一、手写数字识别
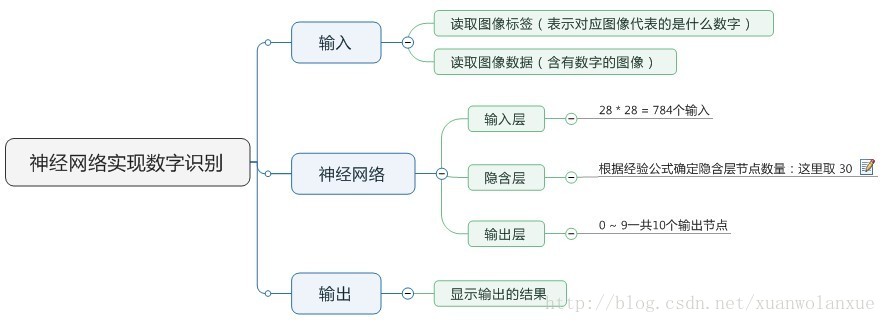
现在就来说说如何使用神经网络实现手写数字识别。 在这里我使用mind manager工具绘制了要实现手写数字识别需要的模块以及模块的功能:
其中隐含层节点数量(即神经细胞数量)计算的公式(这只是经验公式,不一定是最佳值):
m=n+l−−−−√+am=n+l+a
m=log2nm=log2n
m=nl−−√m=nl
- m: 隐含层节点数
- n: 输入层节点数
- l:输出层节点数
- a:1-10之间的常数
本例子当中:
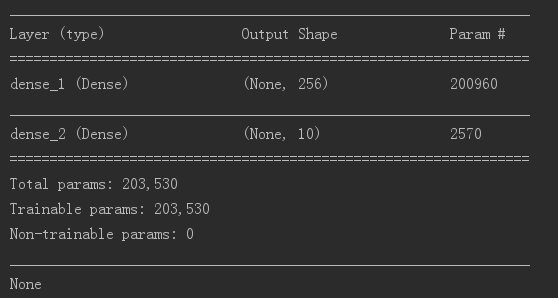
- 输入层节点n:784
- 输出层节点:10 (表示数字 0 ~ 9)
-
隐含层选30个,训练速度虽然快,但是准确率却只有91% 左右,如果将这个数字变为100 或是300,其训练速度回慢一些
,但准确率可以提高到93%~94% 左右。
因为这是使用的MNIST的手写数字训练数据,所以它的图像的分辨率是28 * 28,也就是有784个像素点,其下载地址为:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
二、查看数据程序
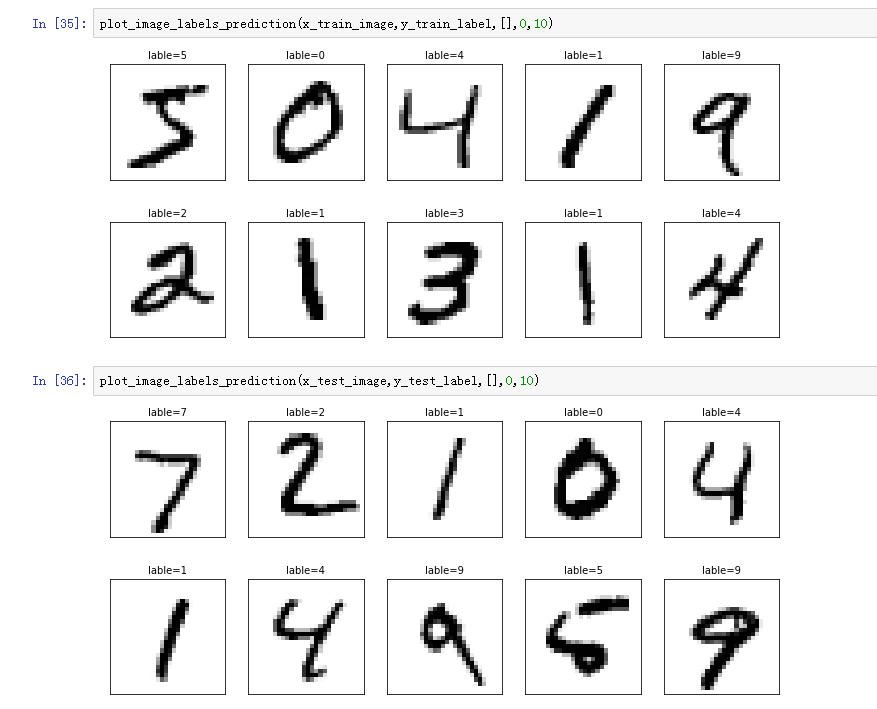
- 48000作为训练数据,12000作为验证数据,10000作为预测数据
-
1 #coding=utf-8 2 import numpy as np #导入模块,numpy是扩展链接库 3 import pandas as pd #类似一个本地的excel,偏向现在的非结构化的数据库 4 import tensorflow as tf 5 import keras 6 from keras.utils import np_utils 7 np.random.seed(10) #设置seed可以产生的随机数据 8 from keras.datasets import mnist #导入模块,下载读取mnist数据 9 (x_train_image,y_train_label), 10 (x_test_image,y_test_label)=mnist.load_data() #下载读取mnist数据 11 print('train data=',len(x_train_image)) 12 print('test data=',len(x_test_image)) 13 print('x_train_image:',x_train_image.shape) 14 print('y_train_label:',y_train_label.shape) #查看数据 15 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 16 def plot_image(image): #定义显示函数 17 fig=plt.gcf() 18 fig.set_size_inches(2,2) #设置显示图形的大小 19 plt.imshow(image,cmap='binary') #黑白灰度显示 20 plt.show() #开始画图 21 y_train_label[0] #查看第0项label数据 22 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 23 def plot_image_labels_prediction(image,lables,prediction,idx,num=10):#显示多项数据 24 fig=plt.gcf() 25 fig.set_size_inches(12,14) #设置显示图形的大小 26 if num>25:num=25 27 for i in range(0,num): #画出num个数字图形 28 ax=plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) #建立subplot字图形为5行5列 29 ax.imshow(image[idx],cmap='binary') #画出subgraph 30 title="lable="+str(lables[idx]) #设置字图形title,显示标签字段 31 if len(prediction)>0: #如果传入了预测结果 32 title+=",predict="+str(prediction[idx]) #标题 33 ax.set_title(title,fontsize=10) #设置字图形的标题 34 ax.set_xticks([]);ax.set_yticks([]) #设置不显示刻度 35 idx+=1 #读取下一项 36 plt.show() 37 plot_image_labels_prediction(x_train_image,y_train_label,[],0,10)#查看训练数据前10项 38 plot_image_labels_prediction(x_test_image,y_test_label,[],0,10) #查看测试数据前10项
三、运行结果
-
四、训练预测识别程序
-
1 #coding=utf-8 2 #1.数据预处理 3 import numpy as np #导入模块,numpy是扩展链接库 4 import pandas as pd 5 import tensorflow 6 import keras 7 from keras.utils import np_utils 8 np.random.seed(10) #设置seed可以产生的随机数据 9 from keras.datasets import mnist #导入模块,下载读取mnist数据 10 (x_train_image,y_train_label), 11 (x_test_image,y_test_label)=mnist.load_data() #下载读取mnist数据 12 print('train data=',len(x_train_image)) 13 print('test data=',len(x_test_image)) 14 print('x_train_image:',x_train_image.shape) 15 print('y_train_label:',y_train_label.shape) 16 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 17 def plot_image(image): 18 fig=plt.gcf() 19 fig.set_size_inches(2,2) 20 plt.imshow(image,cmap='binary') 21 plt.show() 22 y_train_label[0] 23 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 24 def plot_image_labels_prediction(image,lables,prediction,idx,num=10): 25 fig=plt.gcf() 26 fig.set_size_inches(12,14) 27 if num>25:num=25 28 for i in range(0,num): 29 ax=plt.subplot(5,5,i+1) 30 ax.imshow(image[idx],cmap='binary') 31 title="lable="+str(lables[idx]) 32 if len(prediction)>0: 33 title+=",predict="+str(prediction[idx]) 34 ax.set_title(title,fontsize=10) 35 ax.set_xticks([]);ax.set_yticks([]) 36 idx+=1 37 plt.show() 38 plot_image_labels_prediction(x_train_image,y_train_label,[],0,10) 39 plot_image_labels_prediction(x_test_image,y_test_label,[],0,10) 40 x_Train=x_train_image.reshape(60000,784).astype('float32') #以reshape转化成784个float 41 x_Test=x_test_image.reshape(10000,784).astype('float32') 42 x_Train_normalize=x_Train/255 #将features标准化 43 x_Test_normalize=x_Test/255 44 y_Train_OneHot=np_utils.to_categorical(y_train_label)#将训练数据和测试数据的label进行one-hot encoding转化 45 y_Test_OneHot=np_utils.to_categorical(y_test_label) 46 #2.建立模型 47 from keras.models import Sequential #可以通过Sequential模型传递一个layer的list来构造该模型,序惯模型是多个网络层的线性堆叠 48 from keras.layers import Dense #全连接层 49 model=Sequential() 50 #建立输入层、隐藏层 51 model.add(Dense(units=256, 52 input_dim=784, 53 kernel_initializer='normal', 54 activation='relu')) 55 #建立输出层 56 model.add(Dense(units=10, 57 kernel_initializer='normal', 58 activation='softmax')) 59 print(model.summary()) 60 #3、进行训练 61 #对训练模型进行设置,损失函数、优化器、权值 62 model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', 63 optimizer='adam',metrics=['accuracy']) 64 # 设置训练与验证数据比例,80%训练,20%测试,执行10个训练周期,每一个周期200个数据,显示训练过程2次 65 train_history=model.fit(x=x_Train_normalize, 66 y=y_Train_OneHot,validation_split=0.2, 67 epochs=10,batch_size=200,verbose=2) 68 #显示训练过程 69 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 70 def show_train_history(train_history,train,validation): 71 plt.plot(train_history.history[train]) 72 plt.plot(train_history.history[validation]) 73 plt.title('Train History') 74 plt.ylabel(train) 75 plt.xlabel('Epoch') 76 plt.legend(['train','validation'],loc='upper left') #显示左上角标签 77 plt.show() 78 show_train_history(train_history,'acc','val_acc') #画出准确率评估结果 79 show_train_history(train_history,'loss','val_loss') #画出误差执行结果 80 #以测试数据评估模型准确率 81 scores=model.evaluate(x_Test_normalize,y_Test_OneHot) #创建变量存储评估后的准确率数据,(特征值,真实值) 82 print() 83 print('accuracy',scores[1]) 84 #进行预测 85 prediction=model.predict_classes(x_Test) 86 prediction 87 plot_image_labels_prediction(x_test_image,y_test_label,prediction,idx=340)
-
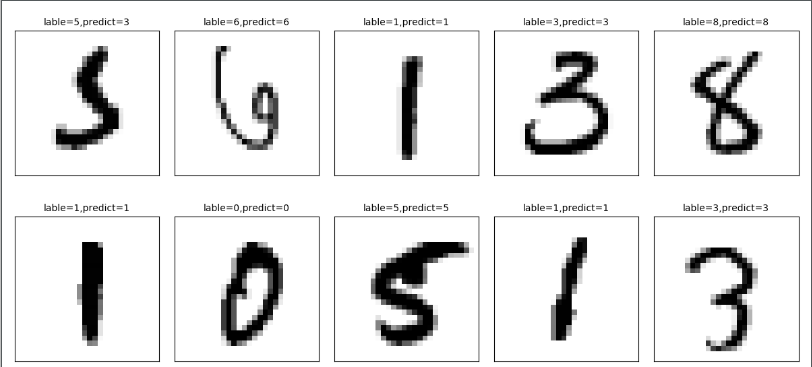
五、运行结果

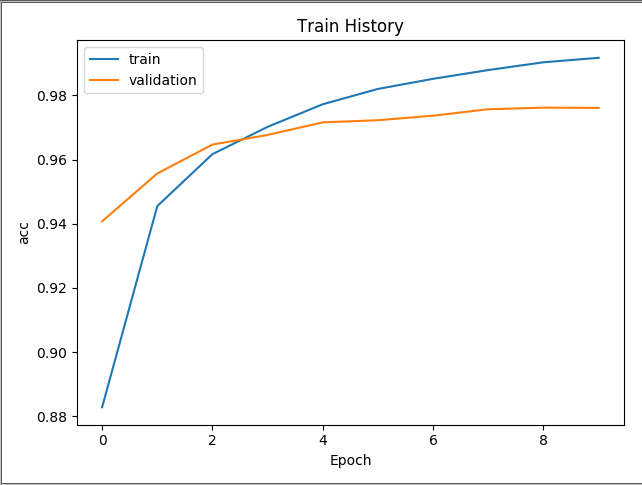

- 评估模型准确率结果为:0.9754
-

- 预测结果:有一个潦草的5预测错误为3