个人项目——求交点个数
| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2020春季计算机学院软件工程(罗杰 任健) |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 个人项目作业 |
| 我在这个课程的目标是 | 学习软工的思想方法,写出好的软件并维护 |
| 这个作业在哪个具体方面帮助我实现目标 | 在写代码的过程中熟悉visual studio的功能以及c++的各种函数类的用法,并复习了一些算法知识。 |
| 班级 | 006 |
| 项目地址 | github |
一.PSP估计
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 600 | 990 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 180 | 480 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 60 | 60 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 20 | 10 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 10 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 40 | 80 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 240 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 20 | 30 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 40 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 15 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 20 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 5 |
| 合计 | 600 | 990 |
二.思路
拿到这个题目的第一想法是暴力求解,对于所有的输入处理后存起来,并将直线两两计算交点,将交点作为key存入map,最后统计map的大小即可。但是在看到数据后犹豫了,对于1000组以下的,这个算法完全没有问题,而且只要计算过程细心,正确率也能有保证,但是对于性能部分,却完全不可行。对直线两两求交点的复杂度是O(n^2)的,这也就导致在数据大于10000时,速度已非常缓慢,更不用说最大数据500000组了。因此我上网搜索了一些资料,唯一比较接近的是一个用扫描线求线段交点的问题,它的时间复杂度是(k+n)log n,其中n是线段的数量,k是交点的个数,在本次作业中可以满足时间的要求,因此我决定对于1000组以下的采用暴力计算法,以此来保证算法的正确性,而对于性能部分,采用扫描线算法,提高运行速度。
三.设计实现过程
1.暴力求交点
我的实现方法是构建两个类分别是Line类和Circle类,其中Line类将输入的两个点坐标转化为直线方程,其形式为$$ Ax+By+c=0 $$而Circle类也做同样的工作,圆的基本方程形式为 $$ (x-m)^2+(y-n)^2=r^2 $$在读入一个数据后用Line或者Circle去存储相关的变量后,将这个类加入到一个vector中,至此预处理结束。
之后要进行的就是两两求交点。首先从Line集合中取两条不同的直线,然后通过调用方法calculate_line_line来计算两条直线的交点,思路很简单,初中数学知识,不多赘述;第二步计算一条直线和一个圆的交点,从Line集合中取出一条直线并从Circle集合中取出一个圆,通过调用方法calculate_line_circle来计算一条直线和一个圆的交点,方法是联立方程后解方程;最后是计算两个圆的交点,从Circle集合中取出两个不同的圆,并调用方法calculate_circle_circle计算出交点,方法的思路也是联立解方程组。这三步需重复n方次以保证任意两个几何图形都已求过交点,并把这些交点作为Key值insert到map中,map会自动去除重复的交点,最后map的size即为交点个数
单元测试主要测试的计算交点的三个函数是否能正确计算出交点。因此我将calculate_line_line,calculate_line_circle,calculate_circle_circle的返回值设置为int,并在单元测试中构建如下测试:
TEST_METHOD(calculate_line_line)
{
Calculate cal;
Line l1(0, 0, 1, 1);
Line l2(0, 0, 0, 1);
int ret = cal.calculate_line_line(l1, l2);
Assert::AreEqual(ret,(int)1);
Line l3(0, 0, 1, 1);
Line l4(1, 0, 2, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_line_line(l3, l4);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)0);
}
这里测试的是两条直线的交点是否计算正确,考虑了特殊的平行以及一条直线无斜率的情况,代码表明能通过测试。
TEST_METHOD(calculate_line_circle)
{
Calculate cal;
Line l1(0, 0, 1, 1);
Circle c1(0, 1, 1);
int ret = cal.calculate_line_circle(l1, c1);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)2);
Line l2(0, 0, 0, 1);
Circle c2(1, 0, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_line_circle(l2, c2);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)1);
Line l3(0, 0, 1, 0);
Circle c3(0, 2, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_line_circle(l3, c3);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)0);
}
这里测试的是一条直线和一个圆的交点是否计算正确,考虑了特殊的直线没有斜率的情况,以及测试了圆和直线有两个,一个,零个交点的情况,代码能通过测试。
TEST_METHOD(calculate_circle_circle)
{
Calculate cal;
Circle c1(0, 0, 1);
Circle c2(1, 1, 1);
int ret = cal.calculate_circle_circle(c1, c2);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)2);
Circle c3(0, 0, 2);
Circle c4(3, 0, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_circle_circle(c3, c4);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)1);
Circle c5(0, 0, 3);
Circle c6(0, 0, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_circle_circle(c5, c6);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)0);
Circle c7(0, 0, 1);
Circle c8(0, 9, 1);
ret = cal.calculate_circle_circle(c7, c8);
Assert::AreEqual(ret, (int)0);
}
这里测试的是两个圆的交点是否计算正确,考虑了两个圆有2个,1个,0个交点的情况,同时还考虑了一个圆在另一个圆内部的情况,代码能通过测试。
至此单元测试结束,而我还进行了一些输出输入的测试,通过输出所有交点的坐标,再与网站GeoGebra的结果比对,发现计算是准确的。
2.扫描线算法
while (!q.empty()) {
Point p = q.top();
q.pop();
if (p.type == 1) {//是左端点
s.insert(p.belong);
set<Line,cmp2>::iterator iter;
iter = s.find(p.belong);
Line l = *iter;
if (iter != s.begin()) {
iter--;
Line l1 = *iter;
iter++;
calculate.calculate_line_line_allinsert(l, l1);
}
iter++;
if (iter != s.end()) {
Line l1 = *iter;
calculate.calculate_line_line_allinsert(l1, l);
}
}
else if (p.type == 2) {//是右端点
set<Line, cmp2>::iterator iter,iter1,del;
iter = s.find(p.belong);
iter1 = iter;
del = iter;
iter1++;
if (iter != s.begin() && iter1 != s.end()) {
iter--;
Line l1 = *iter;
Line l2 = *iter1;
calculate.calculate_line_line_allinsert(l2, l1);
}
s.erase(del);
}
else {//是交点
pointset.insert(p);
set<Line, cmp2>::iterator iter1, iter2, it1, it2;
iter1 = s.find(p.father1);
iter2 = s.find(p.father2);
it1 = iter1;
it2 = iter2;
it1++;
if (it1 != s.end()) {
Line l1 = *it1;
Line l2 = *iter2;
calculate.calculate_line_line_allinsert(l1, l2);
}
if (iter2 != s.begin()) {
it2--;
Line l1 = *iter1;
Line l2 = *it2;
calculate.calculate_line_line_allinsert(l1, l2);
}
}
}
cout << pointset.size() << endl;
扫描线算法虽然写完了,但却发现速度并没有提高,在大量的数据情况下运行速度反而低于暴力,不知道是什么原因,只好只使用暴力的做法。
四.性能分析
首先对于一个500000的数据,如果采用暴力的O(n^2),那么只优化交点到底怎么求来减少每次循环的计算量并不能提高多少性能,为了提高性能需要更换更好的算法。于是我花了大概4小时去学习扫描线(Bentley-Ottmann)算法,只可惜最后不知是set的性能问题还是哪里写错了,复杂度总是不对(经常比暴力还慢很多),原本的复杂度应该是O(nlogn+klogn),其中n是直线的数量,k是交点的数量,这个复杂度在5000条边和500000时应该明显快过5000*5000,但是事实是比暴力慢很多个数量级,只好放弃。希望能得到助教指点。
下面贴出暴力求解的性能分析图
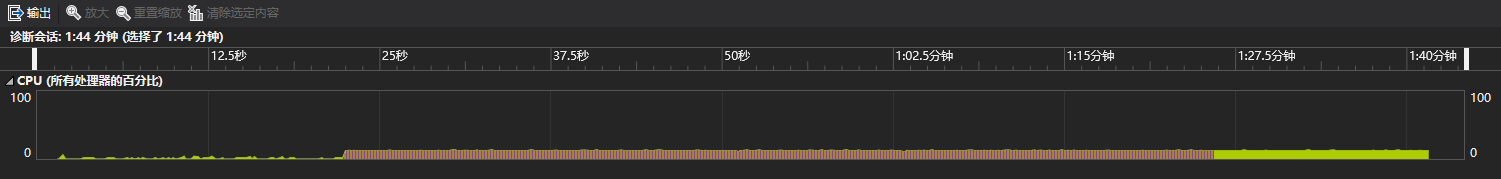
对于一个6000组的数据需要运行1分多钟
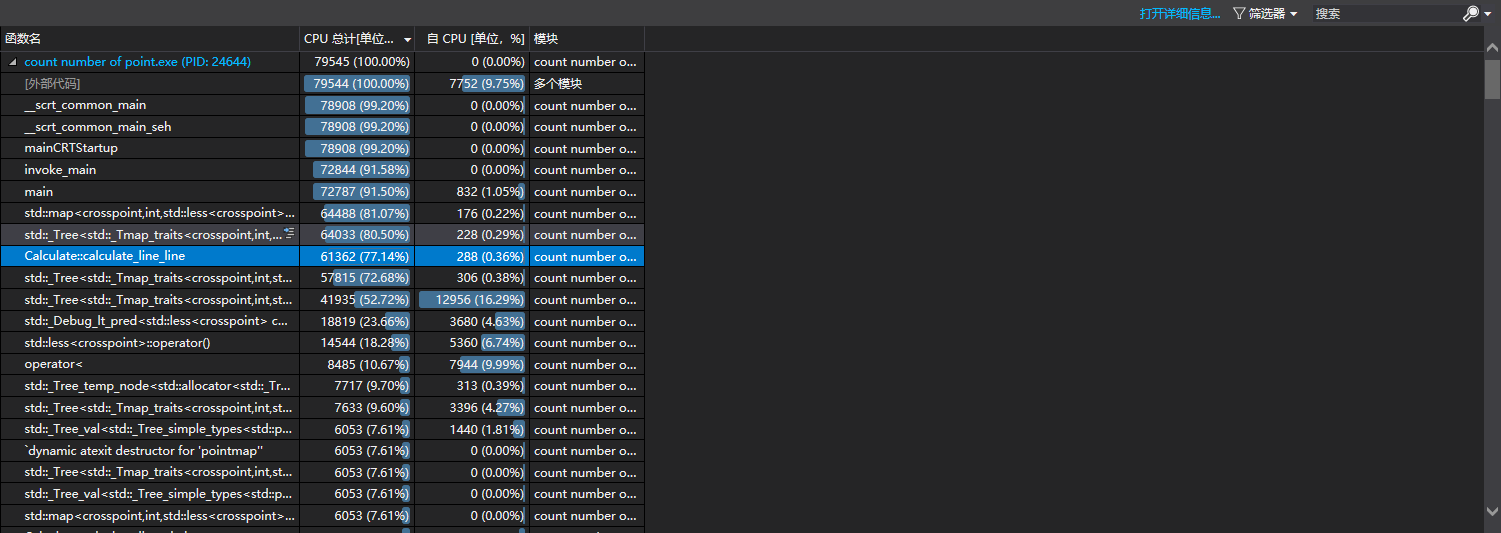
占用时间最多的是main函数这是毫无疑问的,因为所有处理基本都在main中,除去main占用时间最多的是计算两直线的交点,我这组数据直线偏多,因此这个函数占时最多。

其中最耗时的是将交点插入到map中的过程,因此我想能不能改进这里。
因此尝试将map更换为set,使用一样的数据,得到如下结果。
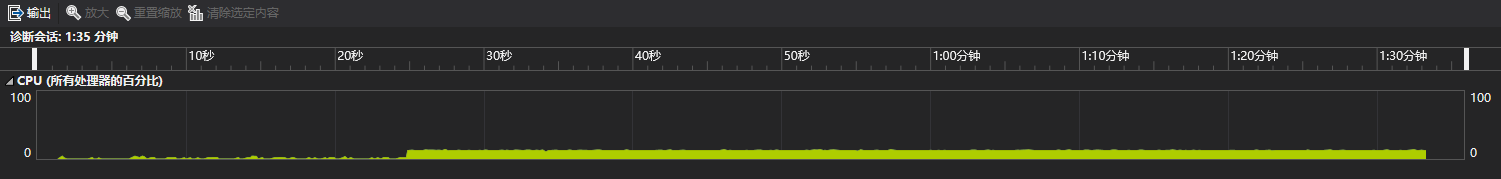
发现总时间变短了
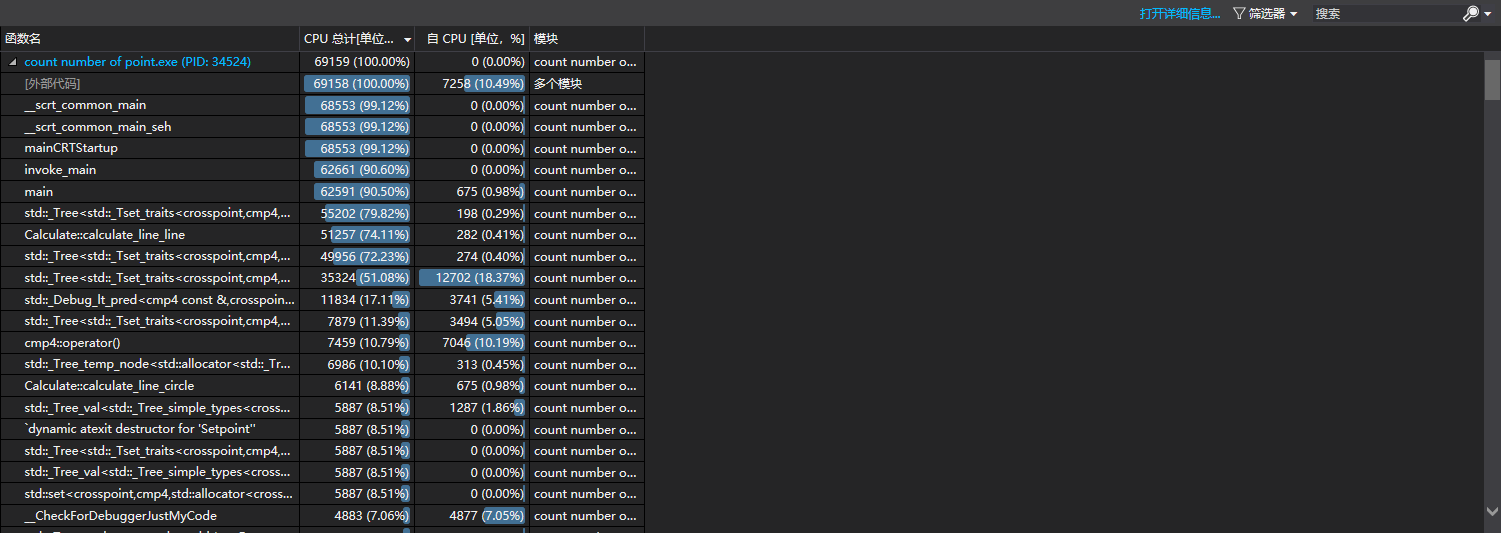
每个函数的比例几乎没变化,但是时间都变短了一些。
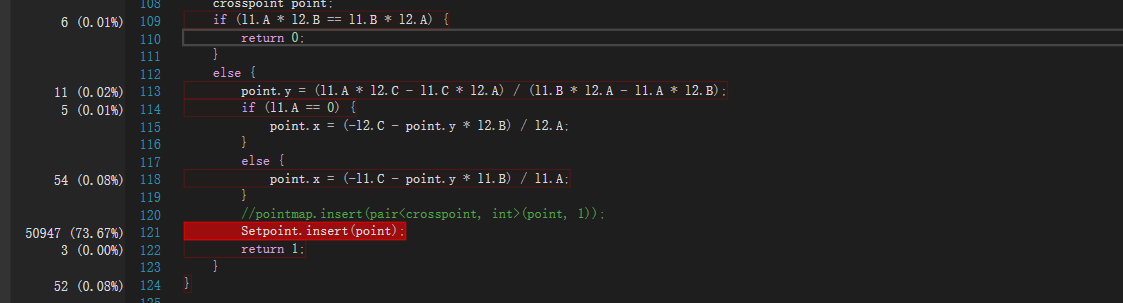
像set中插入point的耗时减少了,那么我们认为set性能更优秀一些,最终选择了set。
五.代码说明
代码的关键函数在于计算交点,而这又分为:两条直线的交点计算,两个圆的交点计算,以及一个圆和一条直线的交点计算,下面分别来说明这三部分函数。
1.两条直线的交点计算
int Calculate::calculate_line_line(Line l1,Line l2) {//caculate the crosspoint of the two lines
//int is eazy to test
crosspoint point;
if (l1.A * l2.B == l1.B * l2.A) {
return 0;
}
else {
point.y = (l1.A * l2.C - l1.C * l2.A) / (l1.B * l2.A - l1.A * l2.B);
if (l1.A == 0) {
point.x = (-l2.C - point.y * l2.B) / l2.A;
}
else {
point.x = (-l1.C - point.y * l1.B) / l1.A;
}
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point, 1));
return 1;
}
}
首先这个函数的返回值是int,这是因为我在单元测试时想要去看它是否计算准确了。而在运行时,我是不管这个int返回值的。我的处理思路是,传入两个Line类参数,根据一般式求交点的公式,可以求出一个交点或者无交点将交点作为Key值insert到map中,map会自动判断这个交点是否已存在,若是存在了,则不再加入map,否则map中加入这个交点。
2.一条直线和一个圆的交点计算
crosspoint point1;
crosspoint point2;
if (l.aNotExist) {
point1.x = l.t;
point2.x = l.t;
double k = ((double)l.t - c.m) * ((double)l.t - c.m);
double r2 = (double)c.r * c.r;
double left = r2 - k;
if (left < 0) {//no result
return 0;
}
else if (left == 0) {//one result
point1.y = c.n;
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
Setpoint.insert(point1);
return 1;
}
else {//two result
point1.y = sqrt(left) + c.n;
point2.y = c.n - sqrt(left);
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point2, 1));
Setpoint.insert(point1);
Setpoint.insert(point2);
return 2;
}
}
else {//ax^2+bx+t=0
double a = l.a * l.a + 1;
double b = 2 * ((l.b - c.n) * l.a - c.m);
double t = (double)c.m * c.m + (l.b - c.n) * (l.b - c.n) - (double)c.r * c.r;
double deta = b * b - 4 * a * t;
if (deta > 0) {
point1.x = (sqrt(deta) - b) / (2 * a);
point2.x = (-1 * sqrt(deta) - b) / (2 * a);
point1.y = l.a * point1.x + l.b;
point2.y = l.a * point2.x + l.b;
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point2, 1));
Setpoint.insert(point1);
Setpoint.insert(point2);
return 2;
}
else if (deta == 0) {
point1.x = (b == 0) ? 0 : -1 * b / (2 * a);
point1.y = l.a * point1.x + l.b;
//pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
Setpoint.insert(point1);
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
求一条直线和一个圆的交点还是联立方程求解,需要注意一点,联立方程后是一个一元二次方程,形式为:$$ ax^2+bx+t=0 $$我们需要根据公式进行计算,其中$$ deta=b^2-4at $$,如果deta的值大于0,那么方程有两个解,等于0有一个解,否则无解。根据这点对deta分类后分别计算,求出一个x值,然后带回方程求出y值,将交点坐标作为Key值插入map中。
3.两个圆的交点计算
int Calculate::calculate_circle_circle(Circle c1, Circle c2) {//calculate the crosspoint of the two circles
crosspoint point1;
crosspoint point2;
if (c2.n == c1.n && c2.m == c1.m) {
return 0;
}
else if (c2.n == c1.n) {
double temp = ((double)c2.m * c2.m - (double)c1.m * c1.m + (double)c2.n * c2.n - (double)c1.n * c1.n + (double)c1.r * c1.r - (double)c2.r * c2.r)
/ ((double)2 * ((double)c2.m - c1.m));
point1.x = temp;
point2.x = temp;
double left = (double)c1.r * c1.r - (temp - c1.m) * (temp - c1.m);
if (left > 0) {
point1.y = sqrt(left) + c1.n;
point2.y = c1.n - sqrt(left);
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point2, 1));
return 2;
}
else if (left == 0) {
point1.y = c1.n;
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
else {
double k = ((double)c1.m - c2.m) / ((double)c2.n - c1.n);
double temp = ((double)c2.m * c2.m - (double)c1.m * c1.m + (double)c2.n * c2.n - (double)c1.n * c1.n + (double)c1.r * c1.r - (double)c2.r * c2.r)
/ ((double)2 * ((double)c2.n - c1.n));
double a = 1 + k * k;
double b = 2 * (k * temp - c1.n * k - c1.m);
double c = (double)c1.m * c1.m + (double)c1.n * c1.n - (double)c1.r * c1.r + temp * temp - 2 * temp * c1.n;
double deta = b * b - 4 * a * c;
if (deta > 0) {
point1.x = (sqrt(deta) - b) / (2 * a);
point2.x = (-1 * sqrt(deta) - b) / (2 * a);
point1.y = point1.x * k + temp;
point2.y = point2.x * k + temp;
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point2, 1));
return 2;
}
else if (deta == 0) {
point1.x = (b == 0) ? 0 : -1 * b / (2 * a);
point1.y = point1.x * k + temp;
pointmap.insert(pair<crosspoint, int>(point1, 1));
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}
两个圆的交点求法同一条直线和一个圆,只不过参数更多更复杂而已,这完全是数学推导,因此不做过多赘述。
六.消除警告
已消除Code Quality Analysis 中的所有警告