APIView使用:luffy项目中关于APIView的使用
在Django之 CBV和FBV中,我们是分析的from django.views import View下的执行流程,以下是代码
from django.views import View class IndexView(View): def get(self,request, *args, **kwargs): return HttpResponse("ok") def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): ret = super(IndexView,self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) return HttpResponse(ret)
这篇博客我们就来了解下APIView是如何执行的,跟django.views模块下的view有何关联?
from rest_framework.views import APIView
我们依然从url配置入手分析
url(r"books/$",views.BookView.as_view())
as_view方法代码如下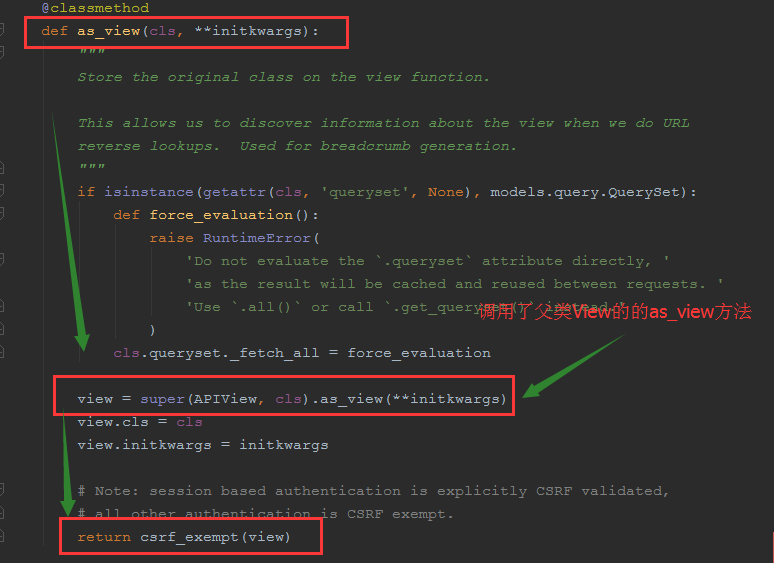
原来APIView类是继承View类,view类正式from django.views import View下的View,
先看as_view方法中的view = super(APIView, cls).as_view(**initkwargs)的这行代码,
是调用了父类View中的as_view方法,这里的initkwargs,及其父类的View中的as_view方法执行流程,之类就不在赘述了
具体流程去看我的博客链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/95lyj/p/9432750.html
所以在APIView类中,我们重点看下return csrf_exempt(view)做了什么操作?
def csrf_exempt(view_func): def wrapped_view(*args, **kwargs): return view_func(*args, **kwargs) wrapped_view.csrf_exempt = True return wraps(view_func, assigned=available_attrs(view_func))(wrapped_view)
wrapped_view.csrf_exempt = True意思是取消当前函数防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中设置了全局中间件,然后将csrf_exempt函数中的内置函数wrapped_view赋值wrapped_view.csrf_exempt = True,使其拥有该属性,
接下来看 wraps(view_func, assigned=available_attrs(view_func))(wrapped_view)函数之前,
我们先看下assigned=available_attrs(view_func)
def available_attrs(fn): if six.PY3: return WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS else: return tuple(a for a in WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS if hasattr(fn, a))
大概意思就是针对py3或者其他版本做了一些判断处理,最后通过WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS定为到
WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS = ('__module__', '__name__', '__qualname__', '__doc__', '__annotations__')
这个逻辑跟我们上一篇的CBV源码有共同之处,就是为某个方法或者函数,添加某些属性
接下来我们看wraps函数吧
def wraps(wrapped, assigned = WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS, updated = WRAPPER_UPDATES): return partial(update_wrapper, wrapped=wrapped, assigned=assigned, updated=updated)
wrapped是我们在def csrf_exempt(view_func):函数中的参数,也就是as_view的返回值,
最后通过functools模块下的partial类进行装饰构造,partial 这个东西是针对函数起作用的,并且是部分的,
场景:有这样的函数:get_useragent(request) 用来获取用户浏览器的ua信息,但是这个函数又不是在主体函数(执行页面渲染的函数)get时调用的,只在模板中的一个filter中调用的(可以理解是在模板渲染时调用的),而filter在执行的时候是不能添加参数的,哪你要怎么处理。
这时partial就得闪亮登场,如下是代码,
def __new__(*args, **keywords): if not args: raise TypeError("descriptor '__new__' of partial needs an argument") if len(args) < 2: raise TypeError("type 'partial' takes at least one argument") cls, func, *args = args if not callable(func): raise TypeError("the first argument must be callable") args = tuple(args) if hasattr(func, "func"): args = func.args + args tmpkw = func.keywords.copy() tmpkw.update(keywords) keywords = tmpkw del tmpkw func = func.func self = super(partial, cls).__new__(cls) self.func = func self.args = args self.keywords = keywords return self def __call__(*args, **keywords): if not args: raise TypeError("descriptor '__call__' of partial needs an argument") self, *args = args newkeywords = self.keywords.copy() newkeywords.update(keywords) return self.func(*self.args, *args, **newkeywords)
最后在csrf_exempt函数中的wraps(view_func, assigned=available_attrs(view_func))(wrapped_view)这里写代码片传入参数wrapped_view,通过对象可调用功能,进行调用__call__方法
到此as_view分析完毕,以上代码好多有迷惑的点,我分析的时候也是很多猜想的
上篇CBV源码分析中我们知道,当as_view执行后,当浏览器访问某个api接口时候,
就会先触发dispatch,然后在dispatch中,如下是父类的dispatch方法
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist, # defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the # request method isn't on the approved list. if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: handler = self.http_method_not_allowed return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
然而API方法中也有自己的dispatch方法,会执行子类的方法,而不是去执行父类的dispatch方法,以下是代码
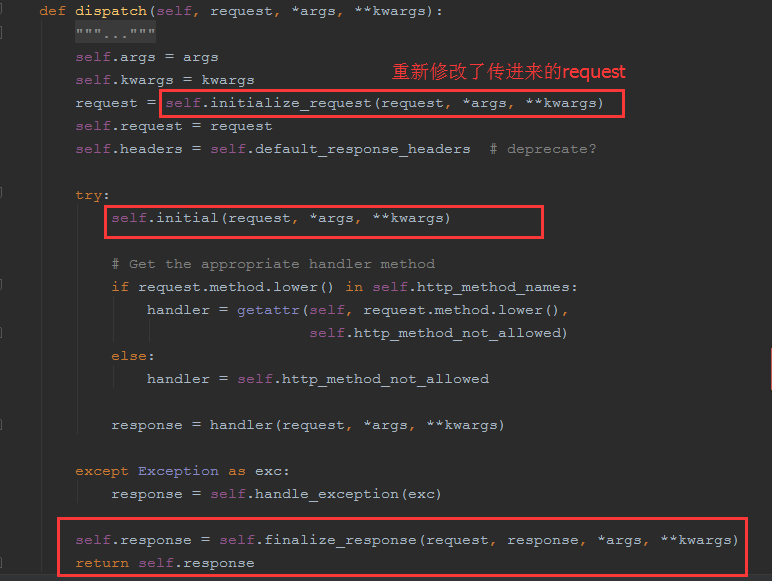
以上dispatch方法中,通过self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
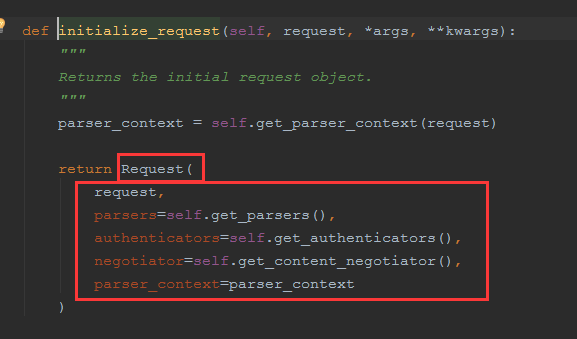
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Returns the initial request object. """ #将请求变成字典格式返回了 parser_context = self.get_parser_context(request) return Request( request, parsers=self.get_parsers(), #解析数据,默认的有三种方式,可点进去看 #self.get_authenticator优先找自己的,没有就找父类的 authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), #获取认证相关的所有类并实例化,传入request对象供Request使用 negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), parser_context=parser_context )
通过initialize_request的到一个Request类对象
在这过程中:
1、获取认证相关的类的具体 authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
def get_authenticators(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of authenticators that this view can use.
"""
#返回的是对象列表
return [auth() for auth in self.authentication_classes] #[SessionAuthentication,BaseAuthentication]
2、查看认证的类:self.authentication_classes
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES #默认的,如果自己有会优先执行自己的
3、接着走进api_settings
api_settings = APISettings(None, DEFAULTS, IMPORT_STRINGS) #点击继承的DEFAULTS类
DEFAULTS = {
# Base API policies
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication', #这时候就找到了他默认认证的类了,可以导入看看
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication'
),
4、导入了类看看类里面具体干了什么
from rest_framework.authentication import SessionAuthentication from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
5、看到里面有个authenticate方法和authenticate_header方法
class BaseAuthentication(object): """ All authentication classes should extend BaseAuthentication. """ def authenticate(self, request): """ Authenticate the request and return a two-tuple of (user, token). """ raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.") def authenticate_header(self, request): """ Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate` header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses. """ pass
6、具体处理认证,从headers里面能获取用户名和密码
class BasicAuthentication(BaseAuthentication): """ HTTP Basic authentication against username/password. """ www_authenticate_realm = 'api' def authenticate(self, request): """ Returns a `User` if a correct username and password have been supplied using HTTP Basic authentication. Otherwise returns `None`. """ auth = get_authorization_header(request).split() if not auth or auth[0].lower() != b'basic': return None #返回none不处理。让下一个处理 if len(auth) == 1: msg = _('Invalid basic header. No credentials provided.') raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) elif len(auth) > 2: msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials string should not contain spaces.') raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) try: auth_parts = base64.b64decode(auth[1]).decode(HTTP_HEADER_ENCODING).partition(':') #用partition切割冒号也包括 except (TypeError, UnicodeDecodeError, binascii.Error): msg = _('Invalid basic header. Credentials not correctly base64 encoded.') raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg) userid, password = auth_parts[0], auth_parts[2] # 返回用户和密码 return self.authenticate_credentials(userid, password, request) def authenticate_credentials(self, userid, password, request=None): """ Authenticate the userid and password against username and password with optional request for context. """ credentials = { get_user_model().USERNAME_FIELD: userid, 'password': password } user = authenticate(request=request, **credentials) if user is None: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('Invalid username/password.')) if not user.is_active: raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(_('User inactive or deleted.')) return (user, None) def authenticate_header(self, request): return 'Basic realm="%s"' % self.www_authenticate_realm
当然restfulframework默认定义了两个类。我们也可以自定制类,自己有就用自己的了,自己没有就去找父类的了,但是里面必须实现authenticate方法,不然会报错。
然后self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs),
- 处理版权信息
- 认证
- 权限
- 请求用户进行访问频率的限制
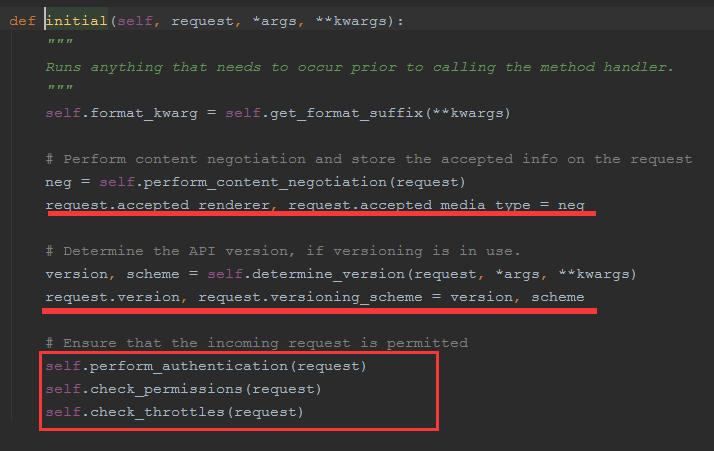
1、首先 self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs)可以看到做了以下操作
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs)
# Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg
# Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
#2.1 处理版本信息
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
#2.2 认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
# 2.3 权限
self.check_permissions(request)
# 2.4 请求用户进行访问频率的限制
self.check_throttles(request)
2、我们先来看认证,self.perform_authentication(request) 具体干了什么,按住ctrl点击进去
def perform_authentication(self, request):
"""
Perform authentication on the incoming request.
Note that if you override this and simply 'pass', then authentication
will instead be performed lazily, the first time either
`request.user` or `request.auth` is accessed.
"""
request.user #执行request的user,这是的request已经是加工后的request了
3、那么我们可以从视图里面导入一下Request,找到request对象的user方法
from rest_framework.views import Request
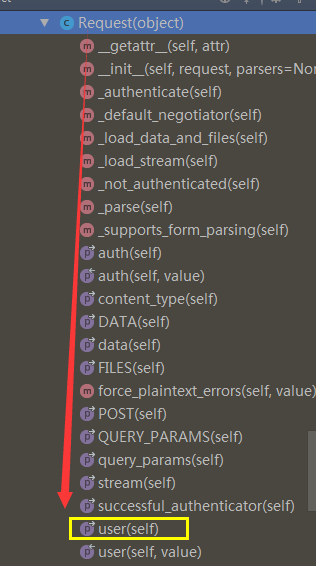
@property
def user(self):
"""
Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated
by the authentication classes provided to the request.
"""
if not hasattr(self, '_user'):
with wrap_attributeerrors():
self._authenticate() #
return self._user #返回user
4、执行self._authenticate() 开始用户认证,如果验证成功后返回元组: (用户,用户Token)
def _authenticate(self):
"""
Attempt to authenticate the request using each authentication instance
in turn.
"""
#循环对象列表
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
#执行每一个对象的authenticate 方法
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self)
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple #返回一个元组,user,和auth,赋给了self,
# 只要实例化Request,就会有一个request对象,就可以request.user,request.auth了
return
self._not_authenticated()
5、在user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) 进行验证,如果验证成功,执行类里的authenticatie方法
6、如果用户没有认证成功:self._not_authenticated()
def _not_authenticated(self):
"""
Set authenticator, user & authtoken representing an unauthenticated request.
Defaults are None, AnonymousUser & None.
"""
#如果跳过了所有认证,默认用户和Token和使用配置文件进行设置
self._authenticator = None #
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER:
self.user = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER() # 默认值为:匿名用户AnonymousUser
else:
self.user = None # None 表示跳过该认证
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN:
self.auth = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN() # 默认值为:None
else:
self.auth = None
# (user, token)
# 表示验证通过并设置用户名和Token;
# AuthenticationFailed异常
完善request请求的一些注意事项,例如用户登录、检测权限等等
然后response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs)这里面是执行了对应的请求操作,如getpost请求,也就是执行了我们自定义视图里面的get方法等,在处理完毕后,赋值response然后作为参数进行如下的操作
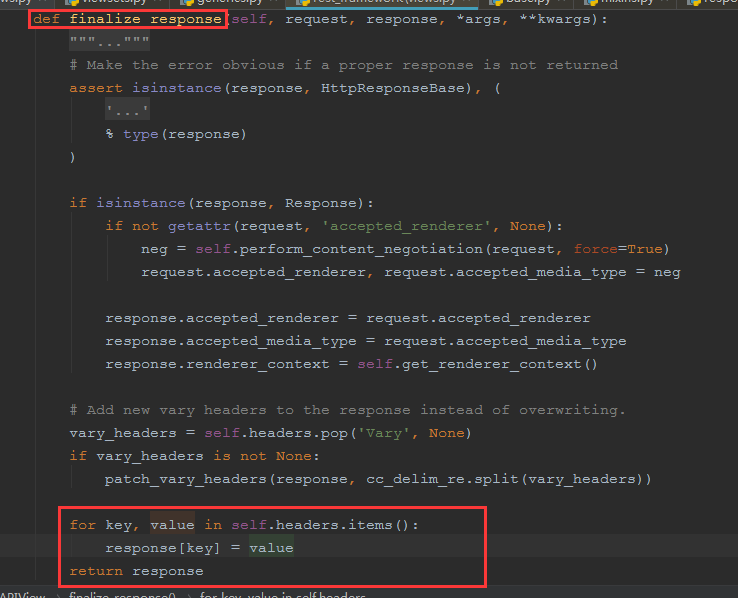
随后self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)返回,这一部操作,跟它的父类View是不同的,
在继承APIView的视图中,getpost需要返回HttpResponse,然后在通过self.finalize_response进一步封装,最后返回
最后在dispatch中
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs) return self.response