一、定义和使用函数。
直接通过例子进行说明吧
class Program { static void Write() { Console.WriteLine("Test output from function"); } static void Main(string[] args) { Write(); Console.ReadKey(); } }
1、函数的构架
(1)关键字:static 和 void
static与面向对象的思维有关系,我们在这里先默认每个函数都需要加上这个关键字;
void即使便是返回值为空的意思。、
(2)函数名后跟圆括号 e.g Write();
(3)圆括号里面可以有参数,这个放在后面再讨论,
(4)一个要执行的代码块,放在花括号里面。
2、返回值
(1)当函数返回一个值时,可以采用以下两种方式修改函数
a、在函数声明中指定返回值得类型,但不使用关键字void;
b、使用return关键字结束函数的执行,把返回值传送给调用代码。
static <returnType> <functionName>() { …… return <returnValue>; }
(2)return 不一定要放在最后一行,也很经常用于直接跳出函数。
3、参数
(1)当函数接受参数的时候,就必须指定下列内容
a、函数在其定义指定接受的参数列表,以及这些参数的类型;
b、在每个函数调用中匹配的参数列表。
c、其中可以有任意多个参数,每个参数都有一个类型和一个名称,参数用逗号隔开。每个参数都在函数的代码中用作一个变量。
(2)一个demo
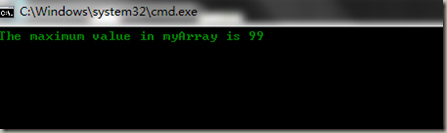
namespace Exercise { class Program { static int MaxValue(int[] intArray) { int maxVal = intArray[0]; for(int i=1;i<intArray.Length;i++) { if(intArray[i]>maxVal) { maxVal = intArray[i]; } } return maxVal; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] myArray = { 1, 5, 7, 99, 7, 8, 9, 3 }; int maxVal = MaxValue(myArray); Console.WriteLine("The maximum value in myArray is {0}", maxVal); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
运行结果是:
(3)参数匹配
在调用函数时,必须使参数与函数定义中指定的参数完全匹配,这意味着要匹配参数的类型、个数和顺序。当然这样子会导致我们重复写同样的代码,仅仅是因为参数类型的小改变,但是后面我们会有传说中的重载函数来解决这个问题。
(4)参数数组
C#允许定义一个(只能指定一个)特定的参数,这个参数必须是函数定义中参数列表的最后一个,称之为参数数组。参数数组可以使用个数不定的参数调用函数,规定用关键字params关键字定义。
一个demo:
namespace Exercise { class Program { static int SumVals(params int[] vals) { int sum = 0; foreach (int val in vals) { sum += val; } return sum; } static void Main(string[] args) { int sum = SumVals(1, 5, 7, 9, 05, 4, 8, 0, 6, 4); Console.WriteLine(sum); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(5)引用参数和值参数
然后我们调用这个函数
我们会发现,我们对参数进行的double操作并不会影响Main()中的值
但是我们在这里有一个引用的方法,可以讲参数和引入变量绑定在一起,也就是说参数成为了引入变量的一个别名,实际上是一样的东东,方法就是使用ref关键字进行指定才参数。
然后在函数调用中我们需要再一次指定ref参数,demo如下
class Program { static void ShowDouble(ref int val) { val *= 2; Console.WriteLine("val doubled = {0}",val); } static void Main(string[] args) { int myNumeber = 5; Console.WriteLine("myNumber = {0}", myNumeber); ShowDouble(ref myNumeber); Console.WriteLine("myNumber = {0}", myNumeber); } }
Attention:C#不允许假定ref参数在使用它的函数中初始化,也就是说调用的参数一定要有赋值过。
(6)输出参数
除了按引用传递值之外,还可以使用out关键字,指定所给的的参数是一个输出参数,out关键字和ref关键字的使用方法相同,执行的原理与引用参数一样,但是有一些重要的区别:
a、把未赋值的变量用作ref参数是非法的,但可以把未赋值的变量作out参数。
b、另外,在函数使用out参数时,out参数必须看成未赋值。换句话说,out参数会遗忘原有的数值。
现在写一个demo
class Program { static int MaxValue(int[] intArray,out int maxIndex) { int maxVal = intArray[0]; maxIndex = 0; for(int i=1;i<intArray.Length;i++) { if(intArray[i]>maxVal) { maxVal = intArray[i]; maxIndex = i; } } return maxVal; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] myArray = {3,5,6,77,4,24,234,26,536,7,6577,8}; int maxIndex; Console.WriteLine("The maximum value in myArray is {0}",MaxValue(myArray,out maxIndex)); Console.WriteLine("The first occurrence of this value is at element {0}",maxIndex); Console.ReadKey(); } }
二、变量的作用域
1、变量的作用域包含定义他们的代码块和直接嵌套在其中的代码块。(包括循环和条件语句)
namespace Exercise { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { string text = "Line" + Convert.ToString(i); Console.WriteLine("{0}", text); } Console.WriteLine("Last text output in loop: {0}", text); } } }
由于text是循环里的局部变量,所以跳出循环之后就不能在使用text了。然后修改一下
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int i; string text; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { text = "Line" + Convert.ToString(i); Console.WriteLine("{0}", text); } Console.WriteLine("Last text output in loop: {0}", text); } }
这段代码依旧会是编译出错,原因是必须在使用变量前对其进行声明和初始化,而text是在for循环里面初始化的,赋给text的值在循环快退出时就丢失了,但是还可以进行如下的修改
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int i; string text=""; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { text = "Line" + Convert.ToString(i); Console.WriteLine("{0}", text); } Console.WriteLine("Last text output in loop: {0}", text); } }
这次代码就是先在循环外进行了初始化。所以在这里我们需要掌握一个好的习惯就是在声明一个变量的时候最好是记得进行初始化,这样的话即使出错,我们也可以很容易的得知是那个变量出现了问题,还有就是避免这些问题的发生,
2、全局变量
这钟变量最好是少使用,一般我们也是很少进行使用的,尽量的进行避免。但是如果全局都需要经常访问的话,全局变量的优势就会体现出来。
在局部变量和全局变量的名字发生冲突的时候,局部变量会掩盖全局变量。
三、Main()函数
Main()是C#应用程序的入口和出口。就是说Main()函数是整个函数的框架。
1、Main()的四种形式
(1)第三四种版本会返回一个int值,他们可以用于表示程序如何终止,通常作为一种错误提示,如果是正常关闭的话,就是返回0。
(2)Main()的可选参数args是从应用程序的外部接受信息的方法,这些信息在运行期间指定,其形式是命令行参数。也就是说在执行控制台应用程序时,指定的任何命令参数都放在这个args数组中,然后可以根据需要在Main()中使用这些参数。
然后这里有个简单的demo
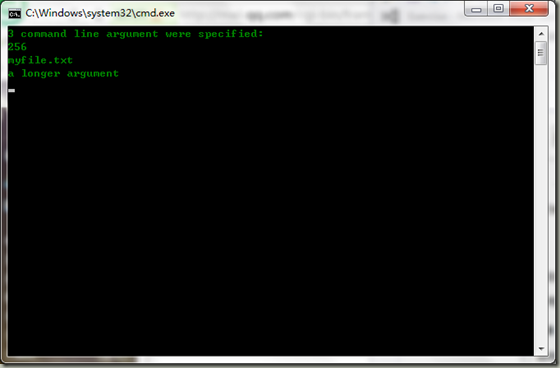
namespace Exercise { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("{0} command line argument were specified:", args.Length); foreach(string arg in args) { Console.WriteLine(arg); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
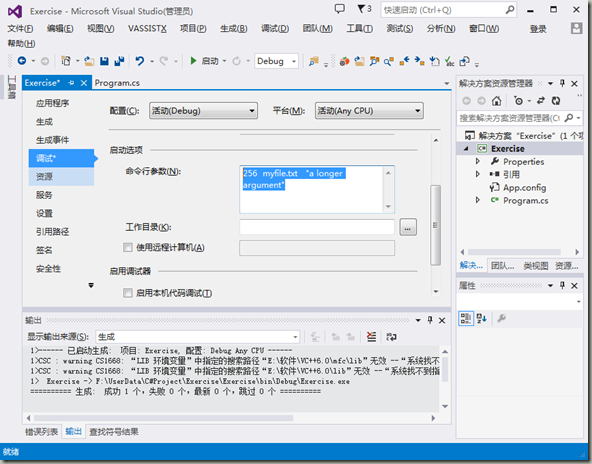
然后我们要在项目属性中进行设置,如图(在调试那一栏)
在命令参数行:我们可以加入很多的命令- -,在这里就随意加一点,只是实现这个功能而已,如果单词和单词之间有空格存在的话,我们就需要用“”括起来,这样子才不会被当成是多个命令。效果如图
四、结构函数
就是结构体中可以不仅仅可以加入变量,而且可以加入函数。那么我们就用一个demo来解决吧。
namespace Exercise { class Program { struct customerName { public string firstName, lastName; public string Name() { return firstName + " " + lastName; } } static void Main(string[] args) { customerName myCustomerName; myCustomerName.firstName = "Chen"; myCustomerName.lastName = "Xuewen"; Console.WriteLine("{0}", myCustomerName.Name()); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
然后函数的可以在结构体内可以看做是全局函数。
五、函数的重载
重载就是“重复”,函数的重载也就是说函数可以有同样的名字,但是有着不同的功能,比如说如果我们要求一个数组里面的最大值,但是数组又有不同的类型,如果再取不同 的名字会很麻烦,于是哦我们就可以使用函数重载,保持函数名称不变,而实现功能。现在有个demo、
static int MaxValue(int[] intArray) { int maxVal = intArray[0]; for(int i=0;i<intArray.Length;i++) { if(intArray[i]>maxVal) { maxVal = intArray[i]; } } return maxVal; } static double MaxValue(double[] doubleArray) { double maxVal = doubleArray[0]; for (int i = 0; i < doubleArray.Length; i++) { if (doubleArray[i] > maxVal) { maxVal = doubleArray[i]; } } return maxVal; }
这两个函数就实现了函数的重载,但请注意,如果仅仅只是改变return(也就是返回值的类型)的类型,C#是不会认为是2个重载的函数,而是会发生错误。大家要小心
六、委托
委托的声明非常类似于函数,但是不带函数体,但是要使用delegate关键字,委托声明指定了一个返回类型和一个参数列表。
在定义了委托后,就可以声明该委托类型的变量,接着把这个变量初始化为与委托有相同返回类型和桉树列表的函数引用。之后就可以使用这个委托来调用这个函数,就像这个变量就是一个函数的样子。
namespace Exercise { class Program { delegate double ProcessDelegate(double param1, double param2); //设置一个委托 static double Mulitiply(double param1, double param2) { return param1 * param2; } static double Division(double param1,double param2) { return param1 / param2; } static void Main(string[] args) { ProcessDelegate process;//声明一个委托(但是还没有绑定函数) //下面这段代码就是用来分割出来两个数字的- -,比C++麻烦很多- - Console.WriteLine("Enter 2 number separated with a comma:"); string input = Console.ReadLine(); int commaPos = input.IndexOf(","); double param1 = Convert.ToDouble(input.Substring(0, commaPos)); double param2 = Convert.ToDouble(input.Substring(commaPos + 1, input.Length - commaPos - 1)); //选择功能 Console.WriteLine("Enter M to multiply or D to divide:"); input = Console.ReadLine(); input = input.ToUpper(); if(input == "M") { process = new ProcessDelegate(Mulitiply); } else { process = new ProcessDelegate(Division); } Console.WriteLine("Result:{0}", process(param1, param2)); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
然后委托主要是用于事件,这个在第13章中会用到哈。