Ⅰ. SpringApplication
1. Startup Failure 启动失败
注入FailureAnalyzers 获得一个机会去提供一个详细的错误信息
SpringBoot提供了很多FailureAnalyzer 的实现类,也可以添加自定义的
如果没有failure analyzers 可以开启debug模式 java -jar xxx.jar --debug
FailureAnalyzer实现必须在META-INF/spring.factories中注册,如:
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer= com.example.ProjectConstraintViolationFailureAnalyzer
2. Customizing the Banner 自定义横幅
https://blog.csdn.net/u011447164/article/details/86009262
3. Customizing SpringApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootJarApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(SpringBootJarApplication.class);
app.setBanner((e, c, o) -> o.println("BINGJJFLY") );
app.run(args);
}
}
4. Fluent Builder API 流畅的Builder API
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootJarApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder()
.sources(SpringBootJarApplication.class)
.bannerMode(Banner.Mode.CONSOLE)
.banner((e, c, o) -> o.println("BINGJJFLY"))
.run(args);
}
}
5. Application Events and Listeners 应用事件和监听器
除了常见的spring框架事件(如ContextRefreshedEvent)之外,SpringApplication还发送一些额外的应用程序事件
添加监听器方式:
(1)SpringApplication.addListeners(…)
(2)SpringApplicationBuilder.listeners(…)
(3)META-INF/spring.factories 文件中添加:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.example.project.MyListener
事件发送顺序:
(1)ApplicationStartingEvent:在运行开始时但在任何处理之前发送,除非用于注册侦听器和初始化器
(2)ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent:在已知上下文中要使用的Environment,但在创建上下文之前发送
(3)ApplicationPreparedEvent:在刷新开始之前但在加载bean定义之后发送
(4)ApplicationStartedEvent:在刷新上下文之后,但在调用任何应用程序和命令行运行程序之前发送
(5)ApplicationReadyEvent:在调用任何应用程序和命令行运行程序后发送。它表示应用程序已准备好为请求提供服务
(6)ApplicationFailedEvent:启动出现异常时发送
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1617119527751442850&wfr=spider&for=pc
6. Web Environment
web环境设置,test环境可以指定为非web
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootJarApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(SpringBootJarApplication.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.NONE)
.run(args);
}
}
7. Accessing Application Arguments 获得系统运行参数
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/args")
public class ArgsController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationArguments args;
@Value("profile")
private String profile;
@RequestMapping("/application")
public void application() {
List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs();
nonOptionArgs.forEach(o -> System.out.println("运行参数(ApplicationArguments方式):" + o));
System.out.println("运行参数(@Value方式):" + profile);
}
}
8. Using the ApplicationRunner or CommandLineRunner
在SpringApplication完全启动之前(run方法执行完之前、发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件之前) 进行特殊操作
@Slf4j
@Order(1) // 两个都存在时可以加顺序
@Component
public class ArgsCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
log.info("CommandLineRunner方式获得运行参数:{}", args);
}
}
@Slf4j
@Order(2)
@Component
public class ArgsApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
log.info("ApplicationRunner方式获得运行参数:{}", args.getNonOptionArgs());
}
}
9. Application Exit 优雅的退出
每个Spring应用都会向JVM注册一个关机钩子以优雅的退出,Spring标准回调方式:DisposableBean、@PreDestroy
SpringBoot额外提供ExitCodeGenerator
@Bean
public ExitCodeGenerator ecg() {
return () -> 17;
}
10. Admin Features
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a9e35674c530
Ⅱ. Externalized Configuration 外部化配置
外部化配置文件方式:properties、yaml,获取配置信息方式:@Value、Environment、@ConfigurationProperties
1. Configuring Random Values
my.secret=${random.value}
my.number=${random.int}
my.bignumber=${random.long}
my.uuid=${random.uuid}
my.number.less.than.ten=${random.int(10)}
my.number.in.range=${random.int[1024,65536]}
2. Accessing Command Line Properties
SpringApplication可以转换所有命令行参数(--arg=val)到Environment,如果不想映射到其中可以:
SpringApplication.setAddCommandLineProperties(false)
3. Application Property Files
加载application.properties的顺序(First Match Wins策略):
根目录下/config目录及子目录
根目录
类路径下/config目录及子目录
重定义配置文件信息
java -jar myproject.jar --spring.config.name=myproject java -jar myproject.jar --spring.config.location=classpath:/default.properties,classpath:/ override.properties
spring.config.location如果是目录必须以'/'结尾, 且在spring.config.name加载,加载顺序正好和First Match Wins相反(Last Match Wins),且覆盖上述的加载顺序
spring.config.additional-location扩展加载范围,且在上述加载顺序之前
4. Profile-specific Properties
加后缀配置文件总是覆盖非特定配置文件
application.properties(公共配置信息)
spring.profiles.active=@{spring.active}
application-dev.properties(开发环境配置信息)
server.port=8081
application-prod.properties(生产环境配置信息)
server.port=8082
重定义resources插件的分隔符,SpringBoot将分隔符修改成了 '@'(@spring.active@)
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<delimiters>
<delimiter>@{*}</delimiter>
</delimiters>
<useDefaultDelimiters>false</useDefaultDelimiters>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/webapp</directory>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<spring.active>dev</spring.active>
</properties>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<spring.active>prod</spring.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
打包命令
mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true -P prod
5. Placeholders in Properties 占位符
app.name=MyApp
app.description=${app.name} is a Spring Boot application
# --port=7797 代替 --server.port=7797
server.port=${port:8080}
6. Encrypting Properties 加密属性
SpringBoot不支持直接对属性加密,但是提供EnvironmentPostProcessor(自定义参考SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor)对Environment进行操作在应用启动之前
resources下添加META-INF/spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor= com.wjz.config.processor.EnvironmentPostProcessorExample
创建一个包含敏感信息的配置文件encrypting.properties
db.password=encrypt_password
自定义EnvironmentPostProcessor,order大则优先级低
package com.wjz.config.processor;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.boot.env.OriginTrackedMapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
public class EnvironmentPostProcessorExample implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, Ordered {
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 100;
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
private final PropertiesPropertySourceLoader loader = new PropertiesPropertySourceLoader();
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
Resource path = new ClassPathResource("encrypting.properties");
PropertySource<Map<String, Object>> propertySource = loadProperties(path);
environment.getPropertySources().addLast(propertySource);
}
private PropertySource<Map<String, Object>> loadProperties(Resource path) {
if (!path.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Resource "+ path + "does not exist");
}
try {
return new DecryptedMapPropertySource((OriginTrackedMapPropertySource) loader.load("custom-resource", path).get(0));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to load properties configuration from " + path, e);
}
}
private static class DecryptedMapPropertySource extends MapPropertySource {
public DecryptedMapPropertySource(OriginTrackedMapPropertySource propertySource) {
super(propertySource.getName(), propertySource.getSource());
}
@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
Object val = super.getProperty(name);
if ("db.password".equals(name)) {
return "DecryptedValue";
}
return val;
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return order;
}
}
7. Using YAML Instead of Properties
YamlPropertySourceLoader可以加载yaml文件为PropertySource,这样就可以使用@Value获得属性值
private final YamlPropertySourceLoader loader = new YamlPropertySourceLoader();
PropertySource<?> propertySource = loadYaml(path);
private PropertySource<?> loadYaml(Resource path) {
if (!path.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Resource " + path + " does not exist");
}
try {
return this.loader.load("custom-resource", path).get(0);
}catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to load yaml configuration from " + path, ex);
}
}
spring.profiles既支持字面量(prod)也支持表达式(prod & prev),表达式运算符(‘!’、‘&’、‘|’)
production & us-east | eu-central 无效,production & (us-east | eu-central) 有效
Yaml缺点:
1. 不能使用@PropertySource获得属性值
2. 特定profile文件和多文档不能结合使用,如 application-dev.yml
server: port: 8000 --- spring: profiles: !test security: user: password: weak
8. Type-safe Configuration Properties 属性映射为对象
1. Map初始化后可省略setter
2. Collection或Array推荐添加setter,即使初始化不能添加final
3. POJO一般可省略setter
4. 如果使用Lombok则确保没有特殊的构造器
5. 静态变量不能被映射
配置类中使用配置信息参考git:spring-boot-jar.EmailAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AcmeProperties.class)
public class MyConfiguration {
}
这种形式下,AcmeProperties的BeanName为<profile>-<fqn>(前缀-类的全限定名),形如:acme-com.example.AcmeProperties
除了上述这种形式还可以将配置信息类作为Bean组件(即添加@Component)
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="acme")
public class AcmeProperties {
}
使用@configurationproperties还可以生成元数据文件(spring-configuration-metadata.json),IDE可以根据该文件在配置文件中进行提示
{
"groups": [
{
"name": "boot.email",
"type": "com.wjz.config.EmailProperties",
"sourceType": "com.wjz.config.EmailProperties"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "boot.email.power",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "com.wjz.config.EmailProperties"
}
],
"hints": []
}
前提条件是添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency>
Third-party Configuration 第三方依赖配置
类似于web有service的依赖,但是web想为service的某个类映射属性值
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "service")
@Bean
public AnotherComponent anotherComponent() {
return new AnotherComponent();
}
Relaxed Binding 松散绑定
连接号形式(驼峰格式):context-path == contextPath
大写形式(系统变量):PORT == port
松散绑定方式
acme.my-project.person.first-name Kebab case格式,推荐使用在.properties和.yml文件中 acme.myProject.person.firstName 标准驼峰格式 acme.my_project.person.first_name 下划线格式 ACME_MYPROJECT_PERSON_FIRSTNAME 全大写格式,为系统变量时推荐使用
@ConfigurationProperties的prefix属性必须为kebab case格式
Merging Complex Types 映射复杂类型
当在多个位置配置集合时,重写通过替换整个集合来工作
List在多个profile中配置时,只有一个profile起作用
Map在多个文件中配置时,只有一个文件(优先级高的)起作用
Properties Conversion 属性转换
如果想自定义属性类型转换,提供一个ConversionService(BeanName为conversionService) 、自定义属性编辑器(通过CustomEditorConfigurer)、自定义Converters(通过@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding)
Converting durations jdk8新特性日期类型
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS) private Duration sessionTimeout = Duration.ofSeconds(30);
映射类型:秒 30,PT30s,30s、毫秒 500, PT0.5S and 500ms,默认为毫秒除非指定了@DurationUnit
Converting Data Sizes 数据大小
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.MEGABYTES) private DataSize bufferSize = DataSize.ofMegabytes(2);
映射类型:M 10,10MB、B 256,256B,默认为B除非指定了@DataSizeUnit
@ConfigurationProperties Validation JSR-303数据校验
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="acme")
@Validated
public class AcmeProperties {
@NotNull
private InetAddress remoteAddress;
}
默认的@Validated也可以用在@Bean修饰的方法上
@Configuration
public class AcmeConfiguration {
@Bean
@Validated
private InetAddress remoteAddress(){
return new InetAddress();
}
}
尽管内嵌属性在绑定时也将被验证,但最好同时注释关联字段为@Valid
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="acme")
@Validated
public class AcmeProperties {
@NotNull
private InetAddress remoteAddress;
@Valid
private final Security security = new Security();
public static class Security {
@NotEmpty
public String username;
}
}
还可以通过创建一个名为configurationPropertiesValidator的bean定义来添加一个自定义的Spring验证器,@Bean修饰的方法必须为static的
spring-boot-sample-property-validation
@ConfigurationProperties vs. @Value
功能 批量映射 逐一映射
松散绑定 支持 不支持
SpEL 不支持 支持
JSP303数据校验 支持 不支持
复杂类型 支持 不支持
Ⅲ. Profiles
任意一个@Component或@Configuration都可以注释一个@Profile以适应不同的环境,不符合条件的组件不会被注入到容器中
@Configuration
@Profile("production")
public class ProductionConfiguration {
}
application.properties中
spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb
命令行中
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb
1. Adding Active Profiles
即使指定了spring.profiles.active=prod,profiles也包含prev
application.properties
spring.profiles.include=prev
API
new SpringApplicationBuilder(SpringBootJarApplication.class)
.profiles("prev")
.run(args);
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(SpringBootJarApplication.class);
application.setAdditionalProfiles("prev");
application.run(args);
Ⅳ. Logging
1. File Output 输出到文件
默认的Spring Boot只输出日志到控制台,修改则设置logging.file或logging.path
logging.file 指定的日志文件,可以是确切的位置或相对于当前目录
logging.path 指定日志存放目录,可以使确切目录或相对于当前目录
默认的日志文件大小为10M,超过限制则创建新的日志文件,且无数量限制
logging.file.max-size=5KB logging.file.max-history=3
2. Log Levels
logging.level.root=WARN logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG logging.level.org.hibernate=ERROR
3. Log Groups
logging.group.tomcat=org.apache.catalina, org.apache.coyote, org.apache.tomcat logging.level.tomcat=TRACE # 两个开箱即用的日志组web,sql # logging.group.web=org.springframework.core.codec, org.springframework.http, org.springframework.web # logging.group.sql=org.springframework.jdbc.core, org.hibernate.SQL logging.level.web=TRACE logging.level.sql=TRACE
4. Custom Log Configuration
可以自定义日志配置文件,在类路径下或在“logging.config=classpath:logback-spring.xml”(Springboot推荐加‘-spring’)指定的路径下
可以通过系统属性指定日志系统,日志部分源码分析
System.setProperty("org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingSystem", LoggingSystem.NONE);
System.setProperty("org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingSystem", LogbackLoggingSystem.class.getName());
参考LoggingApplicationListener源码可知,日志组件先于ApplicationContext创建,所以不可能通过配置文件修改(@PropertySources或@Configuration),唯一修改或禁用的方式就是通过设置系统属性
如果自定义日志系统的话,“logging.file”、“logging.path”等在配置文件中的配置则不起作用,Springboot提供了一些Environment转为System Properteis的配置项
logging.file --> LOG_FILE logging.path --> LOG_PATH ...
5. Logback Extensions 扩展功能
文件名为“logback-spring.xml”才可以使用扩展功能
指定Profile,不同的环境使用不同的配置信息
<springProfile name="staging"> <!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active --> </springProfile> <springProfile name="dev | staging"> <!-- configuration to be enabled when the "dev" or "staging" profiles are active --> </springProfile>
获取环境变量,获得application.properties中配置的信息
scope为变量作用域、source为配置文件key(必须是kebab case),defaultValue为默认值
<springProperty scope="context" name="fluentHost" source="myapp.fluentd.host"
defaultValue="localhost"/>
<appender name="FLUENT" class="ch.qos.logback.more.appenders.DataFluentAppender">
<remoteHost>${fluentHost}</remoteHost>
</appender>
Ⅴ. Internationalization 国际化
国际化资源配置信息
spring.messages.basename=messages,config.i18n.messages spring.messages.fallback-to-system-locale=false
自动化配置类:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration
国际化资源可配置信息及作用:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceProperties
Ⅵ. JSON
SpringBoot提供三种方式:Gson、Jackson、JSON-B,推荐使用的是Jackson
支持Jackson的自动化配置,并且提供了启动器spring-boot-starter-json
自定义ObjectMapper
Spring MVC使用HttpMessageConverters进行服务器端和客户端的数据类型转换,Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder会通过自动化配置注入到容器中
默认的自定义属性,参见JackAutoConfiguration、Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder(customizeDefaultFeatures方法)
MapperFeature.DEFAULT_VIEW_INCLUSION is disabled DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES is disabled SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS is disabled
Springboot提供了大量的开关配置以自定义特性
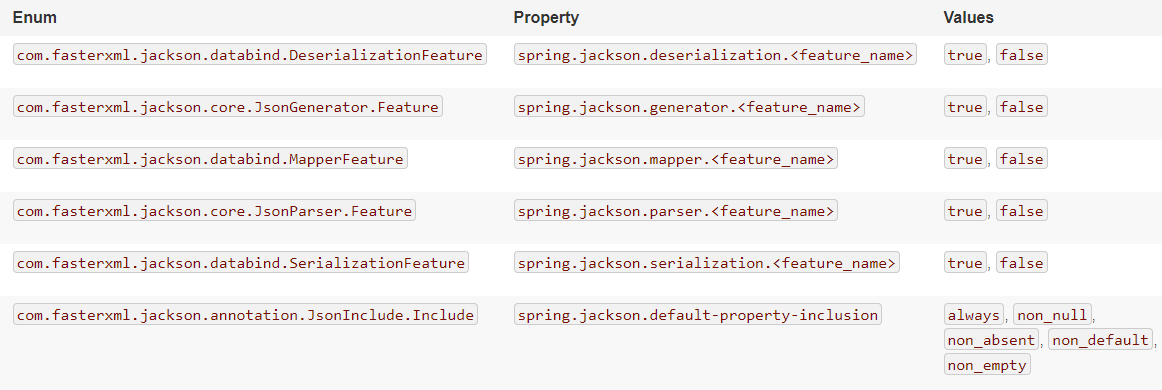
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder 可以通过一个或多个 Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer 进行自定义 ObjectMapper,支持排序可在默认之前或之后(实现Ordered
接口,重写getOrder方法或使用@Order注解)
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.Module 的Bean会自动注册到 Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder
如果想替换掉默认的ObjectMapper 使用 @Bean 注释且标记 @Primary
JacksonAutoConfiguration 注入 Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder、StandardJackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer、ObjectMapper
HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration(数据转换器自动配置器)注入 StringHttpMessageConverter
JacksonHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration 注入 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 和 MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter
添加自定义的转换器,与MVC不同的是,这种方法是添加额外的而不是替换默认的
@Configuration
public class JacksonConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = new Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder()
.indentOutput(true)
.dateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"))
.modulesToInstall(new ParameterNamesModule());
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
Ⅶ. Developing Web Applications
Spring MVC框架
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
自动配置提供的特性(WebMvcAutoConfiguration):
1. InternalResourceViewResolver、ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 和 BeanNameViewResolver
2. 支持依赖方式引入静态资源,支持WebJars
3. 自动注册 Converter、GenericConverter 和 Formatter
4. 支持 HttpMessageConverters 消息转换器
5. 自动注册 MessageCodesResolver
6. 支持静态 index.html 文件,欢迎页
7. 自定义 Favicon 网站图标
8. 自动使用 ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
如果想保持Spring Boot MVC的特性并且想添加自己的特性(拦截器、视图解析器等),创建一个类实现 WebMvcConfigurer,
注释@Configuration且不能注释@EnableWebMvc
HttpMessageConverters
Spring MVC使用HttpMessageConverter进行信息转换,Spring Boot提供 HttpMessageConverters 自定义 HttpMessageConverter,添加了这个默认的HttpMessageConverters 就失效了
@Configuration
public class HttpMessageConvertersConfiguration {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters messageConverters() {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder = new Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder()
.indentOutput(true)
.dateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"))
.modulesToInstall(new ParameterNamesModule());
return new HttpMessageConverters(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(builder.build()));
}
}
Custom JSON Serializers and Deserializers
覆盖默认ObjectMapper
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ObjectMapper.class)
public ObjectMapper jacksonObjectMapper(Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = builder.createXmlMapper(false).build();
SerializerProvider serializerProvider = objectMapper.getSerializerProvider();
serializerProvider.setNullValueSerializer(new NullValueSerializer());
return objectMapper;
}
创建NullValueSerializer
public class NullValueSerializer extends JsonSerializer<Object> {
@Override
public void serialize(Object value, JsonGenerator jgen, SerializerProvider provider) throws IOException {
try {
jgen.writeString("");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
MessageCodesResolver
当指定一个“spring.mvc.message-codes-resolver-format”时,Spring Boot会创建一个MessageCodesResolver
Static Content 静态资源
Spring Boot默认四个静态文件读取路径:/static、/public、/resources、/META-INF/resources,是因为使用了ResourceHttpRequestHandler (xml配置方式:<mvc:resources mapping="/static/**" location="/static/" />),我们可以通过实现 WebMvcConfigurer 接口覆盖 addResourceHandlers 方法
@Component
public class AdditionalResourceHandler implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
public AdditionalResourceHandler(ResourceProperties resourceProperties) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
Duration cachePeriod = resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
registry.addResourceHandler("/additional/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/additional/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod))
.setCacheControl(cacheControl);
}
private Integer getSeconds(Duration cachePeriod) {
return cachePeriod != null ? (int) cachePeriod.getSeconds() : null;
}
}
修改默认读取路径
# 默认的spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/,访问地址:http://127.0.0.1:8080/1.js # 替换后访问地址:http://127.0.0.1:8080/static/1.js spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/** # 替换默认的静态资源读取路径 spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/static,classpath:/public
webJars 方式引入静态文件,参考 WebMvcAutoConfiguration.addResourceHandlers,访问地址:http://127.0.0.1:8080/webjars/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.js
<dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.4.1</version> </dependency>
静态资源缓存破坏,参考:https://www.iteye.com/blog/412887952-qq-com-2342354
默认的Thymeleaf和FreeMarker可以直接配置ResourceUrlEncodingFilter
@Bean
public ResourceUrlEncodingFilter resourceUrlEncodingFilter() {
return new ResourceUrlEncodingFilter();
}
如果是JSP则可以使用ResourceUrlProvider
@ControllerAdvice
public class UrlProviderController {
@Autowired
private ResourceUrlProvider provider;
@ModelAttribute("urls")
public ResourceUrlProvider urls() {
return provider;
}
}
MD5方式
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=true spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/**
版本方式
spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.enabled=true spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.paths=/js/,/css/,/img/ spring.resources.chain.strategy.fixed.version=1.0.0
版本方式添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>webjars-locator-core</artifactId> <version>0.40</version> </dependency>
版本方式目录结构
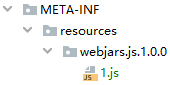
页面配置(必须 '/' 开头)
<link th:href="@{/1.css}" rel="stylesheet"/>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/webjars/js/1.js}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/webjars/jquery/jquery.js}"></script>
Welcome Page
SpringBoot 提供静态的和模板形式的欢迎页,首先会找静态资源路径下的index.html文件,如果没有再找index模板页
WebMvcAutoConfiguration中的WelcomePageHandlerMapping
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders, ApplicationContext applicationContext, Optional<Resource> welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage.isPresent() && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage.get());
this.setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
} else if (this.welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
this.setRootViewName("index");
}
}
private boolean welcomeTemplateExists(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
return templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider("index", applicationContext) != null;
}
TemplateAvailabilityProviders中会读取spring.factories配置文件(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(TemplateAvailabilityProvider.class, classLoader);)
# Template availability providers org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
以ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider为例
public boolean isTemplateAvailable(String view, Environment environment, ClassLoader classLoader, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine", classLoader)) {
String prefix = environment.getProperty("spring.thymeleaf.prefix", "classpath:/templates/");
String suffix = environment.getProperty("spring.thymeleaf.suffix", ".html");
return resourceLoader.getResource(prefix + view + suffix).exists();
} else {
return false;
}
}
Custom Favicon 自定义标签小图标
SpringBoot会在静态资源路径和根路径下寻找favicon.ico,参考:WebMvcAutoConfiguration.FaviconConfiguration
Path Matching and Content Negotiation 路径匹配和内容协商
Springboot默认的不开启后缀方式(GET /projects/spring-boot.json" 不能匹配 @GetMapping("/projects/spring-boot"))
除了后缀方式还可以不用发送带“Accept”请求头信息的方式,参数方式(GET /projects/spring-boot?format=json)
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=true spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name=myparam spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.markdown=text/markdown
仍然想使用后缀方式
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-path-extension=true spring.mvc.pathmatch.use-suffix-pattern=true
与其开放所有后缀方式,不如只支持注册了的
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-path-extension=true spring.mvc.pathmatch.use-registered-suffix-pattern=true
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
SpringBoot使用WebBindingInitializer初始化WebDataBinder应对特殊的请求,覆盖方式
// 继承ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer并将组件加入容器中,参考WebMvcAutoConfiguration和WebMvcConfigurationSupport
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer() {
try {
return (ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer)this.beanFactory.getBean(ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer.class);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var2) {
return super.getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer();
}
}
Error Handling
默认的SpringBoot提供了 /error 的映射来处理所有的错误请求
参考ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,注入了DefaultErrorAttributes(包含错误信息,可以覆盖以添加更丰富的内容)、BasicErrorController(映射 ${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}} 路径的Controller)、ErrorPageCustomizer(错误跳转地址)、DefaultErrorViewResolver(错误页面解析器)
当发生错误时,发起 ‘/error’请求,先通过错误页面解析获得视图,没获得则返回 error 视图
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
可以使用@ControllerAdvice和@ExceptionHandler将错误请求转发至 ‘/error’
package com.wjz.error;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ErrorControllerAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(ErrorException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest req) {
Map<String, Object> messages = new HashMap<>();
messages.put("code", "000");
messages.put("message", e.getMessage());
req.setAttribute("messages", messages);
req.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
return "forward:/error";
}
}
重写默认的ErrorAttributes添加额外的信息
package com.wjz.error;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.DefaultErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletWebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes.SCOPE_REQUEST;
@Component
public class AdditionalErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> attributes = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
attributes.put("messages", ((ServletWebRequest) webRequest).getAttribute("messages", SCOPE_REQUEST));
return attributes;
}
}
Custom Error Pages
可以以静态文件方式放在静态资源路径下的 /error 目录下(404.html,500.html)
可以以模板文件方式放在 classpath:templates路劲下的 /error 目录下
4xx.html可以匹配所有客户端错误,5xx.html可以匹配所有服务端错误
还可以自定义错误页面解析器,参考AbstractErrorController.resolveErrorView()方法、DefaultErrorViewResolver
CORS Support 跨域请求
单一请求跨域支持,Controller层方法上添加@CrossOrigin注解
全局请求跨域支持
@Configuration
public class CorsConfiguration {
public WebMvcConfigurer corsFilter() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedHeaders("*");
}
};
}
}
JAX-RS and Jersey RESTFul方式和集成Jersey框架
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/c14a9028e6e7
Embedded Servlet Container Support 嵌入式Servlet容器支持
Servlets, Filters, and listeners
默认的SpringBoot会提供一些Filter,如字符集Filter(OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter,参考HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration)
@ServletComponentScan扫描@WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener注释的类
ServletRegistrationBean、FilterRegistrationBean和ServletListenerRegistrationBean形式注入
@Configuration
@ServletComponentScan({"com.wjz.filter", "com.wjz.servlet", "com.wjz.listener"})
public class FilterConfiguration {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filter_1() {
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(new Filter_1());
registrationBean.addInitParameter("target", "true");
registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return registrationBean;
}
}
注解形式注入
@WebFilter(filterName = "filter_2", initParams = {@WebInitParam(name = "target", value = "true")}, urlPatterns = "/filter_2/*")
public class Filter_2 extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
filterChain.doFilter(httpServletRequest, httpServletResponse);
}
}
Servlet Context Initialization
web容器启动时,为提供给第三方组件机会做一些初始化的工作,例如注册servlet或者filtes等,servlet规范中通过ServletContainerInitializer实现此功能,SpringBoot为避免风险提供了ServletContextInitializer,其onStartup方法提供了javax.servlet.ServletContext,可以利用后者添加servlet、filter
具体可参考ServletRegistrationBean、FilterRegistrationBean和ServletListenerRegistrationBean
Customizing Embedded Servlet Containers
可以通过application.properties配置文件自定义嵌入式Servlet容器,如端口(server.port)、项目缺省路径(server.servlet.context-path)等,具体可参考ServerProperties
Ⅷ. Working With SQL Databases
SpringBoot整合Mybatis
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35206261/article/details/81778224
自定义数据源
@ConfigurationProperties可以使用在被@Bean修饰的public方法上,利用ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor后置处理为实例设置属性值
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new HikariDataSource();
}
配置文件内容
spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root
其他组件注入DataSource时会为其设置用户名、密码信息,因此指定DataSource类型时,需要提前指定
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
SpringBoot内置数据库
参考https://blog.csdn.net/zyhlwzy/article/details/78733644
Ⅸ. Working with NoSQL Technologies
SpringBoot提供两种连接API,Lettuce和Jedis,推荐使用前者,参考RedisAutoConfiguration
spring.redis.database=7 spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8