函数
#定义函数 def greet_user(): print("Hello!")
greet_user()
Hello!
#向函数传递信息 def greet_user(username): print("Hello, " + username.title() + "!")
greet_user('jesse')
Hello, Jesse!
#实参和形参
'''
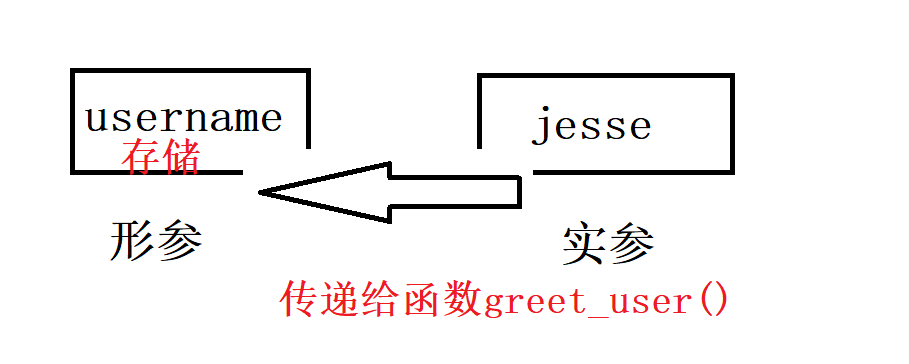
username是一个形参——函数完成其工作所需的一项信息;
jesse是一个实参,调用函数时传递给函数的信息;
调用函数时,将要让函数使用的信息放在括号内greet_user('jesse')中
将实参jesse传递给了函数greet_user(),这个值被存储在username中
'''
#传递实参 ''' 将函数调用中的每一个实参都关联到函数定义中的一个形参 基于实参的顺序——位置实参 ''' def describe_pet(animal_type, pet_name): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet('tugou','xiaohei')
I have a pet tugou. My tugou's name is xiaohei.
#调用函数多次 def describe_pet(animal_type, pet_name): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet('tugou','xiaohei') describe_pet('xiaomao','miao')
I have a pet tugou. My tugou's name is xiaohei. I have a pet xiaomao. My xiaomao's name is miao.
#位置实参的顺序很重要 def describe_pet(animal_type, pet_name): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet('xiaohei','tugou')
I have a pet xiaohei. My xiaohei's name is tugou.
#关键字实参 ''' 关键字实参是传递给函数的名称-值对。无需考虑函数调用中的实参顺序。 ''' def describe_pet(animal_type, pet_name): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet(animal_type='tugou',pet_name='xiaohei')
I have a pet tugou. My tugou's name is xiaohei.
#默认值 ''' 可以给每个形参指定默认值, ''' def describe_pet(pet_name, animal_type='dog'): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet(pet_name='xiaohei')
I have a pet dog. My dog's name is xiaohei.
describe_pet('xiaohei')
I have a pet dog. My dog's name is xiaohei.
describe_pet(animal_type='xiaomao',pet_name='miao')
I have a pet xiaomao. My xiaomao's name is miao.
#等效的函数调用 def describe_pet(pet_name, animal_type='dog'): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet(pet_name='xiaohei') describe_pet('xiaohei') describe_pet('miao','xiaomao') describe_pet(animal_type='xiaomao',pet_name='miao') describe_pet(pet_name='miao',animal_type='xiaomao')
I have a pet dog. My dog's name is xiaohei. I have a pet dog. My dog's name is xiaohei. I have a pet xiaomao. My xiaomao's name is miao. I have a pet xiaomao. My xiaomao's name is miao. I have a pet xiaomao. My xiaomao's name is miao.
#避免实参错误 def describe_pet(pet_name, animal_type='dog'): print(" I have a pet " + animal_type + ".") print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".") describe_pet()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-14-0f39ed801838> in <module>
4 print("My " + animal_type + "'s name is " + pet_name + ".")
5
----> 6 describe_pet()
TypeError: describe_pet() missing 1 required positional argument: 'pet_name'
#返回值 def get_formatted_name(first_name, last_name): full_name = first_name + ' '+ last_name return full_name.title()
musician = get_formatted_name('jimi', 'hendrix')
print(musician)
Jimi Hendrix
#让实参变成可选的 def get_formatted_name(first_name, middle_name, last_name): full_name = first_name + ' '+ middle_name + ' ' + last_name return full_name.title() musician = get_formatted_name('john', 'lee', 'hooker')
print(musician)
John Lee Hooker
def get_formatted_name(first_name, last_name, middle_name=''): if middle_name: full_name = first_name + ' ' + middle_name + ' ' + last_name else: full_name = first_name + ' '+ last_name return full_name.title()
musician1 = get_formatted_name('jimi', 'hendrix') musician2 = get_formatted_name('john', 'lee', 'hooker')
print(musician1) print(musician2)
Jimi Hendrix John Hooker Lee
#返回字典 def build_person(first_name, last_name): person = {'first':first_name,'last':last_name} return person musician = build_person('jimi', 'hendrix') print(musician)
{'first': 'jimi', 'last': 'hendrix'}
def build_person(first_name, last_name, age=''): person = {'first':first_name,'last':last_name} if age: person['age']=age return person musician = build_person('jimi', 'hendrix', age=27) print(musician)
{'first': 'jimi', 'last': 'hendrix', 'age': 27}
#结合使用函数和while循环 def get_formatted_name(first_name, last_name): full_name = first_name + ' '+ last_name return full_name.title() while True: print(" Please tell me your name:") print("(enter 'q' at any time to quit)") f_name = input("First name:") if f_name =='q': break l_name = input("Last name:") if f_name =='q': break formatted_name = get_formatted_name(f_name, l_name) print(" Hello, " + formatted_name + "!")
Please tell me your name: (enter 'q' at any time to quit) First name:cui Last name:jingjing Hello, Cui Jingjing! Please tell me your name: (enter 'q' at any time to quit) First name:wang Last name:lulu Hello, Wang Lulu! Please tell me your name: (enter 'q' at any time to quit) First name:q
#传递列表 def greet_users(names): for name in names: msg = "Hello, " + name.title() + "!" print(msg)
usernames = ['hannah', 'try', 'margot'] greet_users(usernames)
Hello, Hannah! Hello, Try! Hello, Margot!
def cui_family(names): for name in names: txt = "my name is " + name.title() + "." print(txt) a = ['cuirongsheng','zhoujianfeng','cuijingjing'] cui_family(a)
my name is Cuirongsheng. my name is Zhoujianfeng. my name is Cuijingjing.
#在函数中修改列表 ''' 从列表unprinted_designs末尾删除一个设计,存储到中间变量current_design,显示一条消息,正在打印的设计,再将设计添加到新列表completed_models中 ''' unprinted_designs = ['iphones case','robot pendant','dodecahedron'] completed_models = [] while unprinted_designs: current_design = unprinted_designs.pop() print("printing model: " + current_design) completed_models.append(current_design)
printing model: dodecahedron printing model: robot pendant printing model: iphones case
print(" The following models have been printed:") for completed_model in completed_models: print(completed_model)
The following models have been printed: dodecahedron robot pendant iphones case
#第一个函数负责处理打印设计的工作,第二个概述打印了哪些设计 def print_models(unprinted_designs, completed_models): while unprinted_designs: current_design = unprinted_designs.pop() print("printing model: " + current_design) completed_models.append(current_design) def show_completed_models(completed_models): print(" The following models have been printed:") for completed_model in completed_models: print(completed_model) unprinted_designs = ['iphones case','robot pendant','dodecahedron'] completed_models = [] print_models(unprinted_designs, completed_models) show_completed_models(completed_models)
printing model: dodecahedron printing model: robot pendant printing model: iphones case The following models have been printed: dodecahedron robot pendant iphones case
print(unprinted_designs)
[]
#禁止函数修改列表 ''' 保留未打印的设计列表,已备案 向函数传递的是副本,而不是原件 ''' function_name(list_name[:]) print_models(unprinted_designs[:], completed_models)
def print_models(unprinted_designs, completed_models): while unprinted_designs: current_design = unprinted_designs.pop() print("printing model: " + current_design) completed_models.append(current_design) def show_completed_models(completed_models): print(" The following models have been printed:") for completed_model in completed_models: print(completed_model) unprinted_designs = ['iphones case','robot pendant','dodecahedron'] completed_models = [] print_models(unprinted_designs[:], completed_models) show_completed_models(completed_models)
printing model: dodecahedron printing model: robot pendant printing model: iphones case The following models have been printed: dodecahedron robot pendant iphones case
print(unprinted_designs)
['iphones case', 'robot pendant', 'dodecahedron']
#传递任意数量的实参 ''' 预先不知道函数需要接受多少个实参 ''' def make_pizza(*toppings): print(toppings) make_pizza('pepperoni') make_pizza('pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
('pepperoni',)
('pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
def make_pizza(*toppings): print(" Making a pizza with the following toppings:") for topping in toppings: print("- " + topping) make_pizza('pepperoni') make_pizza('pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
Making a pizza with the following toppings: - pepperoni Making a pizza with the following toppings: - pepperoni - green peppers - extra cheese
#结合使用位置实参和任意数量实参,将接纳任意实参的形参放在最后 def make_pizza(size, *toppings): print(" Making a " + str(size) + "-inch pizza with the following toppings:") for topping in toppings: print("- " + topping) make_pizza(16, 'pepperoni') make_pizza(12, 'pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
Making a 16-inch pizza with the following toppings: - pepperoni Making a 12-inch pizza with the following toppings: - pepperoni - green peppers - extra cheese
#使用任意数量的关键字实参,**user_info创建一个空字典,遍历字典中的键值对,并将每个键值对都加入到字典profile中 def build_profile(first, last, **user_info): profile = {} profile['first_name'] = first profile['last_name'] = last for key, value in user_info.items(): profile[key] = value return profile user_profile = build_profile('albert','einstein',location='princeton',field='physics') print(user_profile)
{'first_name': 'albert', 'last_name': 'einstein', 'location': 'princeton', 'field': 'physics'}
#将函数存储在模块中 ''' 代码块与主程序分离,通过函数指定描述性名称,让主程序容易理解;将函数存储在被称为模块的独立文件中,再将模块导入到主程序,import ''' def make_pizza(size, *toppings): print(" Making a " + str(size) + "-inch pizza with the following toppings:") for topping in toppings: print("- " + topping)
import pizza pizza.make_pizza(16, 'pepperoni') pizza.make_pizza(12, 'pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
#使用as给函数指定别名 from pizza import make_pizza as mp mp(16, 'pepperoni') mp(12, 'pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
#使用as给模块指定别名 import pizza as p p.make_pizza(16, 'pepperoni') p.make_pizza(12, 'pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
#导入模块中的所有函数 ''' 使用并非自己编写的大型模块时,最好不要使用这种导入方法,如果模块中有函数的名称与项目中使用的名称相同,会出意外 只导入自己需要的函数or导入整个模块并使用句点表示法 ''' from pizza import * make_pizza(16, 'pepperoni') make_pizza(12, 'pepperoni', 'green peppers', 'extra cheese')
#给形参指定默认值时,等号两边不要有空格 def function_name(parameter_0, parameter_1='default value') #函数中调用关键字段 function_name(value_0, parameter_1='value')