一、前言
Vector的中文翻译是向量的意思,在平时使用的不比ArrayList和LinkedList多,但是我们有必要了解一下它的使用和实现。
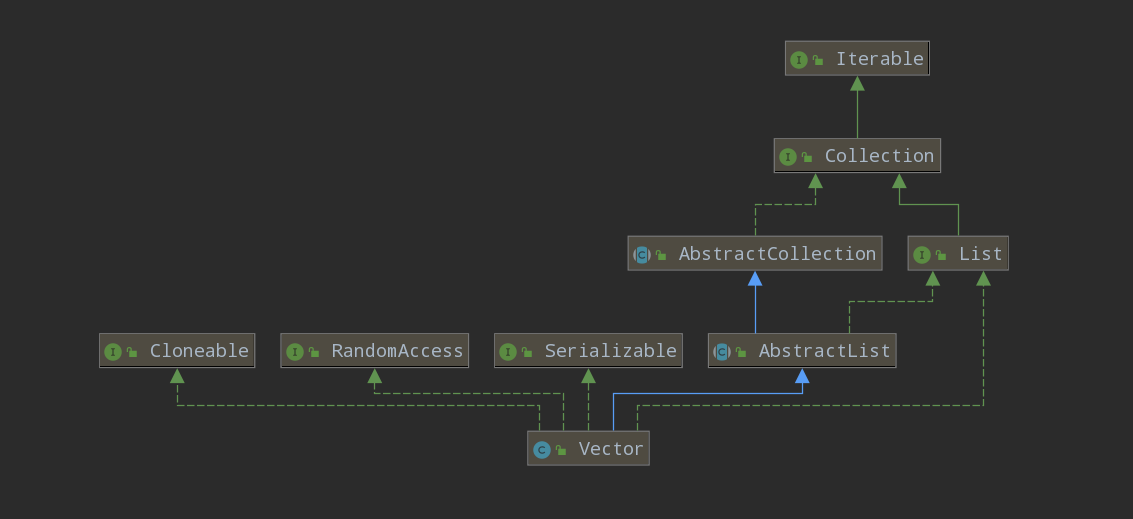
二、Vector的继承关系
我们看一下Vector的类继承关系。Vector的类继承关系和ArrayList是一样的,因此Vector的功能和ArrayList很相似。
三、定义Vector
3.1 Vector的属性定义
Vector主要定义了三个属性。elementData用于存储数据;elementCount用来记录存储元素的数量;capacityIncrement表示向量的容量,注释上说当向量的数量大于容量时,容量值会增加一倍。
/** * The array buffer into which the components of the vector are * stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer, * and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements. * * <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null. * * @serial */ protected Object[] elementData; /** * The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object. * Components {@code elementData[0]} through * {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items. * * @serial */ protected int elementCount; /** * The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically * incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If * the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity * of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow. * * @serial */ protected int capacityIncrement;
3.2 Vector的构造函数
Vector提供了四个构造函数:
-
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)
-
public Vector(int initialCapacity)
-
public Vector()
-
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c)
参数capacityincrement给定了每次扩充的扩充值。当capacityincrement为0的时候,则每次扩充一倍,利用这个功能可以优化存储。
// capacity是Vector的默认容量大小,capacityIncrement是每次Vector容量增加时的增量值。
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement; }
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
四、Vector的源码解析
先来看一下添加方法:
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) { modCount++;
//确保容量不超限制 ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = obj; } private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { // 如果超过容量大小,进行扩容 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } //扩容逻辑和ArrayList相同 private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
再来看一下移除某个位置元素的方法
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) { modCount++;
//判断位置是否越界 if (index >= elementCount) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount); } else if (index < 0) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); }
//得到要移除元素的位置 int j = elementCount - index - 1; if (j > 0) {
//移动元素 System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j); } elementCount--; elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */ }
移动逻辑很简单,与ArrayList也很相似,就不多加以介绍了。
五、Vector、ArrayList和LinkedList的对比
LinkedList与Vector和ArrayList有本置的区别,LinkedList是基于双向链表实现的,而ArrayList和LinkedList是基于数组实现的。
Vector与ArrayList的比较:
1、 Vector的实现逻辑与ArrayList十分相似,但需要注意的是Vector是线程安全的,源码中有很多的synchronized可以看出,而ArrayList不是。导致Vector效率无法和ArrayList相比。
2、ArrayList和Vector都采用线性连续存储空间,当存储空间不足的时候,ArrayList默认增加为原来的50%,Vector默认增加为原来的一倍;
3、Vector可以设置capacityIncrement,而ArrayList不可以,从字面理解就是capacity容量,Increment增加,容量增长的参数。
谈谈不同容器类型适合的场景:
Vector 和 ArrayList 作为动态数组,其内部元素以数组形式顺序存储的,内存为一连续的区域,所以非常适合随机访问的场合。除了尾部插入和删除元素,往往性能会相对较差,比如我们在中间位置插入一个元素,需要移动后续所有元素。数组大小固定,不适合动态存储,不方便动态添加。
LinkedList 进行节点插入、删除却要高效得多,大小可变 ,内存可能是不连续内存,链式存储。但是只能通过顺次指针访问,查询效率低,随机访问性能则要比动态数组慢。
因此,在应用开发中,如果事先可以估计到,应用操作是偏向于插入、删除,还是随机访问较多,就可以针对性的进行选择。
六、总结
本文对Vector类进行了介绍,并对比了ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList三者的不同并分析了他们的使用场景。接下来会对Map接口的实现进行分析,希望大家多多关注。