STL(Standard Template Library即,模板库)包括六个部分:容器(containers)、迭代器(iterators)、空间配置器(allocator)、配接器(adapters)、算法(algorithms)、仿函数(functors)
vector
1、vector:连续存储
(1)头文件,#include<vector>
(2)创建vector对象,vector<int> vec;
(3)尾部插入元素,vec.push_back(a);
(4)使用下标访问元素,cout<<vec[0]<<endl;
(5)使用迭代访问元素
1 vector<int>::iterator it; 2 for(it=vec.begin();it!=vec.end();it++) 3 cout<<(*it)<<endl;
(6)插入元素,vec.insert(vec.begin()+i,a);在第i+1个元素前面插入a
(7)删除元素,vec.erase(vec.begin()+2);删除第3个元素
vec.erase(vec.begin()+i,vec.end()+j);删除区间[i,j-1];区间从0开始
(8)向量大小,vec.size();
(9)清空,vec.clear();
vector的元素不仅仅只限于int型,int、double、string、全局结构体等都可以。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 struct Student 6 { 7 int num; 8 double score; 9 double operator< (const Student &stu) const 10 { 11 if(stu.score>score) 12 return stu.score; 13 else 14 return score; 15 } 16 }; 17 18 int main() 19 { 20 vector<Student> stu; 21 //student 1 22 Student stu_temp; 23 stu_temp.num = 1; 24 stu_temp.score =9.9; 25 stu.push_back(stu_temp); 26 //student 2 27 Student stu_temp1; 28 stu_temp1.num = 2; 29 stu_temp1.score =8.8; 30 stu.push_back(stu_temp1); 31 //student 3 32 Student stu_temp2; 33 stu_temp2.num = 3; 34 stu_temp2.score =7.7; 35 stu.push_back(stu_temp2); 36 //print all the students 37 cout<<"the number of student:"<<stu.size()<<endl; 38 vector<Student>::iterator it; 39 for(it=stu.begin();it!=stu.end();it++) 40 cout<<"number:"<<(*it).num<<" score:"<<(*it).score<<endl; 41 //delete one student 42 stu.erase(stu.begin()+1); 43 cout<<endl; 44 cout<<"the number of student:"<<stu.size()<<endl; 45 for(it=stu.begin();it!=stu.end();it++) 46 cout<<"number:"<<(*it).num<<" score:"<<(*it).score<<endl; 47 //print the better score 48 double _result = stu_temp<stu_temp1; 49 cout<<endl; 50 cout<<"the better score:"<<_result<<endl; 51 52 return 0; 53 }
string
2、string
平时最常用的一个,这里就不做过多说明了
map
3、map:关联容器,提供一对一的数据映射(关键字,值);数据结构为红黑树(RB-Tree)
关键字只能在map中出现一次;另外,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的;
(1)头文件,#include<map>;
(2)创建map对象,map<int,string> mapStudent;
(3)插入数据,
第一种:用insert函数插入pair数据
1 mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"Christal")); 2 mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(2,"Carl"));
第二种:用insert函数插入value_type数据
1 mapStudent.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (1,"Christal")); 2 mapStudent.insert(map<int,string>::value_type (2,"Carl"));
第三种:用数组方式插入数据
1 mapStudent[1] = "Christal"; 2 mapStudent[2] = "Carl";
输出均为:

如果用前两种方法插入数据,因为关键字是唯一的,所以当关键字已经存在的时候,再插入相同关键字的map是不成功的;而第三种用数组插入的方法是仍然可以的,会将原来的关键字所对应的值进行更改,相当于被覆盖掉了。
所以要想知道前两种方法的插入是否成功,应该用一个返回值来检验。

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<map> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 map<int,string> mapStudent; 8 pair<map<int,string>::iterator,bool> insert_pairl; 9 10 //insert 1 and check 11 insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"Christal")); 12 if(insert_pairl.second == true) 13 cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl; 14 else 15 cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; 16 17 //insert 2 and check 18 insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(2,"Carl")); 19 if(insert_pairl.second == true) 20 cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl; 21 else 22 cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl; 23 24 //insert 3 and check 25 insert_pairl = mapStudent.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"Jerry")); 26 if(insert_pairl.second == true) 27 cout<<"Insert Successfully"<<endl<<endl; 28 else 29 cout<<"Insert Failure"<<endl<<endl; 30 31 //print 32 map<int,string>::iterator it; 33 for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++) 34 cout<<(*it).first<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl; 35 36 return 0; 37 }
正如上面所说,当要插入的关键字已经存在,是插入失败的,所以输出结果为:

而采用数组插入方式会直接覆盖
1 mapStudent[1] = "Christal"; 2 mapStudent[2] = "Carl"; 3 mapStudent[1] = "Jerry";
输出结果为:

(4)数据的遍历,当然分为用迭代器遍历的方式和用数组遍历的方式,其中以迭代器遍历中又分为正向遍历和反向遍历,正向遍历就是我们所熟知的迭代器遍历方式,反向遍历如下:
1 map<int,string>::iterator it; //print 2 for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++) 3 cout<<(*it).first<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl;
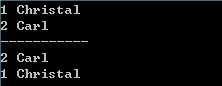
4 5 map<int,string>::reverse_iterator rit; //reverse print 6 for(rit=mapStudent.rbegin();rit!=mapStudent.rend();rit++) 7 cout<<(*rit).first<<" "<<(*rit).second<<endl;
输出结果为:
(5)查找数据,一是用count()函数查找,存在返回1,否者返回0;二是用find()函数来定位数据出现的位置;
find()函数返回一个迭代器,如果找到数据,则返回数据所在位置的迭代器;如果不存在,则返回值与end()函数的返回值相同;
1 map<int,string>::iterator _iter; 2 _iter = mapStudent.find(1); 3 if(_iter != mapStudent.end()) 4 cout<<"Find Successfully"<<endl; 5 else 6 cout<<"Find Failure"<<endl;
(6)删除数据,clear()和erase()
清空map中的所有数据用clear()函数,判定map中是否有数据用empty()函数,为空返回true。
选择性的删除用erase()函数,可以实现三种方式的删除,
用迭代器删除:
1 map<int,string>::iterator _iter; 2 _iter = mapStudent.find(1); 3 mapStudent.erase(_iter);
用关键字删除:
1 int n = mapStudent.erase(1); 2if(n == 1) 3 cout<<"Erase Successfully"<<endl; 4else 5 cout<<"Erase Failure"<<endl;
用迭代器成片删除,删除区间是一个前闭后开[ )的集合:
1 mapStudent.erase(mapStudent.begin(),mapStudent.end());
set
4、set:用来存储同一数据类型的数据,内部每个元素都是唯一的,且自动排序;数据结构为红黑树(RB-Tree)
(1)构造函数,set<int> c;
(2)查找函数,find()函数和count()函数;
(3)数据访问函数,begin()、end()、rbegin()、rend();
(4)插入数据,insert(element)、insert(position,element)、insert(begin,end);
(5)删除数据,erase(position)、erase(element)、erase(begin,end);
hash_map&hash_set
5、hash_map和hash_set:底层数据结构是哈希表
hash_map与map用法类似,只是内部数据结构不同,hash_map提供内部数据随机、更快的访问;hash_set同理。
总结
6、总结:
(1)vector封装数组,list封装链表,map和set封装了二叉树;
(2)对于这些STL,应当掌握基本的插入、删除、排序、查找等操作;
(3)对于结构体类型的vector、map、set、hash_map、hash_set等,需要对运算符 ‘ < ’ 进行重载。
例如在map中引入结构体,对 ‘ < ’ 运算符进行重载:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<map> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct Student 7 { 8 int num; 9 string name; 10 Student(int nu,string na) //constructor 11 { 12 name = na; 13 num = nu; 14 } 15 public: 16 bool operator< (const Student& stu) const //operator the < 17 { 18 return stu.num<num; 19 } 20 }; 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 map<Student,double> mapStudent; 25 //student information 26 Student stu1(1,"Christal"); 27 Student stu2(2,"Carl"); 28 Student stu3(3,"Jerry"); 29 //insert 30 mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu1,9.9)); 31 mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu2,8.8)); 32 mapStudent.insert(pair<Student,double>(stu3,7.7)); 33 //print 34 map<Student,double>::iterator it; 35 for(it=mapStudent.begin();it!=mapStudent.end();it++) 36 cout<<(*it).first.num<<" "<<(*it).first.name<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl; 37 38 return 0; 39 }
