.push(node(0, 0, k, 0));
while(!que.empty()) {
node cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(grid[cur.r][cur.c])
cur.k--;
vis[cur.r][cur.c][k-cur.k] = true;
if(cur.r == n - 1 && cur.c == m - 1 && cur.k >= 0) {
ans = min(ans, cur.s);
}
for(int i = 0, rr, cc; i < 4; ++i) {
rr = cur.r + dr[i], cc = cur.c + dc[i];
if(inBound(rr, cc) && !vis[rr][cc][k-cur.k] && k-cur.k <= n*m) {
que.push(node(rr, cc, cur.k, cur.s + 1));
vis[rr][cc][k-cur.k] = true;
}
}
}
return ans == inf ? -1: ans;
}
private :
struct node {
int r, c, k, s;
node(int _r,int _c,int _k,int _s):r(_r),c(_c),k(_k),s(_s){};
};
inline bool inBound(int r, int c) {
return r >= 0 && r < n && c >= 0 && c < m;
}
const int dr[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
const int dc[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int n,m;
bool vis[41][41][41*41];
};