一.AOP的整理总结
aop面向切面编程
横向重复代码,纵向抽取
动态代理
1.通过动态代理可以体现aop思想
2.为什么要哦用动态代理:对目标对象中的方法进行增强
spring aop开发
spring封装了动态代理代码,我们不需要手写动态代理代码
还封装了cglib代理——>可以对任何类进行代理增强
spring中的名词
连接点(Joinpoint),切入点(Ponitcut),通知(Advise),织入(weaving),切面(aspect),目标对象(target),代理(proxy)
二.Spring的AOP事务
1 什么是事务?
事务特性:acid
事务并发问题:脏读,不可重复读,幻读
事务的隔离级别:
(1) 1:读未提交
(2) 2:读已提交
(3) 4:可重复读
(4) 8:串行化
2 spring封装了事务管理的代码
事务操作:(1) 打开事务(2) 提交事务(3) 回滚事务
事务操作对象:因为在不同平台,操作事务的代码各不相同,所以spring提供了一个接口PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager接口(核心对象): JDBCTransactionManager,HibernateTransactionManager,DataSourceTransactionManager(Mybaits)。在spring中的事务管理最为核心的对象就是TransactionManager
spring管理事务的属性:(1)事务隔离级别 (2)是否只读(true只读,false可操作) (3) 事务的传播行为:决定业务方法之间调用,事务应该如何处理
3 spring管理事务方式
(1)编码式
(2) xml配置(aop)
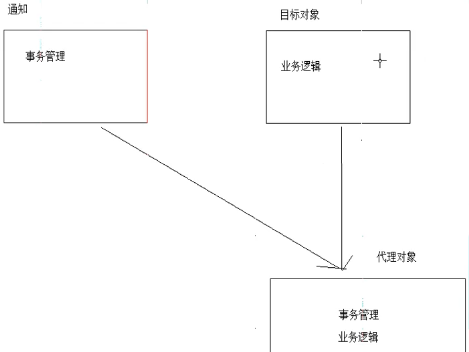
springAOP准备了事务通知(已经写好,环绕通知),目标对象也已经根据自身情况编写好业务逻辑,所以只剩下配置文件,来将通知织入目标对象,生成代理对象。
<!-- 配置事务通知 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <!-- 企业开发中,基本上都是用通配符的方式配置,只要service的方法名有这些开头,就会有事务属性 其中isolation表示事务隔离级别 propagation表示事务传播行为一般都是required read-only表示是否只读 --> <tx:method name="save*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="persist*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="modify*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="delete*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="remove*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="get*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> <tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- 配置织入 --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="txPc" expression="execution(* com.javaweb.service..*ServiceImpl.*(..))" /> <!-- 配置切面:通知+切入点 --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPc" /> </aop:config>
(3) 注解配置(aop)
需要在配置文件中开启注解在管理事务
@Transaction(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=true),该注解可以在类上,也可以在方法上。
<!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven/>