闲来无事一套CF啊,我觉得这几个题还是有套路的,但是很明显,这个题并不难
Ted has a pineapple. This pineapple is able to bark like a bulldog! At time t (in seconds) it barks for the first time. Then every s seconds after it, it barks twice with 1 second interval. Thus it barks at times t, t + s, t + s + 1, t + 2s, t + 2s + 1, etc.

Barney woke up in the morning and wants to eat the pineapple, but he can't eat it when it's barking. Barney plans to eat it at time x (in seconds), so he asked you to tell him if it's gonna bark at that time.
The first and only line of input contains three integers t, s and x (0 ≤ t, x ≤ 109, 2 ≤ s ≤ 109) — the time the pineapple barks for the first time, the pineapple barking interval, and the time Barney wants to eat the pineapple respectively.
Print a single "YES" (without quotes) if the pineapple will bark at time x or a single "NO" (without quotes) otherwise in the only line of output.
3 10 4
NO
3 10 3
YES
3 8 51
YES
3 8 52
YES
In the first and the second sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 13, 14, ..., so it won't bark at the moment 4 and will bark at the moment 3.
In the third and fourth sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 11, 12, 19, 20, 27, 28, 35, 36, 43, 44, 51, 52, 59, ..., so it will bark at both moments 51 and 52.
就是检查下x在不在这个数列,数列眉两项之间增加s,有的相邻两项差值是1
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { int t,s,x; cin>>t>>s>>x; if(x<t+s){puts(x==t?"YES":"NO");return 0;} int k=(x-t)/s; if(t+k*s==x||t+k*s+1==x)puts("YES");else puts("NO"); return 0; }
Barney is standing in a bar and starring at a pretty girl. He wants to shoot her with his heart arrow but he needs to know the distance between him and the girl to make his shot accurate.

Barney asked the bar tender Carl about this distance value, but Carl was so busy talking to the customers so he wrote the distance value (it's a real number) on a napkin. The problem is that he wrote it in scientific notation. The scientific notation of some real number x is the notation of form AeB, where A is a real number and B is an integer and x = A × 10B is true. In our case A is between 0 and 9 and B is non-negative.
Barney doesn't know anything about scientific notation (as well as anything scientific at all). So he asked you to tell him the distance value in usual decimal representation with minimal number of digits after the decimal point (and no decimal point if it is an integer). See the output format for better understanding.
The first and only line of input contains a single string of form a.deb where a, d and b are integers and e is usual character 'e' (0 ≤ a ≤ 9, 0 ≤ d < 10100, 0 ≤ b ≤ 100) — the scientific notation of the desired distance value.
a and b contain no leading zeros and d contains no trailing zeros (but may be equal to 0). Also, b can not be non-zero if a is zero.
Print the only real number x (the desired distance value) in the only line in its decimal notation.
Thus if x is an integer, print it's integer value without decimal part and decimal point and without leading zeroes.
Otherwise print x in a form of p.q such that p is an integer that have no leading zeroes (but may be equal to zero), and q is an integer that have no trailing zeroes (and may not be equal to zero).
8.549e2
854.9
8.549e3
8549
0.33e0
0.33
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char a[1000000]; int main() { int ex=0; scanf("%c.%[0-9]e%d",&a[0],a+1,&ex); int f=0; for(int i=1; a[i]; i++) { if(a[i]!='0') { f=1; } } if(!f&&!ex) printf("%c",a[0]); else { for(int i=0; i<ex+1||a[i]; i++) { if(i==ex+1) printf("."); printf("%c",!a[i]?'0':a[i]); } } return 0; }
Barney lives in NYC. NYC has infinite number of intersections numbered with positive integers starting from 1. There exists a bidirectional road between intersections i and 2i and another road between i and 2i + 1 for every positive integer i. You can clearly see that there exists a unique shortest path between any two intersections.

Initially anyone can pass any road for free. But since SlapsGiving is ahead of us, there will q consecutive events happen soon. There are two types of events:
1. Government makes a new rule. A rule can be denoted by integers v, u and w. As the result of this action, the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v increases by w dollars.
2. Barney starts moving from some intersection v and goes to intersection u where there's a girl he wants to cuddle (using his fake name Lorenzo Von Matterhorn). He always uses the shortest path (visiting minimum number of intersections or roads) between two intersections.
Government needs your calculations. For each time Barney goes to cuddle a girl, you need to tell the government how much money he should pay (sum of passing fee of all roads he passes).
The first line of input contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1 000).
The next q lines contain the information about the events in chronological order. Each event is described in form 1 v u w if it's an event when government makes a new rule about increasing the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v by w dollars, or in form 2v u if it's an event when Barnie goes to cuddle from the intersection v to the intersection u.
1 ≤ v, u ≤ 1018, v ≠ u, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109 states for every description line.
For each event of second type print the sum of passing fee of all roads Barney passes in this event, in one line. Print the answers in chronological order of corresponding events.
7
1 3 4 30
1 4 1 2
1 3 6 8
2 4 3
1 6 1 40
2 3 7
2 2 4
94
0
32
In the example testcase:
Here are the intersections used:
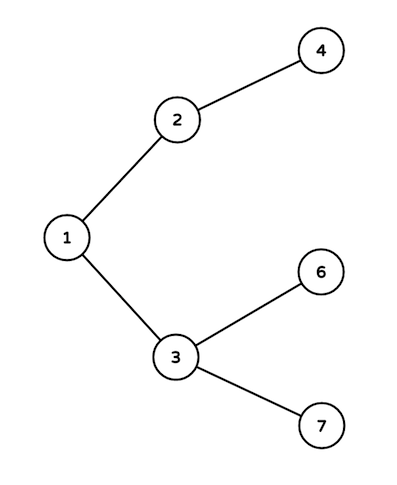
- Intersections on the path are 3, 1, 2 and 4.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are only 3 and 6.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2, 1 and 3. Passing fee of roads on the path are 32, 32 and 30 in order. So answer equals to 32 + 32 + 30 = 94.
- Intersections on the path are 6, 3 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are 3 and 7. Passing fee of the road between them is 0.
- Intersections on the path are 2 and 4. Passing fee of the road between them is 32 (increased by 30 in the first event and by 2 in the second).
Do what problem wants from you. The only thing is to find the path between the two vertices (or LCA) in the tree. You can do this in 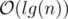 since the height of the tree is
since the height of the tree is 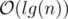 . You can keep edge weights in a map and get/set the value whenever you want. Here's a code for LCA:
. You can keep edge weights in a map and get/set the value whenever you want. Here's a code for LCA:
LCA(v, u):
while v != u:
if depth[v] < depth[u]:
swap(v, u)
v = v/2 // v/2 is parent of vertex v
Time Complexity: 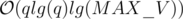
这个C就是有个树,让你统计下这个树的LCA的边值
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; map<ll,ll>road; int main() { ll q,rule,u,v,w,ans; cin>>q; while(q--) { cin>>rule; if(rule==1) { cin>>u>>v>>w; while(u!=v) { if(u<v) swap(u,v); road[u]+= w; u /= 2; } } else { cin>>u>>v; ans = 0; while(u!=v) { if(u<v) swap(u,v); ans += road[u]; u /= 2; } cout << ans << endl; } } return 0; }