120min, 5题。本菜鸡怒跪。
1、变身程序员
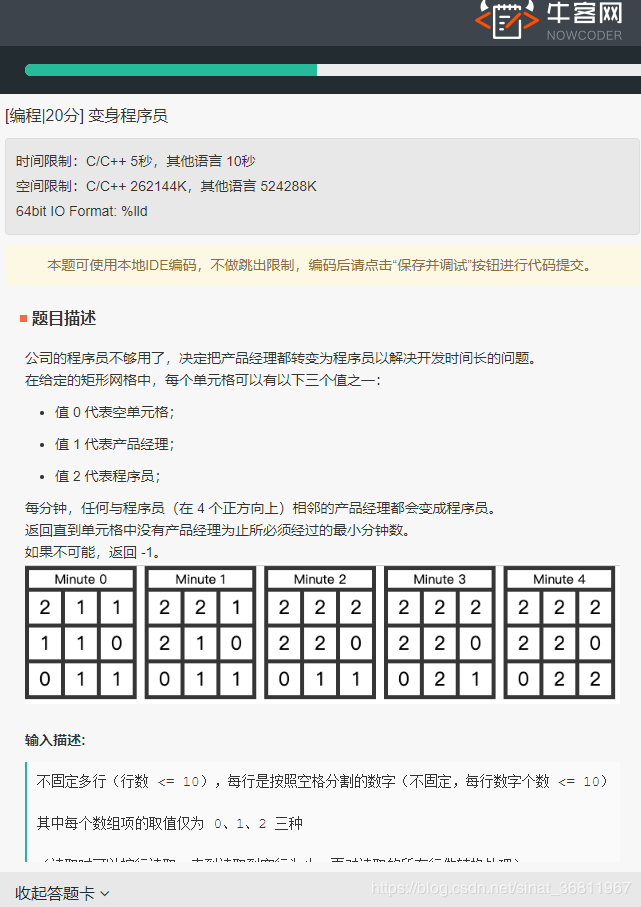
(读取时可以按行读取,直到读到空行为止,再对读取过的所有行做转换处理)
输出描述:
如果能将所有的产品经理变成程序员,输出最小的分钟数;
如果不能将所有的产品经理变成程序员,输出-1。
示例1:
输入:
0 2
1 0
输出:
-1
示例2:
输入:
1 2 1
1 1 0
0 1 1
输出:
3
示例3:
输入:
1 2
2 1
1 2
0 1
0 1
1 1
输出:
4
此题与https://leetcode.com/problems/rotting-oranges/类似。
基本思想就是将所有的程序员入队,BFS所有的产品经理,最后检查是否还有产品经理存在。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cstdio> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <queue> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 struct node { 12 int x, y; 13 int time; 14 node() {} 15 node(int xx, int yy, int t) :x(xx), y(yy), time(t) {} 16 }; 17 18 queue<node> q; 19 20 int dir[4][2] = { {0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0},{1,0} }; 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 int grid[10][10]; 25 int row = 0, col = 0; 26 string str; 27 28 /*按行读取输入*/ 29 while (getline(cin, str)) 30 { 31 col = 0; 32 for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++) 33 { 34 if (str[i] != ' ') 35 { 36 grid[row][col++] = str[i] - '0'; 37 } 38 } 39 40 row++; 41 } 42 43 for(int i = 0;i < row;i++) 44 for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) 45 { 46 if (grid[i][j] == 2) 47 { 48 //将所有程序员入队 49 q.push(node(i, j, 0)); 50 } 51 } 52 53 node s; 54 while (!q.empty()) 55 { 56 s = q.front(); 57 58 /*四个方向遍历*/ 59 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 60 { 61 int newx = s.x + dir[i][0]; 62 int newy = s.y + dir[i][1]; 63 64 //没有越界并且找到一枚产品经理 65 if (newx >= 0 && newx < row && newy >= 0 && newy < col && grid[newx][newy] == 1) 66 { 67 grid[newx][newy] = 2; 68 q.push(node(newx, newy, s.time + 1)); 69 } 70 } 71 q.pop(); 72 } 73 74 for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) 75 for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) 76 { 77 if (grid[i][j] == 1) 78 { 79 printf("-1 "); 80 return 0; 81 } 82 } 83 84 printf("%d ", s.time); 85 86 return 0; 87 }
2、特征提取
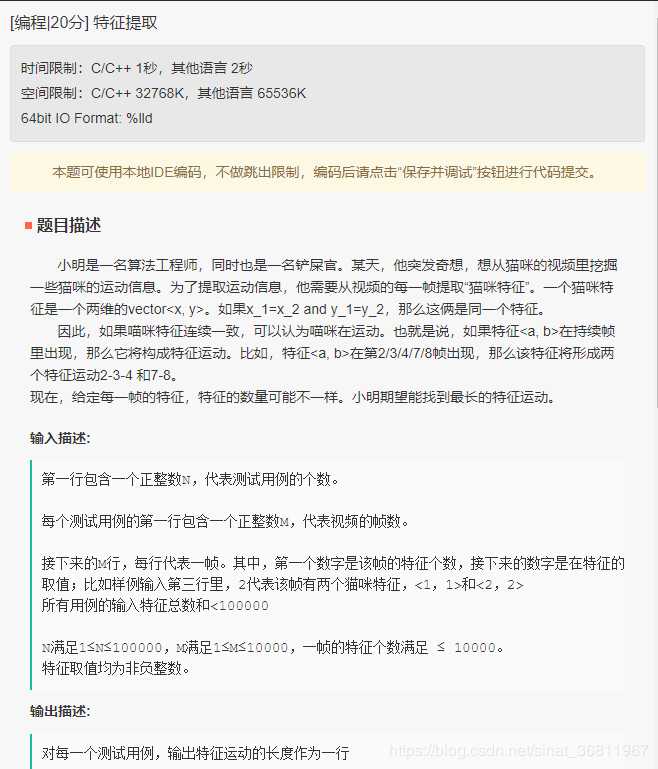
示例: 输入: 1 8 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 4
2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 4 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 输出: 3 说明: 特征<1,1>在连续的帧中出现3次,相比其他特征连续出现的次数大,所以输出3 备注: 如果没有长度大于2的特征运动,返回1
可以使用pair存储当前特征,使用map存储当前特征上一次出现的行数以及当前特征连续出现的长度。
还是对C++不熟唉
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <utility> 5 #include <map> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 int N, M, fea_num, res; 13 scanf("%d", &N); 14 15 while (N--) 16 { 17 scanf("%d", &M); 18 res = 0; 19 pair<int, int> cur; 20 //当前特征上一次出现的行数以及连续出现的长度 21 map<pair<int, int>, int> lastIndex, length; 22 for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) 23 { 24 scanf("%d", &fea_num); 25 for (int j = 0; j < fea_num; j++) 26 { 27 scanf("%d%d", &cur.first, &cur.second); 28 if (lastIndex[cur] == i) 29 { 30 length[cur]++; 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 length[cur] = 1; 35 } 36 lastIndex[cur] = i + 1; 37 res = max(res, length[cur]); 38 } 39 } 40 if (res <= 2) 41 printf("1 "); 42 else 43 printf("%d ", res); 44 } 45 46 return 0; 47 }
3、机器人跳跃
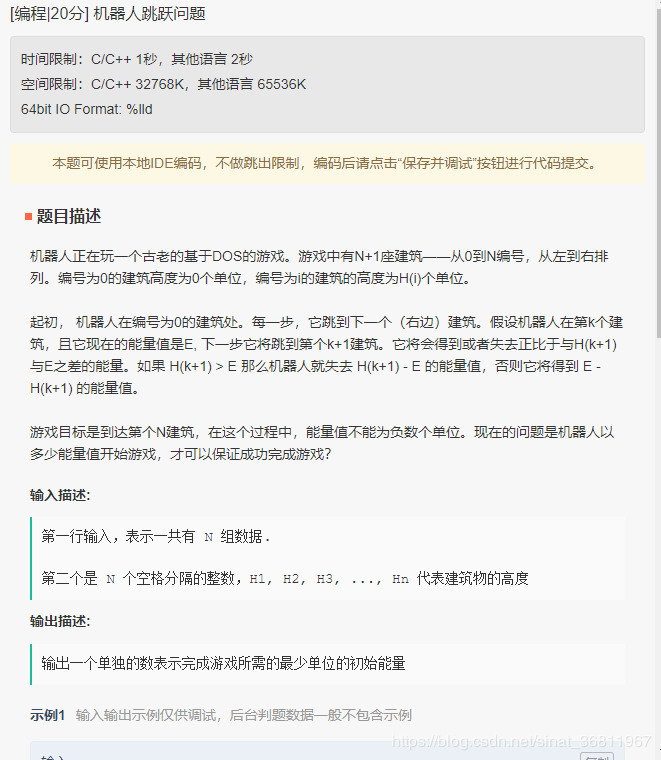
示例1: 输入: 5 3 4 3 2 4 输出: 4 示例2: 输入: 3 4 4 4 输出: 4 示例3: 输入: 3 1 6 4 输出: 3 备注: 1 <= N <= 10^5 1 <= H(i) <= 10^5
据说是小学数学,还想了半天。
根据题意可推出:$dp[k + 1] = 2*dp[k] - H[k + 1]$
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cmath> 5 #include <vector> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 int N; 12 scanf("%d", &N); 13 vector<int> H(N + 1); 14 15 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) 16 { 17 scanf("%d", &H[i + 1]); 18 } 19 20 vector<int> dp(N + 1); //dp[k]表示从第k级开始需要的能量 21 22 for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) 23 { 24 dp[i] = ceil((dp[i + 1] + H[i + 1]) / 2.0); 25 } 26 27 printf("%d ", dp[0]); 28 29 return 0; 30 }
4、毕业旅行问题
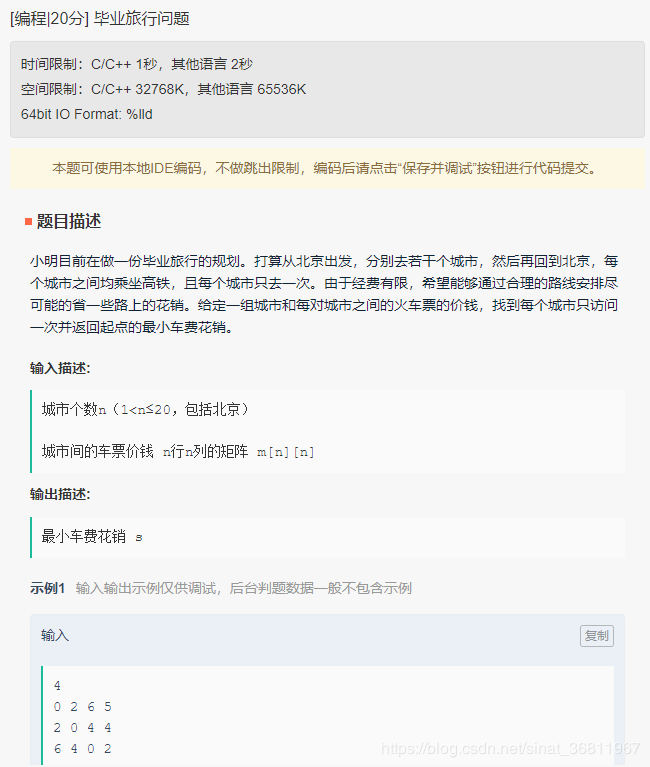
示例: 输入: 4 0 2 6 5 2 0 4 4 6 4 0 2 5 4 2 0 输出: 13
典型的TSP问题,据说动态规划能够得到理论最优解,然而本渣看不懂状态转移方程。
贪心算法:从某城市出发,每次在未到达的城市中选择最近的一个,直到遍历完所有城市,最后回到出发地。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 3 #include <cstdio> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 #define INF 1<<30; 8 9 int main() 10 { 11 int n, m[20][20], res = 0; 12 int edge_count = 0, flag[20] = { 1,0 }; 13 int cur = 0, next; 14 scanf("%d", &n); 15 16 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 17 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 18 { 19 scanf("%d", &m[i][j]); 20 } 21 22 while (edge_count < n) 23 { 24 int min = INF; 25 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) 26 { 27 if (!flag[j] && m[cur][j] && m[cur][j] < min) 28 { 29 next = j; 30 min = m[cur][j]; 31 } 32 } 33 res += m[cur][next]; 34 flag[next] = 1; 35 edge_count++; 36 cur = next; 37 } 38 39 res += m[cur][0]; 40 41 return 0; 42 }
5、过河
示例: 输入: 2 2 1 2 4 1 1 1 1 输出: 2 3
每次过河只能2个或3个人,这种过河问题遵循“能者多劳”原则,即花费时间少的人折返去接其他人。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int a[100010], dp[100010]; 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 int n, N; 13 scanf("%d", &N); 14 15 while (N--) 16 { 17 scanf("%d", &n); 18 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 19 { 20 scanf("%d", &a[i]); 21 } 22 23 sort(a, a + n); 24 dp[2] = a[1], dp[3] = a[2]; 25 for (int i = 4; i <= n; i++) 26 { 27 //前i个人过河的最短时间 28 dp[i] = min( dp[i - 1] + a[0] + a[i - 1],dp[i - 2] + a[1] + a[i - 1] ); 29 } 30 31 printf("%d ", dp[n]); 32 } 33 34 return 0; 35 }