走进堆
堆分为大根堆和小根堆,大根堆堆顶元素最大,越往下元素越小,小根堆相反,堆顶元素最小,越往下元素越大
1.定义
手写堆是什么,表示从来没用过,要写堆当然要用我STL的优先队列啦
priority_queue<int> q;//默认的优先队列是大根堆
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> >;//大根堆的展开,注意:less<int>后必须加个空格,否则会CE
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >;//小根堆
2.函数
当然是跟队列一样,插入的话就不用管了,优先队列自动给排
q.push(a);//插入a这个元素
q.top();//堆顶
q.pop();//弹出堆顶元素
例题:洛谷P3378 堆
对顶堆
对顶堆,故明此意,是这样滴:

(摘自洛谷博主婷菡)
其实就是用一个大根堆和一个小根堆,大根堆在上,小跟堆在下,从上到下依次增大
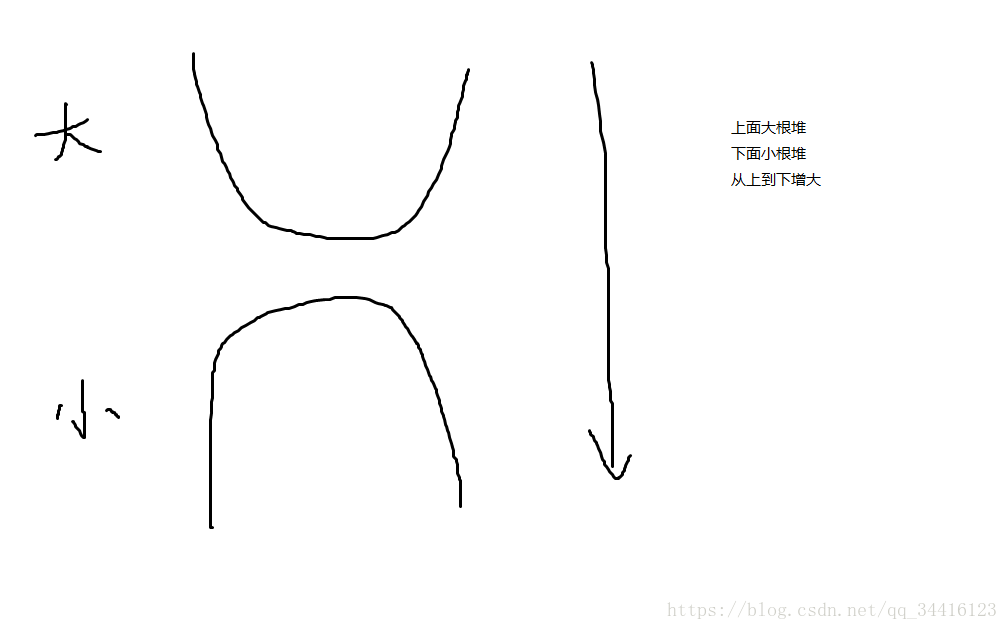
(摘自Sugewud_的CSDN博客)
对顶堆的性质
1.大根堆在上,小跟堆在下,从上到下依次增大
2.序列的中位数是大小根堆中较大根堆的堆顶
代码:
详见例题:洛谷P1168 中位数
写法1:假的对顶堆(中位数不在两个堆中)(极不推荐)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6+5,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,a[maxn],mid;
inline int read(){
int s=0,w=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return s*w;
}
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > q1;//大根堆
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q2;//小根堆
int main(){
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
int n=read();
a[1]=read();
mid=a[1];
cout<<a[1]<<endl;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
a[i]=read();
if(a[i]>mid)q2.push(a[i]);//大进大的小根堆
else q1.push(a[i]);//小进小的大根堆
if(i%2==1){
while(q1.size()!=q2.size()){//维护堆,因为中位数不在堆中,所以while条件为q1.size()!=q2.size()
if(q1.size()>q2.size()){
q2.push(mid);
mid=q1.top();
q1.pop();
}else{
q1.push(mid);
mid=q2.top();
q2.pop();
}
}
cout<<mid<<endl;
}
}
}
写法2:真的对顶堆(极度推荐)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6+5,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,a[maxn],mid;
inline int read(){
int s=0,w=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return s*w;
}
priority_queue<int> q1;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q2;
int main(){
n=read();
a[1]=read();
cout<<a[1]<<endl;
q1.push(a[1]);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
int x=read();
if(x>q1.top())q2.push(x);//大进大的小根堆
else q1.push(x);//小进小的大根堆
while(abs(int(q1.size()-q2.size()))>1){//维护堆,!!!注意:必须加int,因为size()的返回类型是unsigned,没有负数
if(q1.size()>q2.size())q2.push(q1.top()),q1.pop();
else q1.push(q2.top()),q2.pop();
}
if(i%2==1){
if(q1.size()>q2.size())cout<<q1.top()<<endl;
else cout<<q2.top()<<endl;
}
}
}
例题: P1801 黑匣子
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6+5,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,a[maxn],mid,l=1,r,m;
inline int read(){
int s=0,w=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return s*w;
}
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > q1;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q2;
int main(){
//freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
n=read();m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)a[i]=read();
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
r=read();
for(int j=l;j<=r;j++){
q1.push(a[j]);
}
while(q1.size()>=i)q2.push(q1.top()),q1.pop();
l=r+1;
cout<<q2.top()<<endl;
q1.push(q2.top());q2.pop();
}
}
OVER~