问题
- session 如何生成的?sessionId为什么不直接使用时间戳+单机名
- sessionid 关闭的时候的逻辑,sessionid 的维护是由各节点还是leader ?
会话相关
sessionid 生成
我们看一下session 管理类 SessionTrackerImpl。 它主要维护三个字段
//根据 sessionid 存放的 session
HashMap<Long, SessionImpl> sessionsById = new HashMap<Long, SessionImpl>();
//key 是时间 ,用于根据下次会话超时时间点来归纳会话,便于进行会话管理和超时检查,(分桶策略容器)
HashMap<Long, SessionSet> sessionSets = new HashMap<Long, SessionSet>();
//key 是 sessionId , value 是过期时间
ConcurrentHashMap<Long, Integer> sessionsWithTimeout;
其他的都是操作 session 的方法,我们看一下创建sessionId的过程,SessionImpl 类
public static long initializeNextSession(long id) {
long nextSid = 0;
nextSid = (Time.currentElapsedTime() << 24) >>> 8;
nextSid = nextSid | (id <<56);
return nextSid;
}
得出的 sessionid前8位确定所在的机器,后56位使用当前时间的毫秒数表示进行随机。
session 管理
使用的是分桶策略,如下图所示。
以时间戳为节点,每个桶装这该时间点(过期的时间)的 session集合,然后有一个线程那桶里的多个session 进行检查,加入过期时间被延长,那么session 进行迁移到其他的桶,否则将被清理。
创建会话执行事务过程
创建会话之前我们要先知道zk服务器是如何和客户端连接的。上一篇文章结尾处,我们知道了处理与 客户端的连接主要是由 NIOServerCnxnFactory 来负责的。而真正处理的逻辑就在 run 方法。
/**
* 默认允许连接 60个客户端,
* 这个(一个)线程会处理
* - 来自客户端的连接
* - 来自客户端的读
* - 来自客户端的写
*
*
*/
public void run() {
//只要没有断开,循环一直进行
//下面连接就是我们熟悉的 java NIO 的运用
while (!ss.socket().isClosed()) {
try {
//select 方法一直就阻塞
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selected;
//这里为什么要加锁呢?可能有多个线程
synchronized (this) {
selected = selector.selectedKeys();
}
ArrayList<SelectionKey> selectedList = new ArrayList<SelectionKey>(
selected);
Collections.shuffle(selectedList);
for (SelectionKey k : selectedList) {
if ((k.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) != 0) {
SocketChannel sc = ((ServerSocketChannel) k
.channel()).accept();
InetAddress ia = sc.socket().getInetAddress();
int cnxncount = getClientCnxnCount(ia);
//客户端可以保存 60 个连接
if (maxClientCnxns > 0 && cnxncount >= maxClientCnxns){
LOG.warn("Too many connections from " + ia
+ " - max is " + maxClientCnxns );
sc.close();
} else {
LOG.info("Accepted socket connection from "
+ sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress());
sc.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey sk = sc.register(selector,
SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//创建连接,连接用 NIOServerCnxn这个类来维护
NIOServerCnxn cnxn = createConnection(sc, sk);
sk.attach(cnxn);
addCnxn(cnxn);
}
} else if ((k.readyOps() & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE)) != 0) {
//处理客户端读写操作,重点看 doIO 方法
NIOServerCnxn c = (NIOServerCnxn) k.attachment();
c.doIO(k);
} else {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Unexpected ops in select "
+ k.readyOps());
}
}
}
selected.clear();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
LOG.warn("Ignoring unexpected runtime exception", e);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Ignoring exception", e);
}
}
closeAll();
LOG.info("NIOServerCnxn factory exited run method");
}
我们再来看一下 doIO这个方法 , 位于 NIOServerCnxn 内
/**
* Handles read/write IO on connection.
*/
void doIO(SelectionKey k) throws InterruptedException {
try {
if (isSocketOpen() == false) {
LOG.warn("trying to do i/o on a null socket for session:0x"
+ Long.toHexString(sessionId));
return;
}
//可读类型
if (k.isReadable()) {
int rc = sock.read(incomingBuffer);
if (rc < 0) {
throw new EndOfStreamException(
"Unable to read additional data from client sessionid 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(sessionId)
+ ", likely client has closed socket");
}
if (incomingBuffer.remaining() == 0) {
boolean isPayload;
//读取下一个请求
if (incomingBuffer == lenBuffer) { // start of next request
//翻转缓存区,可读
incomingBuffer.flip();
//读取lenBuffer的前四个字节,当读取的是内容长度时则为true,否则为false
isPayload = readLength(k);
//清空缓存
incomingBuffer.clear();
} else {
// continuation
isPayload = true;
}
// isPayload 为 true ,表示buffer 里面是负载
if (isPayload) { // not the case for 4letterword
readPayload();
}
else {
// four letter words take care
// need not do anything else
return;
}
}
}
//可写类型
if (k.isWritable()) {
// ZooLog.logTraceMessage(LOG,
// ZooLog.CLIENT_DATA_PACKET_TRACE_MASK
// "outgoingBuffers.size() = " +
// outgoingBuffers.size());
if (outgoingBuffers.size() > 0) {
// ZooLog.logTraceMessage(LOG,
// ZooLog.CLIENT_DATA_PACKET_TRACE_MASK,
// "sk " + k + " is valid: " +
// k.isValid());
/*
* This is going to reset the buffer position to 0 and the
* limit to the size of the buffer, so that we can fill it
* with data from the non-direct buffers that we need to
* send.
*/
ByteBuffer directBuffer = factory.directBuffer;
directBuffer.clear();
for (ByteBuffer b : outgoingBuffers) {
if (directBuffer.remaining() < b.remaining()) {
/*
* When we call put later, if the directBuffer is to
* small to hold everything, nothing will be copied,
* so we've got to slice the buffer if it's too big.
*/
b = (ByteBuffer) b.slice().limit(
directBuffer.remaining());
}
/*
* put() is going to modify the positions of both
* buffers, put we don't want to change the position of
* the source buffers (we'll do that after the send, if
* needed), so we save and reset the position after the
* copy
*/
int p = b.position();
directBuffer.put(b);
b.position(p);
if (directBuffer.remaining() == 0) {
break;
}
}
/*
* Do the flip: limit becomes position, position gets set to
* 0. This sets us up for the write.
*/
directBuffer.flip();
int sent = sock.write(directBuffer);
ByteBuffer bb;
// Remove the buffers that we have sent
while (outgoingBuffers.size() > 0) {
bb = outgoingBuffers.peek();
if (bb == ServerCnxnFactory.closeConn) {
throw new CloseRequestException("close requested");
}
int left = bb.remaining() - sent;
if (left > 0) {
/*
* We only partially sent this buffer, so we update
* the position and exit the loop.
*/
bb.position(bb.position() + sent);
break;
}
packetSent();
/* We've sent the whole buffer, so drop the buffer */
sent -= bb.remaining();
outgoingBuffers.remove();
}
// ZooLog.logTraceMessage(LOG,
// ZooLog.CLIENT_DATA_PACKET_TRACE_MASK, "after send,
// outgoingBuffers.size() = " + outgoingBuffers.size());
}
synchronized(this.factory){
if (outgoingBuffers.size() == 0) {
if (!initialized
&& (sk.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == 0) {
throw new CloseRequestException("responded to info probe");
}
sk.interestOps(sk.interestOps()
& (~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE));
} else {
sk.interestOps(sk.interestOps()
| SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
LOG.warn("CancelledKeyException causing close of session 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(sessionId));
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("CancelledKeyException stack trace", e);
}
close();
} catch (CloseRequestException e) {
// expecting close to log session closure
close();
} catch (EndOfStreamException e) {
LOG.warn(e.getMessage());
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("EndOfStreamException stack trace", e);
}
// expecting close to log session closure
close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Exception causing close of session 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(sessionId) + ": " + e.getMessage());
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("IOException stack trace", e);
}
close();
}
}
/** Read the request payload (everything following the length prefix) */
private void readPayload() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (incomingBuffer.remaining() != 0) { // have we read length bytes?
int rc = sock.read(incomingBuffer); // sock is non-blocking, so ok
if (rc < 0) {
throw new EndOfStreamException(
"Unable to read additional data from client sessionid 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(sessionId)
+ ", likely client has closed socket");
}
}
if (incomingBuffer.remaining() == 0) { // have we read length bytes?
packetReceived();
incomingBuffer.flip();
//执行读取负载的逻辑
if (!initialized) {
//非初始化
readConnectRequest();
} else {
readRequest();
}
lenBuffer.clear();
incomingBuffer = lenBuffer;
}
}
其中我们看一下如何连接的,即上面的 readConnectRequest 方法
private void readConnectRequest() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (!isZKServerRunning()) {
throw new IOException("ZooKeeperServer not running");
}
zkServer.processConnectRequest(this, incomingBuffer);
initialized = true;
}
于是我们到了ZookeeperServer 的 processConnectRequest 方法
/**
* 封装成一个 connectRequest
* 提交请求到leader
*/
public void processConnectRequest(ServerCnxn cnxn, ByteBuffer incomingBuffer) throws IOException {
BinaryInputArchive bia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(new ByteBufferInputStream(incomingBuffer));
ConnectRequest connReq = new ConnectRequest();
connReq.deserialize(bia, "connect");
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Session establishment request from client "
+ cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ " client's lastZxid is 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(connReq.getLastZxidSeen()));
}
boolean readOnly = false;
try {
readOnly = bia.readBool("readOnly");
cnxn.isOldClient = false;
} catch (IOException e) {
// this is ok -- just a packet from an old client which
// doesn't contain readOnly field
LOG.warn("Connection request from old client "
+ cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ "; will be dropped if server is in r-o mode");
}
if (readOnly == false && this instanceof ReadOnlyZooKeeperServer) {
String msg = "Refusing session request for not-read-only client "
+ cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress();
LOG.info(msg);
throw new CloseRequestException(msg);
}
if (connReq.getLastZxidSeen() > zkDb.dataTree.lastProcessedZxid) {
String msg = "Refusing session request for client "
+ cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress()
+ " as it has seen zxid 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(connReq.getLastZxidSeen())
+ " our last zxid is 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(getZKDatabase().getDataTreeLastProcessedZxid())
+ " client must try another server";
LOG.info(msg);
throw new CloseRequestException(msg);
}
int sessionTimeout = connReq.getTimeOut();
byte passwd[] = connReq.getPasswd();
int minSessionTimeout = getMinSessionTimeout();
if (sessionTimeout < minSessionTimeout) {
sessionTimeout = minSessionTimeout;
}
int maxSessionTimeout = getMaxSessionTimeout();
if (sessionTimeout > maxSessionTimeout) {
sessionTimeout = maxSessionTimeout;
}
cnxn.setSessionTimeout(sessionTimeout);
// We don't want to receive any packets until we are sure that the
// session is setup
cnxn.disableRecv();
long sessionId = connReq.getSessionId();
if (sessionId != 0) {
long clientSessionId = connReq.getSessionId();
LOG.info("Client attempting to renew session 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(clientSessionId)
+ " at " + cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress());
serverCnxnFactory.closeSession(sessionId);
cnxn.setSessionId(sessionId);
reopenSession(cnxn, sessionId, passwd, sessionTimeout);
} else {
LOG.info("Client attempting to establish new session at "
+ cnxn.getRemoteSocketAddress());
//真正执行请求的地方 : 创建 session,提交请求
createSession(cnxn, passwd, sessionTimeout);
}
}
long createSession(ServerCnxn cnxn, byte passwd[], int timeout) {
long sessionId = sessionTracker.createSession(timeout);
Random r = new Random(sessionId ^ superSecret);
r.nextBytes(passwd);
ByteBuffer to = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
to.putInt(timeout);
cnxn.setSessionId(sessionId);
//提交请求
submitRequest(cnxn, sessionId, OpCode.createSession, 0, to, null);
return sessionId;
}
/**
* @param cnxn
* @param sessionId
* @param xid
* @param bb
*/
private void submitRequest(ServerCnxn cnxn, long sessionId, int type,
int xid, ByteBuffer bb, List<Id> authInfo) {
Request si = new Request(cnxn, sessionId, xid, type, bb, authInfo);
submitRequest(si);
}
public void submitRequest(Request si) {
if (firstProcessor == null) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
// Since all requests are passed to the request
// processor it should wait for setting up the request
// processor chain. The state will be updated to RUNNING
// after the setup.
// 在 startup 方法中直到初始化完成才得以接受请求
while (state == State.INITIAL) {
wait(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Unexpected interruption", e);
}
if (firstProcessor == null || state != State.RUNNING) {
throw new RuntimeException("Not started");
}
}
}
try {
//判断 session 是否还存活
touch(si.cnxn);
boolean validpacket = Request.isValid(si.type);
if (validpacket) {
//firstProcessor 开始执行
firstProcessor.processRequest(si);
if (si.cnxn != null) {
incInProcess();
}
} else {
LOG.warn("Received packet at server of unknown type " + si.type);
new UnimplementedRequestProcessor().processRequest(si);
}
} catch (MissingSessionException e) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Dropping request: " + e.getMessage());
}
} catch (RequestProcessorException e) {
LOG.error("Unable to process request:" + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
清楚了服务器与客户端的连接,知道了最终会到执行任务链上。
我们可以连接任意一台 zk服务器,进行事务请求,当follower接受到请求后它就会转发给leader ,而follower 和 leader 都是使用责任链进行处理来自客户端的请求的。
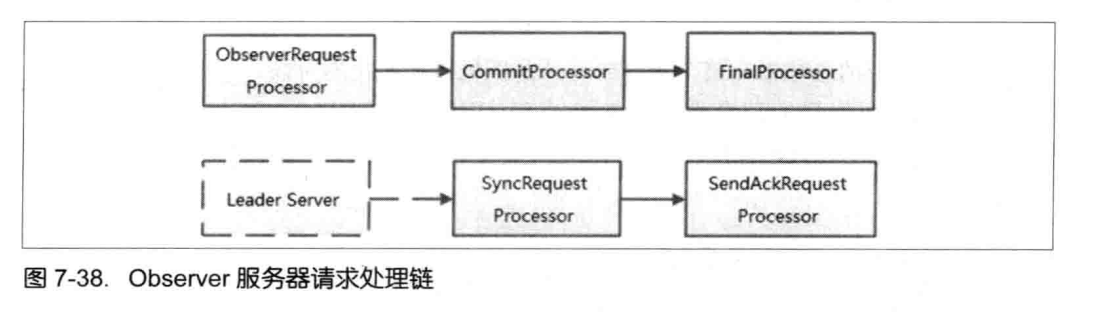
我们先来看一下follower 和 leader 责任链的流程。
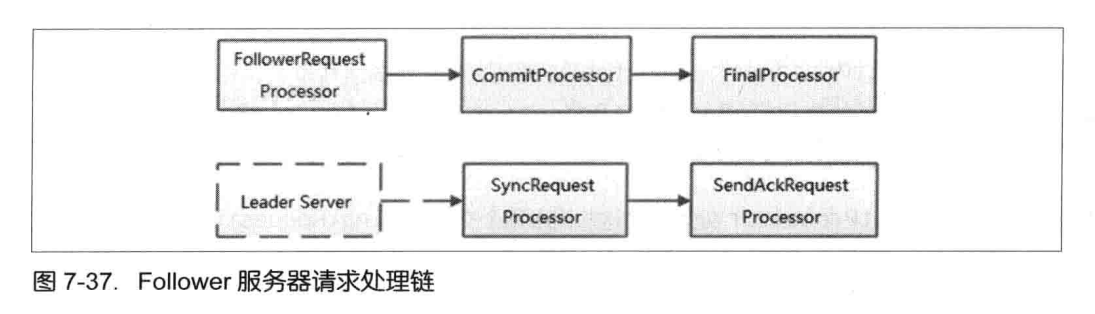
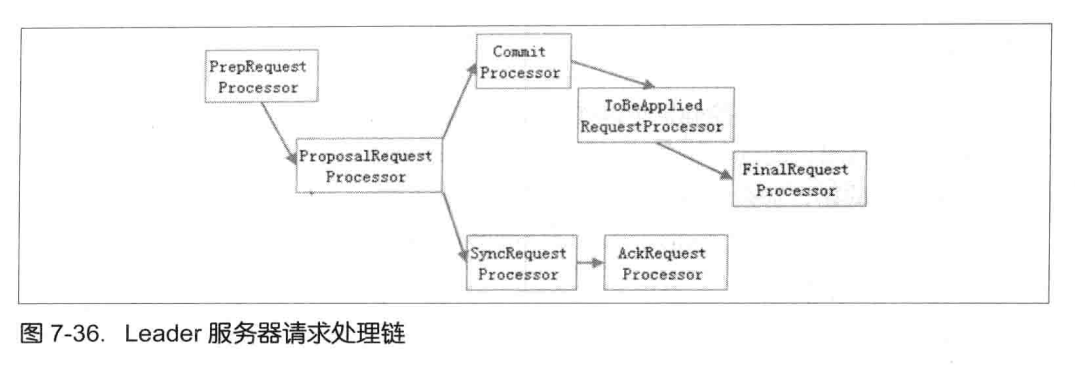
请求处理流程
会话创建请求
我们通过下面的图片先来了解整个过程
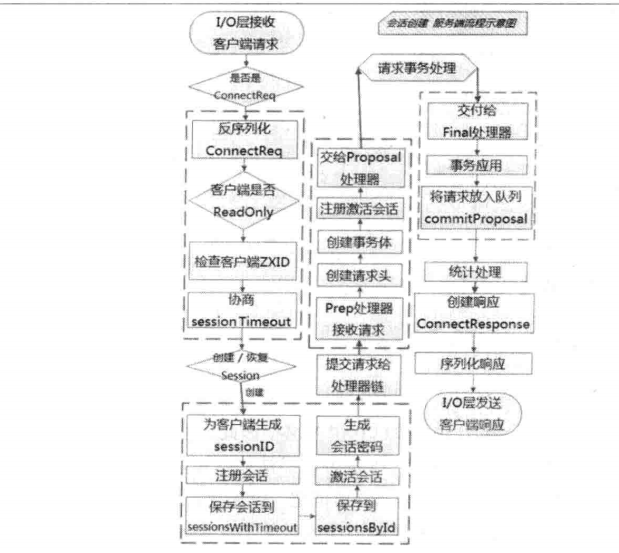
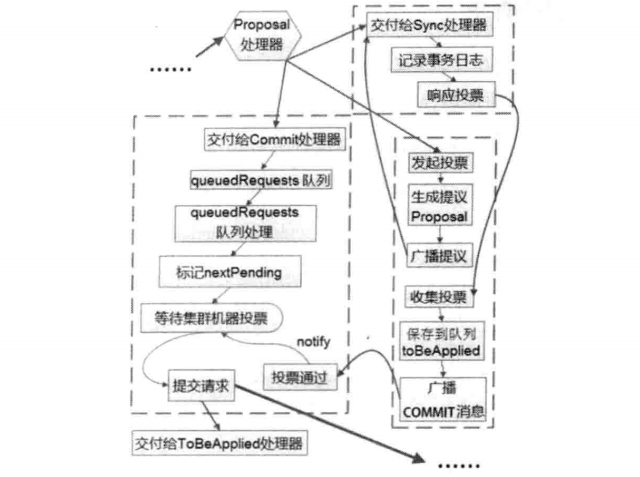
概括起来就是 :
- NIOServerCnxn 接受请求
- 协商 sessionTimeout ,创建 connectRequest
- 创建会话,生成 sessionId,注册会话和激活会话
- 交给 leader 的 PrepRequestProcessor
- 创建请求事务体 createSessionTxn
- 交给 ProposalRequestProcessor,接下来就会进入三个子流程
子流程如下 : - Sync流程,follower做好日志记录,同时返回 ACK 给leader
- Proposal流程,生成proposal ,广播提议,获得半数票后,请求加入到 toBeApplied 队列,广播commit 信息
- Commit流程,将请求交付给CommitProcessor 处理器,等待上阶段的投票结果,提交请求,交付给下一个处理器 : FinalRequestProcessor
- 到此三个子流程走完后,到了最后的阶段,事务应用,之前我们的议案只是应用在日志中,并没有在内存中生效,这阶段需要将请求应用在内存中。
这个就是整个会话创建请求的处理过程,当客户端发出事务请求时也是像处理会话创建一样的流程。
总结
这一篇主要讲了zk 创建session的策略和管理的逻辑,同时介绍了处理事务的过程。