一、thrift简介
thrift是Facebook开源的一套rpc框架,目前被许多公司使用
我理解的特点
- 使用IDL语言生成多语言的实现代码,程序员只需要实现自己的业务逻辑
- 支持序列化和反序列化操作,底层封装协议,传输模块
- 以同步rpc调用为主,使用libevent evhttp支持http形式的异步调用
- rpc服务端线程安全,客户端大多数非线程安全
- 相比protocol buffer效率差些,protocol buffer不支持rpc,需要自己实现rpc扩展,目前有grpc可以使用
由于thrift支持序列化和反序列化,并且支持rpc调用,其代码风格较好并且使用方便,对效率要求不算太高的业务,以及需要rpc的场景,可以选择thrift作为基础库
层次图:
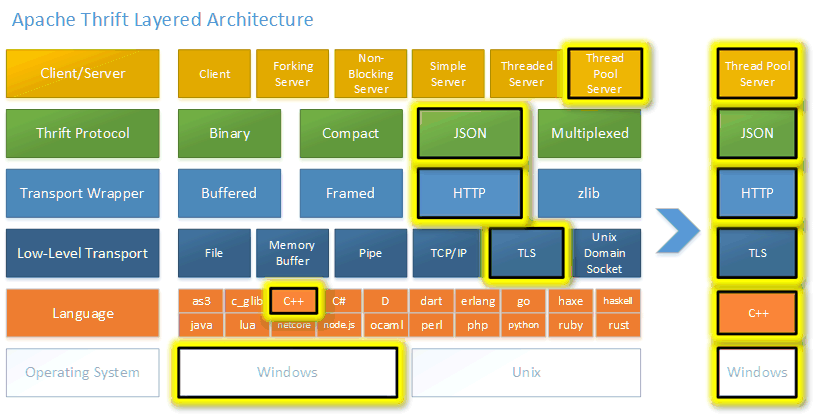
二、编译(thrift for c++ && centos7)
1、官网获取源码包 thrift-0.11.0.tar.gz 解压
tar zxvf thrift-0.11.0.tar.gz
2、安装依赖
yum -y install automake libtool flex bison pkgconfig gcc-c++ boost-devel libevent-devel zlib-devel python-devel ruby-devel openssl-devel
3、编译boost
使用boost_1_63_0.tar.gz
./bootstrap.sh
./b2
4、编译thrift
源码根目录运行
./configure && make
sudo make install
5、验证安装
thrift -version
显示 Thrift version 0.11.0
三、编写使用IDL编写.thrift文件
这里给出一个thrift的IDL基本语法列表,详细用法可以去官网查找
namespace cpp thrift.Test
//typedef 用法
typedef i32 MyInt32;
typedef string MyString;
typedef i32 UserId;
//struct 结构定义
struct TypedefTestStruct
{
1: MyInt32 field_MyInt32;
2: MyString field_MyString;
3: i32 field_Int32;
4: string filed_string;
}
//enum 枚举定义
enum Numberz
{
ONE = 1,
TWO,
THREE,
FIVE = 5,
SIX,
EIGHT = 8
}
//const 用法
const Numberz myNumberz = Numberz.ONE;
struct Bonk
{
1: string message,
2: i32 type
}
//类型嵌套
struct Xtruct
{
1: string string_thing,
2: i8 byte_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing,
4: i64 i64_thing
}
struct Xtruct2
{
1: i8 byte_thing,
2: Xtruct struct_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing
}
//支持map list set类型分别对应C++中的 map = stl::map list = stl::vector set = stl::set
typedef map<string, Bonk> MapType
struct Insanity
{
1: map<Numberz, UserId> userMap;
2: list<Xtruct> xtructs;
}
struct CrazyNesting
{
1: string string_field,
2: optional set<Insanity> set_field;
3: required list<map<set<i32>, map<i32,set<list<map<Insanity,string>>>>>> list_field,
4: binary binary_field
}
//union用法
union SomeUnion
{
1: map<NumberZ, UserId> map_thing,
2: string string_thing,
3: i32 i32_thing,
4: Xtruct3 xtruct_thing,
5: Insanity insanity_thing
}
//exception 异常
exception Xception
{
1: i32 errorCode,
2: string message
}
exception Xception2
{
1: i32 errorCode,
2: Xtruct struct_thing
}
// empty struct
struct EmptyStruct{}
struct OneField
{
1: EmptyStruct field;
}
//service 定义的一组rpc服务,一般是抽象出来的接口调用
service ThriftTest
{
void testVoid(),
string testString(1: string thing),
bool testBool(1: bool thing),
i8 testByte(1: i8 thing),
i32 testI32(1: i32 thing),
i64 testI64(1: i64 thing),
Xtruct testStruct(1: Xtruct thing),
Xtruct2 testNest(1: Xtruct2 thing),
map<string, string> testStringMap(1: map<string, string> thing),
set<i32> testSet(1: set<i32> thing),
list<i32> testList(1: list<i32> thing),
Numberz testEnum(1: Numberz thing),
map<i32, map<i32,i32>> testMapMap(1: i32 hello),
map<UserId, map<Numberz,Insanity>> testInsanity(1: Insanity argument),
Xtruct testMulti(1: i8 arg0, 2: i32 arg1, 3: i64 arg2, 4: map<i16, string> arg3, 5: Numberz arg4, 6: UserId arg5),
void testException(1: string arg) throws(1: Xception err1),
Xtruct testMultiException(1: string arg0, 2: string arg1) throws(1: Xception err1, 2: Xception2 err2),
oneway void testOneway(1:i32 secondsToSleep)
}
四、使用thrift文件生成C++代码
1、生成同步调用的C++代码
thrift -r --gen cpp xxx.thrift
2、生成异步调用的C++代码(同时同步调用的代码也被生成)
thrift --gen cpp:cob_style xxx.thrift
五、thrfit同步调用
1、StressTest.thrift文件
namespace cpp test.stress
service Service {
void echoVoid(),
i8 echoByte(1: i8 arg),
i32 echoI32(1: i32 arg),
i64 echoI64(1: i64 arg),
string echoString(1: string arg),
list<i8> echoList(1: list<i8> arg),
set<i8> echoSet(1: set<i8> arg),
map<i8, i8> echoMap(1: map<i8, i8> arg),
}
2、使用thrift -r --gen cpp StressTest.thrift 生成代码
gen-cpp目录有
StressTest_types.h StressTest_types.cpp StressTest_constants.h StressTest_constants.cpp Service.h Service.cpp Service_server.skeleton.cpp
生成
StressTest_types.h StressTest_constants.h 为相关类型定义文件
Service_server.skeleton为服务端需要的实现文件
3、代码实现
服务端:
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/PlatformThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/Thread.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/server/TNonblockingServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TNonblockingServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TNonblockingServerTransport.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class ServiceHandler : virtual public ServiceIf {
public:
ServiceHandler() {
}
void echoVoid() {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("echoVoid
");
}
int8_t echoByte(const int8_t arg) {
printf("echoByte %c
", arg);
return arg;
}
int32_t echoI32(const int32_t arg) {
printf("echoI32
");
return arg;
}
int64_t echoI64(const int64_t arg) {
printf("echoI64
");
return arg;
}
void echoString(std::string& _return, const std::string& arg) {
printf("echoString
");
}
void echoList(std::vector<int8_t> & _return, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoList
");
}
void echoSet(std::set<int8_t> & _return, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoSet
");
}
void echoMap(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & _return, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoMap
");
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceHandler> handler(new ServiceHandler());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new ServiceProcessor(handler));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TNonblockingServerTransport> serverTransport(new TNonblockingServerSocket(port));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory> threadFactory = std::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory>(new PlatformThreadFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ThreadManager> threadManager = ThreadManager::newSimpleThreadManager(10);
threadManager->threadFactory(threadFactory);
threadManager->start();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TNonblockingServer> server(new TNonblockingServer(processor, protocolFactory, serverTransport, threadManager));
server->serve();
return 0;
}
我们需要实现ServiceHandler继承ServiceIf的相关接口,ServiceHandler是负责相关rpc调用业务的功能实现,
thrift服务器模型基本模型有四种、SimpleServer ThreadedServer ThreadPoolServer NoBlockingServer
SimpleServer 简单的单线程模型
ThreadedServer 一个线程一个连接
ThreadPoolServer 线程池
NoBlockingServer 基于libevent的IO复用模型 libevent在linux平台是基于epoll的reactor模型
还有一个异步Server模型TEvhttpServer 基于libevent的evhttp
这里服务端使用了非阻塞epoll实现的thrift服务端模型
客户端:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::test::stress;
using namespace apache::thrift;
using namespace apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace apache::thrift::transport;
int main()
{
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TSocket> socket(new TSocket("localhost", 9090));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TFramedTransport(socket));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
ServiceClient client(protocol);
transport->open();
std::cout << "client echoByte byte=" << client.echoByte('A') << std::endl;
std::cout << "send_echoByte('B')" << std::endl;
client.send_echoByte('B');
std::cout << "send_echoByte('C')" << std::endl;
client.send_echoByte('C');
std::cout << "recv_echoByte()" << client.recv_echoByte() << std::endl;
std::cout << "recv_echoByte()" << client.recv_echoByte() << std::endl;
transport->close();
return 0;
}
客户端使用则比较简单,Service.h定义了相关接口,ServiceClient则是rpc客户类
TTransport new TFramedTransport(socket) 这里创建基于socket的传输层
TProtocol 协议层,序列化后的数据存储方式,这里以TBinaryProtocol 二进制存储
六、thrift异步调用
1、thrift文件同同步调用一致
2、使用thrift --gen cpp:cob_style StressTest.thrift 生成代码
StressTest_types.h StressTest_types.cpp StressTest_constants.h StressTest_constants.cpp Service.h Service.cpp Service_server.skeleton.cpp Service_async_server.skeleton.cpp
Service_server.skeleton.cpp 同步代码用不到
Service_async_server.skeleton.cpp则为http的异步实现
服务端:
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/async/TAsyncProtocolProcessor.h>
#include <thrift/async/TEvhttpServer.h>
#include <event.h>
#include <evhttp.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "Service.h"
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::async;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class ServiceHandler : virtual public ServiceIf {
public:
ServiceHandler() {
}
void echoVoid() {
printf("echoVoid
");
}
int8_t echoByte(const int8_t arg) {
printf("echoByte %c
", arg);
return arg;
}
int32_t echoI32(const int32_t arg) {
printf("echoI32
");
return arg;
}
int64_t echoI64(const int64_t arg) {
printf("echoI64
");
return arg;
}
void echoString(std::string& _return, const std::string& arg) {
printf("echoString %s
", arg.c_str());
_return = arg;
}
void echoList(std::vector<int8_t> & _return, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoList
");
}
void echoSet(std::set<int8_t> & _return, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoSet
");
}
void echoMap(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & _return, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
printf("echoMap
");
}
};
class ServiceAsyncHandler : public ServiceCobSvIf {
public:
ServiceAsyncHandler() {
syncHandler_ = std::auto_ptr<ServiceHandler>(new ServiceHandler);
// Your initialization goes here
}
virtual ~ServiceAsyncHandler(){}
void echoVoid(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void()> cob) {
syncHandler_->echoVoid();
return cob();
}
void echoByte(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int8_t const& _return)> cob, const int8_t arg) {
int8_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoByte(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoI32(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int32_t const& _return)> cob, const int32_t arg) {
int32_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoI32(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoI64(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(int64_t const& _return)> cob, const int64_t arg) {
int64_t _return = 0;
_return = syncHandler_->echoI64(arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoString(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::string const& _return)> cob, const std::string& arg) {
std::string _return;
syncHandler_->echoString(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoList(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::vector<int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::vector<int8_t> & arg) {
std::vector<int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoList(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoSet(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::set<int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::set<int8_t> & arg) {
std::set<int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoSet(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
void echoMap(::apache::thrift::stdcxx::function<void(std::map<int8_t, int8_t> const& _return)> cob, const std::map<int8_t, int8_t> & arg) {
std::map<int8_t, int8_t> _return;
syncHandler_->echoMap(_return, arg);
return cob(_return);
}
protected:
std::auto_ptr<ServiceHandler> syncHandler_;
};
int main()
{
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceAsyncProcessor> asynProcessor(new ServiceAsyncProcessor(
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<ServiceCobSvIf>(new ServiceAsyncHandler())));
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncProtocolProcessor> asynProtocolProcessor(new TAsyncProtocolProcessor(asynProcessor,
::apache::thrift::stdcxx::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory>(new TBinaryProtocolFactory())));
TEvhttpServer server(asynProtocolProcessor, 9999);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
这里实现ServiceHandler的相关业务接口即可实现rpc服务端的相关功能
客户端:
#include "Service.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/PlatformThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/Thread.h>
#include <thrift/async/TAsyncChannel.h>
#include <thrift/async/TEvhttpClientChannel.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/protocol/TProtocol.h>
#include <event.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::async;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::concurrency;
using namespace ::test::stress;
class MyClient : public ServiceCobClient
{
public:
MyClient(stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel, TProtocolFactory* protocolFactory)
: ServiceCobClient(channel, protocolFactory)
{
}
virtual ~MyClient(){}
virtual void completed__(bool success)
{
if (success)
{
std::cout << "completed" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "completed failed" << std::endl;
}
}
void my_send_byte()
{
std::cout << "begin my_send_byte" << std::endl;
stdcxx::function<void(ServiceCobClient*)> cob = stdcxx::bind(&MyClient::recv_byte_callback, this, stdcxx::placeholders::_1);
echoByte(cob, 'A');
std::cout << "end my_send_byte" << std::endl;
}
void my_send_string()
{
std::cout << "begin my_send_string" << std::endl;
stdcxx::function<void(ServiceCobClient*)> cob = stdcxx::bind(&MyClient::recv_string_callback, this, stdcxx::placeholders::_1);
echoString(cob, "test asynclient");
std::cout << "end my_send_string" << std::endl;
}
void recv_byte_callback(ServiceCobClient* client)
{
std::cout << "recv_byte_callback" << std::endl;
_res_byte = recv_echoByte();
std::cout << "_res_byte =" << _res_byte << std::endl;
}
void recv_string_callback(ServiceCobClient* client)
{
std::cout << "recv_string_callback" << std::endl;
recv_echoString(_res_string);
std::cout << "_res_string=" << _res_string << std::endl;
}
private:
char _res_byte;
std::string _res_string;
};
class ClientThread : public Runnable
{
public:
ClientThread(event_base* base, std::string & host, int port)
: _base(base), _host(host), _port(port)
{
}
virtual ~ClientThread(){}
virtual void run()
{
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel1(new TEvhttpClientChannel(_host, "/", _host.c_str(), _port, _base));
stdcxx::shared_ptr<TAsyncChannel> channel2(new TEvhttpClientChannel(_host, "/", _host.c_str(), _port, _base));
MyClient client1(channel1, new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
MyClient client2(channel2, new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
client1.my_send_byte();
client1.my_send_string();
client2.my_send_byte();
client2.my_send_string();
while (1)
{
client1.my_send_byte();
sleep(1);
}
}
protected:
private:
event_base* _base;
std::string _host;
int _port;
};
int main()
{
std::string host = "192.168.119.129";
int port = 9999;
event_base* base = event_base_new();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory> threadFactory = std::shared_ptr<PlatformThreadFactory>(new PlatformThreadFactory());
stdcxx::shared_ptr<ThreadManager> threadManager = ThreadManager::newSimpleThreadManager(10);
threadManager->threadFactory(threadFactory);
threadManager->start();
stdcxx::shared_ptr<Thread> thread = threadFactory->newThread(std::shared_ptr<ClientThread>(new ClientThread(base, host, port)));
thread->start();
event_base_dispatch(base);
event_base_free(base);
return 0;
}
客户端则实现了MyClient,MyClient继承公共的rpc服务接口,提供了异步回调的recv_byte_callback,recv_string_callback函数, ClientThread的线程函数的实现则对MyClient异步客户端进了测试
七、简单总结
通过这两天的学习,简单总结一下这个库
1、thrift的C++代码实现很漂亮,很规范,适合学习阅读
2、thrift可以满足很多基本的rpc调用场景
3、本文只是简单写了thrift的用法,想深入了解这个库的,其内部实现还是需要花时间好好研究
作者 [@karllen][3]
2018 年 09月 15日
QQ群: 347769318