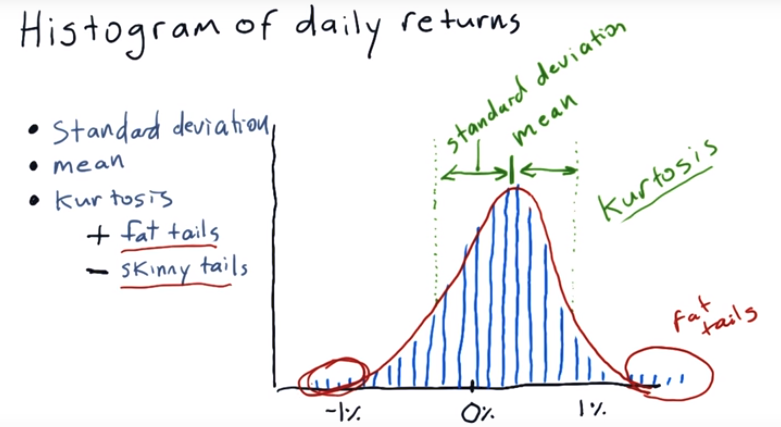
A histogram is an accurate representation of the distribution of numerical data.

Y axis is the occurances, X axis is the % of daily return.
There are three things can meature histogram
1. Standard deviation
2. Mean
3. Kurtosis : In probability theory and statistics, kurtosis is a measure of the "tailedness" of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable.
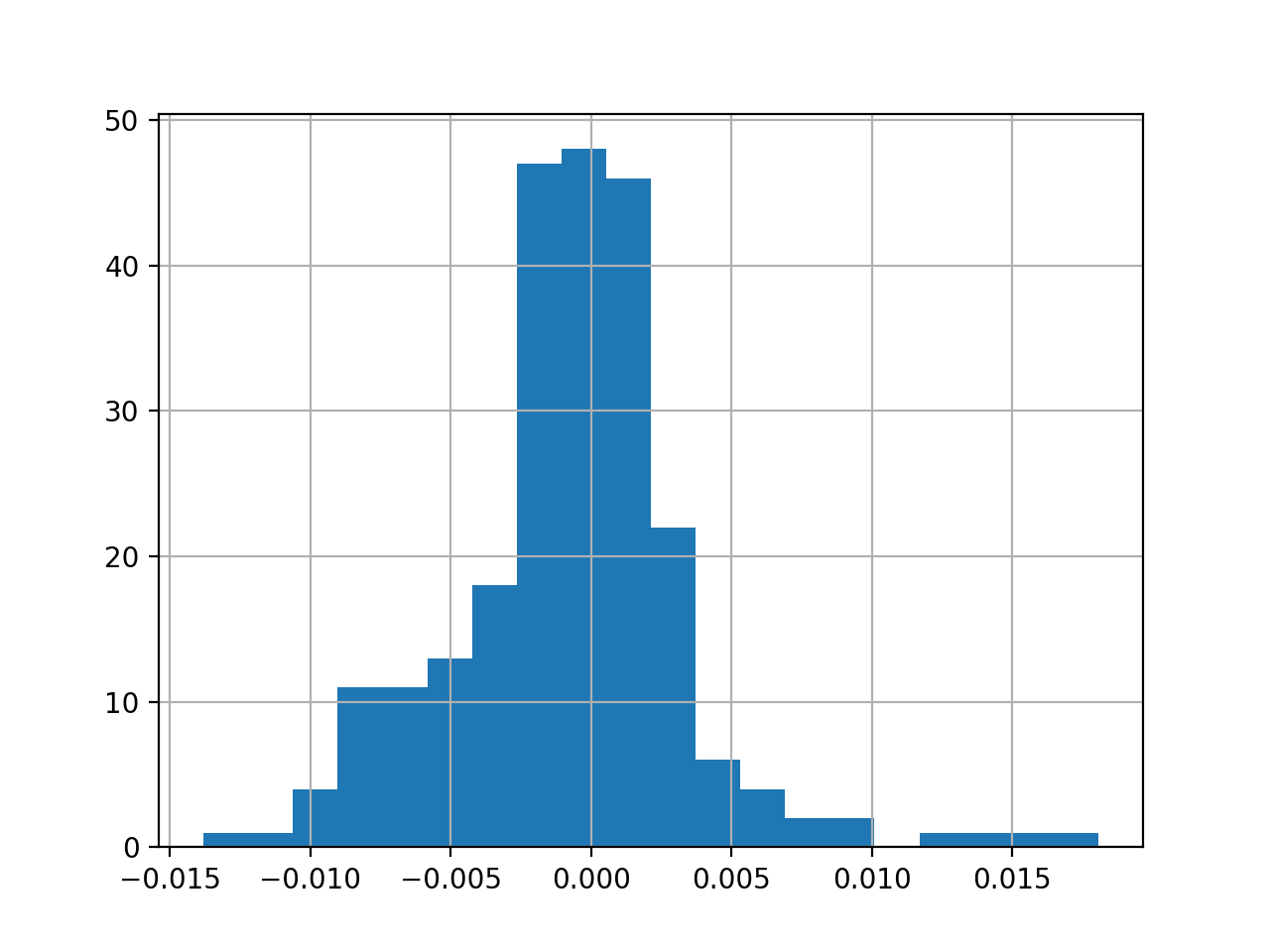
Plot a histogram:
import os import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def compute_daily_return(df): dr = df.copy() dr = (df / df.shift(-1)) -1 return dr def histogram(df): dr = compute_daily_return(df) plot_data(dr, title="Daily returns", yLabel="Daily returns") dr.hist(bins=20) plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': df=test_run() #rolling_mean(df) histogram(df['SPY'])

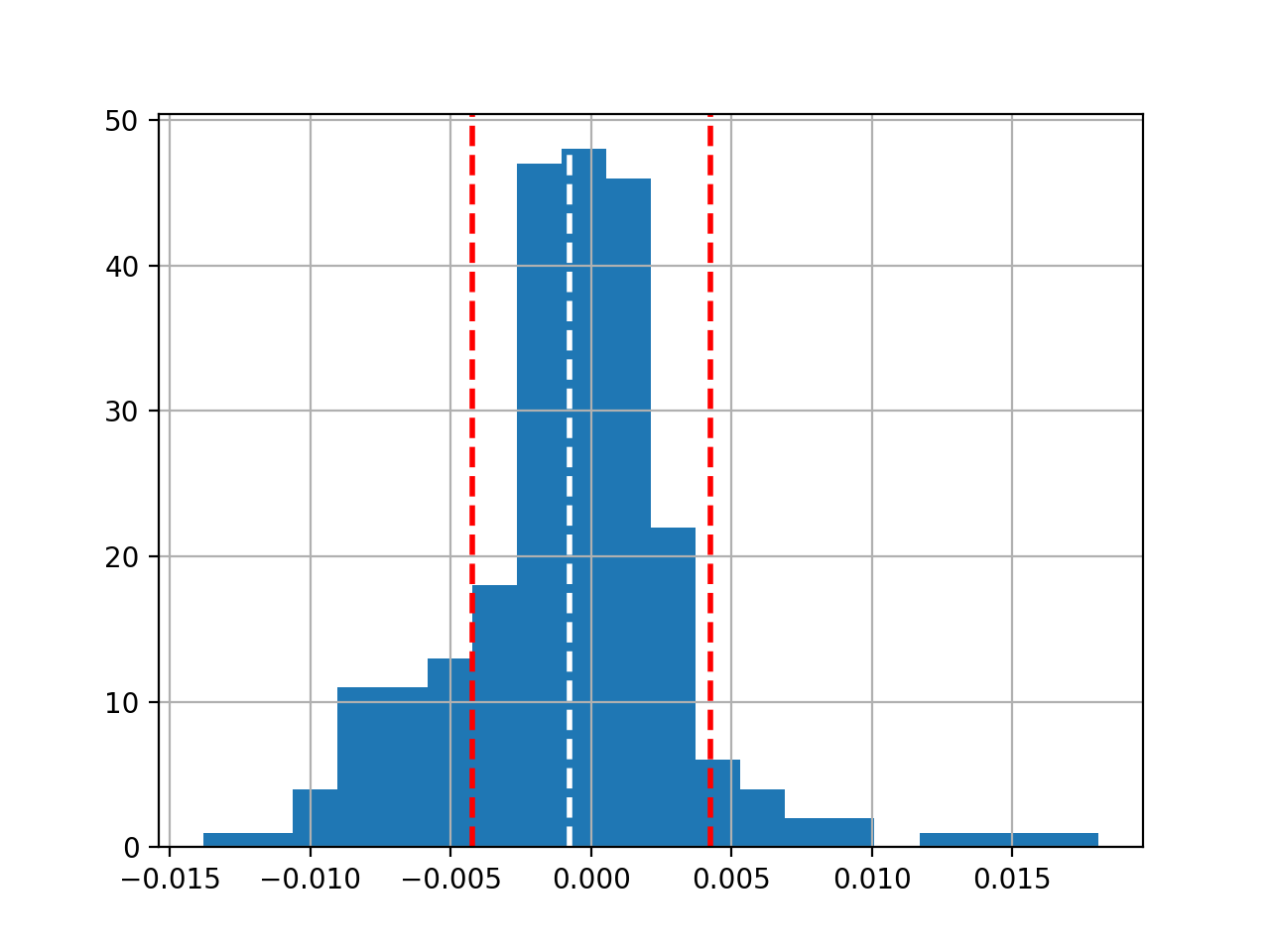
Plot 'mean' and 'std', Get 'kurtosis' value as well:
def histogram(df): dr = compute_daily_return(df) plot_data(dr, title="Daily returns", yLabel="Daily returns") dr.hist(bins=20) # Get mean and standard deviation mean = dr.mean() print("mean=", mean) std = dr.std() print("std=", std) plt.axvline(mean, color='w', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(std, color='r', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(-std, color='r', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.show() # Get kurtosis print("kurtosis=", dr.kurtosis()) if __name__ == '__main__': df=test_run() histogram(df['SPY'])
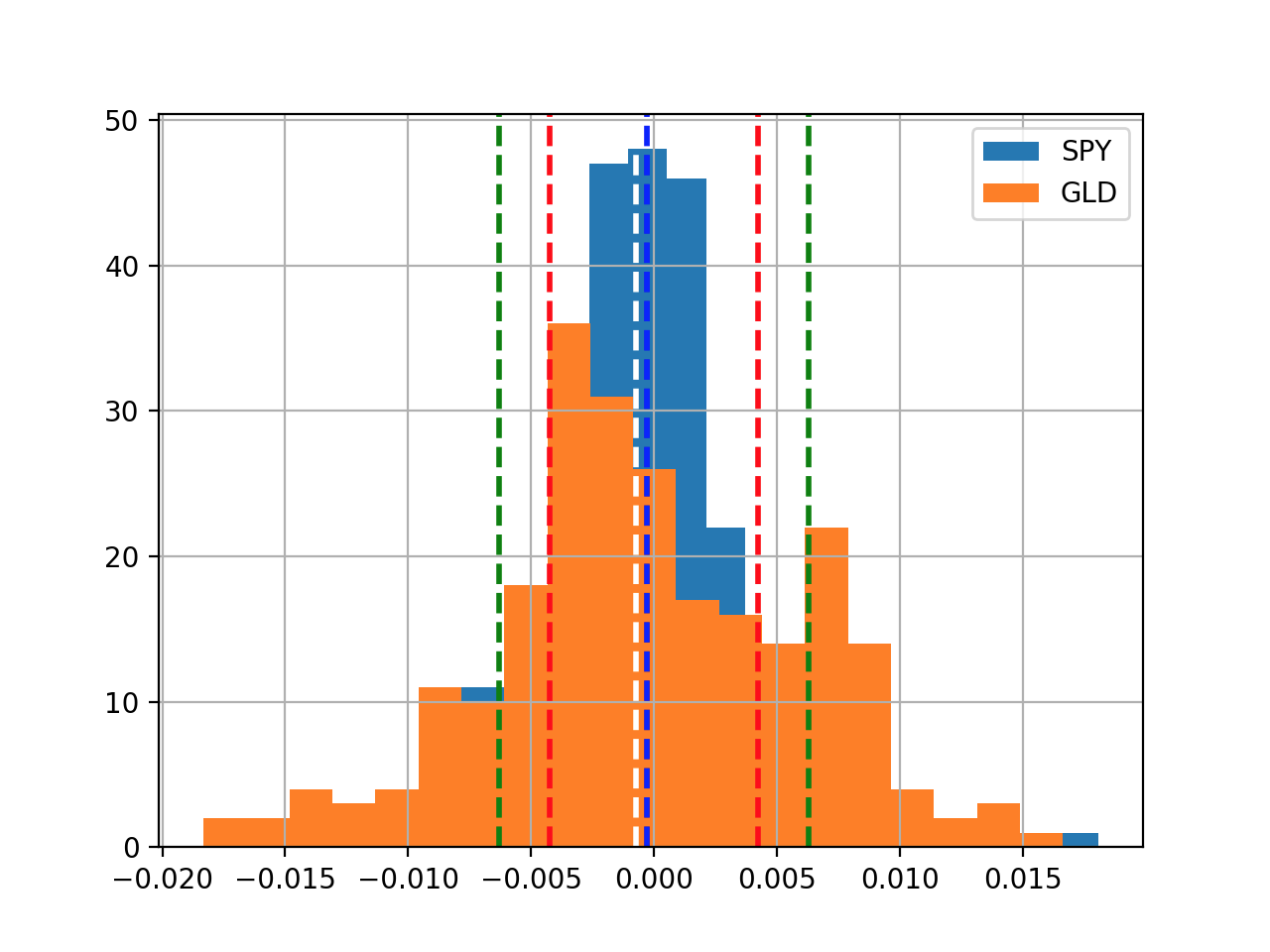
Now, let see how to plot tow histgram in the same plot:
def histogram(df): dr = compute_daily_return(df) plot_data(dr, title="Daily returns", yLabel="Daily returns") dr['SPY'].hist(bins=20, label="SPY") dr['GLD'].hist(bins=20, label="GLD") plt.legend(loc='upper right') # Get mean and standard deviation mean_spy = dr['SPY'].mean() mean_gld = dr['GLD'].mean() std_spy = dr['SPY'].std() std_gld = dr['GLD'].std() plt.axvline(mean_spy, color='w', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(std_spy, color='r', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(-std_spy, color='r', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(mean_gld, color='b', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(std_gld, color='g', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(-std_gld, color='g', linestyle='dashed', linewidth=2) plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': df=test_run() histogram(df[['SPY', 'GLD']])