Content
0. 序
1. 内存池结构
1.1 ngx_pool_t结构
1.2 其他相关结构
1.3 ngx_pool_t的逻辑结构
2. 内存池操作
2.1 创建内存池
2.2 销毁内存池
2.3 重置内存池
2.4 分配内存
2.4.1 ngx_palloc()函数分析
2.4.2 ngx_palloc_block()函数分析
2.5 释放内存
2.6 注册cleanup
2.7 内存池的物理结构
3. 一个例子
3.1 代码
3.2 如何编译
3.3 运行结果
4. 小结
5. 致谢
0. 序
nginx对内存的管理由其自己实现的内存池结构ngx_pool_t来完成,本文重点叙述nginx的内存管理。
nginx内存管理相关文件:
(1) ./src/os/unix/ngx_alloc.h/.c
- 内存相关的操作,封装了最基本的内存分配函数
- 如free/malloc/memalign/posix_memalign,分别被封装为ngx_free,ngx_alloc/ngx_calloc, ngx_memalign
- ngx_alloc:封装malloc分配内存
- ngx_calloc:封装malloc分配内存,并初始化空间内容为0
- ngx_memalign:返回基于一个指定alignment的大小为size的内存空间,且其地址为alignment的整数倍,alignment为2的幂。
(2) ./src/core/ngx_palloc.h/.c
- 封装创建/销毁内存池,从内存池分配空间等函数
.表示nginx-1.0.4代码目录,本文为/usr/src/nginx-1.0.4。
1. 内存池结构
nginx对内存的管理均统一完成,例如,在特定的生命周期统一建立内存池(如main函数系统启动初期即分配1024B大小的内存池),需要内存时统一分配内存池中的内存,在适当的时候释放内存池的内存(如关闭http链接时调用ngx_destroy_pool进行销毁)。
因此,开发者只需在需要内存时进行申请即可,不用过多考虑内存的释放等问题,大大提高了开发的效率。先看一下内存池结构。
1.1 ngx_pool_t结构
此处统一一下概念,内存池的数据块:即分配内存在这些数据块中进行,一个内存池可以有多一个内存池数据块。nginx的内存池结构如下。
- 00048: typedef struct {
- 00049: u_char *last; //当前内存池分配到此处,即下一次分配从此处开始
- 00050: u_char *end; //内存池结束位置
- 00051: ngx_pool_t *next; //内存池里面有很多块内存,这些内存块就是通过该指针连成链表的
- 00052: ngx_uint_t failed; //内存池分配失败次数
- 00053: } ngx_pool_data_t; //内存池的数据块位置信息
- 00054:
- 00055:
- 00056: struct ngx_pool_s{ //内存池头部结构
- 00057: ngx_pool_data_t d; //内存池的数据块
- 00058: size_t max; //内存池数据块的最大值
- 00059: ngx_pool_t *current; //指向当前内存池
- 00060: ngx_chain_t *chain; //该指针挂接一个ngx_chain_t结构
- 00061: ngx_pool_large_t *large; //大块内存链表,即分配空间超过max的内存
- 00062: ngx_pool_cleanup_t *cleanup; //释放内存池的callback
- 00063: ngx_log_t *log; //日志信息
- 00064: };
其中,sizeof(ngx_pool_data_t)=16B,sizeof(ngx_pool_t)=40B。
nginx将几乎所有的结构体放在ngx_core.h文件中重新进行了申明,如下。
- typedef struct ngx_module_s ngx_module_t;
- typedef struct ngx_conf_s ngx_conf_t;
- typedef struct ngx_cycle_s ngx_cycle_t;
- typedef struct ngx_pool_s ngx_pool_t;
- typedef struct ngx_chain_s ngx_chain_t;
- typedef struct ngx_log_s ngx_log_t;
- typedef struct ngx_array_s ngx_array_t;
- typedef struct ngx_open_file_s ngx_open_file_t;
- typedef struct ngx_command_s ngx_command_t;
- typedef struct ngx_file_s ngx_file_t;
- typedef struct ngx_event_s ngx_event_t;
- typedef struct ngx_event_aio_s ngx_event_aio_t;
- typedef struct ngx_connection_s ngx_connection_t;
1.2 其他相关结构
其他与内存池相干的数据结构,如清除资源的cleanup链表,分配的大块内存链表等,如下。
- 00015: /*
- 00016: * NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL should be (ngx_pagesize - 1), i.e. 4095 on x86.
- 00017: * On Windows NT it decreases a number of locked pages in a kernel.
- 00018: */
- 00019: #define NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL (ngx_pagesize - 1) //在x86体系结构下,该值一般为4096B,即4K
- 00020:
- 00021: #define NGX_DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE (16* 1024)
- 00022:
- 00023: #define NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT 16
- 00024: #define NGX_MIN_POOL_SIZE
- 00025: ngx_align((sizeof(ngx_pool_t) + 2 * sizeof(ngx_pool_large_t)),
- 00026: NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT)
- 00027:
- 00028:
- 00029: typedef void (*ngx_pool_cleanup_pt)(void *data); //cleanup的callback类型
- 00030:
- 00031: typedef struct ngx_pool_cleanup_s ngx_pool_cleanup_t;
- 00032:
- 00033: struct ngx_pool_cleanup_s{
- 00034: ngx_pool_cleanup_pt handler;
- 00035: void *data; //指向要清除的数据
- 00036: ngx_pool_cleanup_t *next; //下一个cleanup callback
- 00037: };
- 00038:
- 00039:
- 00040: typedef struct ngx_pool_large_s ngx_pool_large_t;
- 00041:
- 00042: struct ngx_pool_large_s{
- 00043: ngx_pool_large_t *next; //指向下一块大块内存
- 00044: void *alloc; //指向分配的大块内存
- 00045: };
- ...
- ...
- 00067: typedef struct {
- 00068: ngx_fd_t fd;
- 00069: u_char *name;
- 00070: ngx_log_t *log;
- 00071: } ngx_pool_cleanup_file_t;
- 00072:
(gdb) p getpagesize()
$18 = 4096
全局变量ngx_pagesize的初始化是在如下函数中完成的。./src/os/unix/ngx_posix_init.c
- ngx_int_t
- ngx_os_init(ngx_log_t *log)
- {
- ngx_uint_t n;
- #if (NGX_HAVE_OS_SPECIFIC_INIT)
- if (ngx_os_specific_init(log) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- #endif
- ngx_init_setproctitle(log);
- /** 该函数为glibc的库函数,由系统调用实现,返回内核中的PAGE_SIZE,该值依赖体系结构*/
- ngx_pagesize = getpagesize();
- ngx_cacheline_size = NGX_CPU_CACHE_LINE;
- ...
- }
这些数据结构之间的关系,请参考后面的图。
1.3 ngx_pool_t的逻辑结构
这些数据结构逻辑结构图如下。注:本文采用UML的方式画出该图。
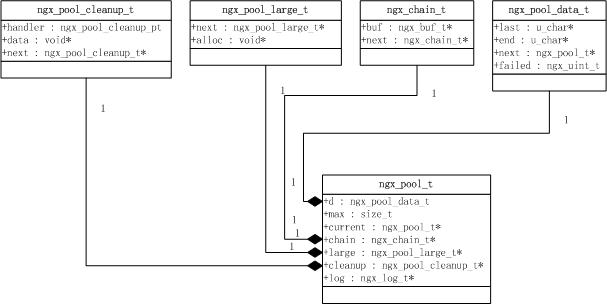
2. 内存池操作
2.1 创建内存池
创建内存池有ngx_create_pool()函数完成,代码如下。
- 00015: ngx_pool_t *
- 00016: ngx_create_pool(size_t size, ngx_log_t *log)
- 00017: {
- 00018: ngx_pool_t *p;
- 00019:
- 00020: p = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, size, log);
- 00021: if (p == NULL) {
- 00022: return NULL;
- 00023: }
- 00024:
- 00025: p->d.last = (u_char *) p + sizeof(ngx_pool_t); //last指向ngx_pool_t结构体之后数据取起始位置
- 00026: p->d.end = (u_char *) p + size; //end指向分配的整个size大小的内存的末尾
- 00027: p->d.next = NULL;
- 00028: p->d.failed = 0;
- 00029:
- 00030: size = size - sizeof(ngx_pool_t);
- 00031: p->max = (size < NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL) ? size : NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL; //最大不超过4095B
- 00032:
- 00033: p->current = p;
- 00034: p->chain = NULL;
- 00035: p->large = NULL;
- 00036: p->cleanup = NULL;
- 00037: p->log = log;
- 00038:
- 00039: return p;
- 00040: }
例如,调用ngx_create_pool(1024, 0x80d1c4c)后,创建的内存池物理结构如下图。
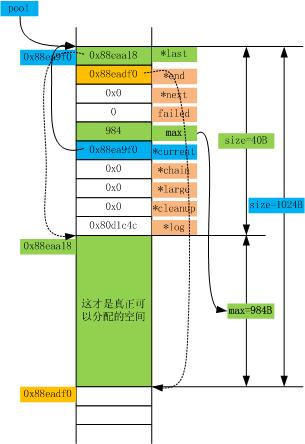
2.2 销毁内存池
销毁内存池由如下函数完成。
void ngx_destroy_pool(ngx_pool_t *pool)
该函数将遍历内存池链表,所有释放内存,如果注册了clenup(也是一个链表结构),亦将遍历该cleanup链表结构依次调用clenup的handler清理。同时,还将遍历large链表,释放大块内存。
2.3 重置内存池
重置内存池由下面的函数完成。
void ngx_reset_pool(ngx_pool_t *pool);
该函数将释放所有large内存,并且将d->last指针重新指向ngx_pool_t结构之后数据区的开始位置,同刚创建后的位置相同。
2.4 分配内存
内存分配的函数如下。
void *ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pnalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pcalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pmemalign(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size, size_t alignment);
返回值为分配的内存起始地址。选择其中的两个函数进行分析,其他的也很好理解,省略。
2.4.1 ngx_palloc()函数分析
ngx_palloc()代码如下,分析请参考笔者所加的注释。
- 00115: void *
- 00116: ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
- 00117: {
- 00118: u_char *m;
- 00119: ngx_pool_t *p;
- 00120:
- 00121: if (size <= pool->max) {//判断待分配内存与max值
- 00122:
- 00123: p = pool->current; //小于max值,则从current节点开始遍历pool链表
- 00124:
- 00125: do {
- 00126: m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT);
- 00127:
- 00128: if ((size_t) (p->d.end - m) >= size) {
- 00129: p->d.last = m + size; //在该节点指向的内存块中分配size大小的内存
- 00130:
- 00131: return m;
- 00132: }
- 00133:
- 00134: p = p->d.next;
- 00135:
- 00136: } while (p);
- 00137:
- 00138: return ngx_palloc_block(pool, size); //链表里没有能分配size大小内存的节点,则生成一个新的节点并在其中分配内存
- 00139: }
- 00140:
- 00141: return ngx_palloc_large(pool, size); //大于max值,则在large链表里分配内存
- 00142: }
例如,在2.1节中创建的内存池中分配200B的内存,调用ngx_palloc(pool, 200)后,该内存池物理结构如下图。
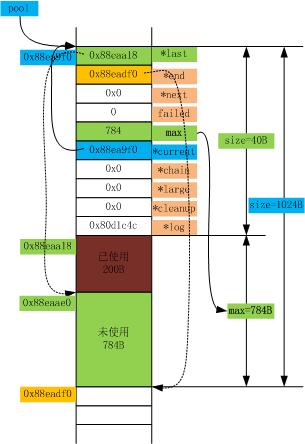
2.4.2 ngx_palloc_block()函数分析
ngx_palloc_block函数代码如下,分析请参考笔者所加的注释。
- 00175: static void *
- 00176: ngx_palloc_block(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
- 00177: {
- 00178: u_char *m;
- 00179: size_t psize;
- 00180: ngx_pool_t *p, *new, *current;
- 00181:
- 00182: psize = (size_t) (pool->d.end - (u_char *) pool); //计算pool的大小
- 00183:
- 00184: m = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, psize, pool->log);//分配一块与pool大小相同的内存
- 00185: if (m == NULL) {
- 00186: return NULL;
- 00187: }
- 00188:
- 00189: new = (ngx_pool_t *) m;
- 00190:
- 00191: new->d.end = m + psize; //设置end指针
- 00192: new->d.next = NULL;
- 00193: new->d.failed = 0;
- 00194:
- 00195: m += sizeof(ngx_pool_data_t); //让m指向该块内存ngx_pool_data_t结构体之后数据区起始位置
- 00196: m = ngx_align_ptr(m, NGX_ALIGNMENT); //按4字节对齐
- 00197: new->d.last = m + size; //在数据区分配size大小的内存并设置last指针
- 00198:
- 00199: current = pool->current;
- 00200:
- 00201: for (p = current; p->d.next; p = p->d.next) {
- 00202: if (p->d.failed++ > 4) { //failed的值只在此处被修改
- 00203: current = p->d.next; //失败4次以上移动current指针
- 00204: }
- 00205: }
- 00206:
- 00207: p->d.next = new; //将这次分配的内存块new加入该内存池
- 00208:
- 00209: pool->current = current ? current : new;
- 00210:
- 00211: return m;
- 00212: }
注意:该函数分配一块内存后,last指针指向的是ngx_pool_data_t结构体(大小16B)之后数据区的起始位置。而创建内存池时时,last指针指向的是ngx_pool_t结构体(大小40B)之后数据区的起始位置。
结合2.7节的内存池的物理结构,更容易理解。
2.5 释放内存
请参考如下函数,不再赘述。
ngx_int_t ngx_pfree(ngx_pool_t *pool, void *p)
需要注意的是该函数只释放large链表中注册的内存,普通内存在ngx_destroy_pool中统一释放。
2.6 注册cleanup
请参考如下函数,该函数实现也很简单,此处不再赘述。
ngx_pool_cleanup_t *ngx_pool_cleanup_add(ngx_pool_t *p, size_t size)
2.7 内存池的物理结构
针对本文第3节的例子,画出的内存池的物理结构如下图。
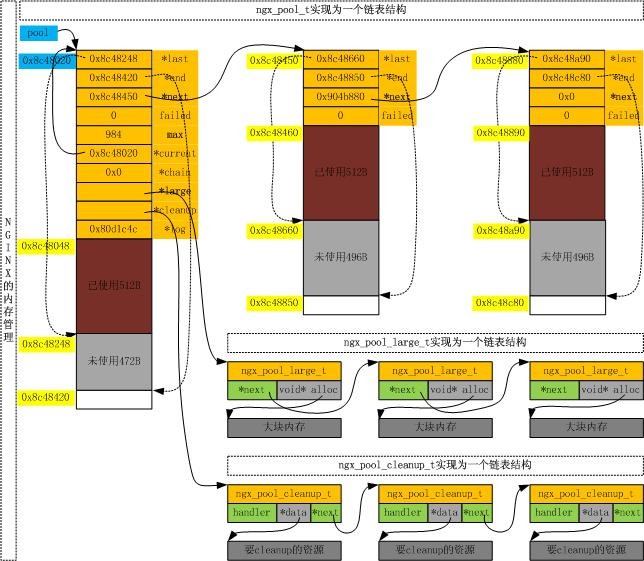
从该图也能看出2.4节的结论,即内存池第一块内存前40字节为ngx_pool_t结构,后续加入的内存块前16个字节为ngx_pool_data_t结构,这两个结构之后便是真正可以分配内存区域。
因此,本文Reference中的内存分配相关中的图是有一点点小问题的,并不是每一个节点的前面都是ngx_pool_t结构。
3. 一个例子
理解并掌握开源软件的最好方式莫过于自己写一些测试代码,或者改写软件本身,并进行调试来进一步理解开源软件的原理和设计方法。本节给出一个创建内存池并从中分配内存的简单例子。
3.1 代码
- /**
- * ngx_pool_t test, to test ngx_palloc, ngx_palloc_block, ngx_palloc_large
- */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include "ngx_config.h"
- #include "ngx_conf_file.h"
- #include "nginx.h"
- #include "ngx_core.h"
- #include "ngx_string.h"
- #include "ngx_palloc.h"
- volatile ngx_cycle_t *ngx_cycle;
- void ngx_log_error_core(ngx_uint_t level, ngx_log_t *log, ngx_err_t err,
- const char *fmt, ...)
- {
- }
- void dump_pool(ngx_pool_t* pool)
- {
- while (pool)
- {
- printf("pool = 0x%x ", pool);
- printf(" .d ");
- printf(" .last = 0x%x ", pool->d.last);
- printf(" .end = 0x%x ", pool->d.end);
- printf(" .next = 0x%x ", pool->d.next);
- printf(" .failed = %d ", pool->d.failed);
- printf(" .max = %d ", pool->max);
- printf(" .current = 0x%x ", pool->current);
- printf(" .chain = 0x%x ", pool->chain);
- printf(" .large = 0x%x ", pool->large);
- printf(" .cleanup = 0x%x ", pool->cleanup);
- printf(" .log = 0x%x ", pool->log);
- printf("available pool memory = %d ", pool->d.end - pool->d.last);
- pool = pool->d.next;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- ngx_pool_t *pool;
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("create a new pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- pool = ngx_create_pool(1024, NULL);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 1 from the pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 2 from the pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 3 from the pool : ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
- return 0;
- }
3.2 如何编译
这个问题是编写测试代码或者改写软件本身最迫切需要解决的问题,否则,编写的代码无从编译或运行,那也无从进行调试并理解软件了。
如何对自己编写的测试代码进行编译,可参考Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-编译过程自动化及对链接的解释、Linux平台如何编译使用Google test写的单元测试?。我们要做的是学习这种编译工程的方法,针对该例子,笔者编写的makefile文件如下。——这便是本节的主要目的。
- CXX = gcc
- CXXFLAGS += -g -Wall -Wextra
- NGX_ROOT = /usr/src/nginx-1.0.4
- TARGETS = ngx_pool_t_test
- TARGETS_C_FILE = $(TARGETS).c
- CLEANUP = rm -f $(TARGETS) *.o
- all: $(TARGETS)
- clean:
- $(CLEANUP)
- CORE_INCS = -I.
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/core
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/event
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/event/modules
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/os/unix
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/objs
- NGX_PALLOC = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/core/ngx_palloc.o
- NGX_STRING = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/core/ngx_string.o
- NGX_ALLOC = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/os/unix/ngx_alloc.o
- $(TARGETS): $(TARGETS_C_FILE)
- $(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $(CORE_INCS) $(NGX_PALLOC) $(NGX_STRING) $(NGX_ALLOC) $^ -o $@
3.3 运行运行结果
- # ./ngx_pool_t_test
- --------------------------------
- create a new pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922048
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 984
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 1 from the pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 2 from the pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x8922450
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- pool = 0x8922450
- .d
- .last = 0x8922660
- .end = 0x8922850
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 3 from the pool :
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x8922450
- .failed = 1
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- pool = 0x8922450
- .d
- .last = 0x8922660
- .end = 0x8922850
- .next = 0x8922880
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
- pool = 0x8922880
- .d
- .last = 0x8922a90
- .end = 0x8922c80
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
4. 小结
本文针对nginx-1.0.4的内存管理进行了较为全面的分析,包括相关内存池数据结构,内存池的创建、销毁,以及从内存池中分配内存等。最后通过一个简单例子向读者展示nginx内存池的创建和分配操作,同时借此向读者展示编译测试代码的方法。
分析完nginx的内存管理,你一定惊叹于nginx作者的聪明才智。这种内存管理的设计方法小巧、快捷,值得借鉴!
Content
0. 序
1. 内存池结构
1.1 ngx_pool_t结构
1.2 其他相关结构
1.3 ngx_pool_t的逻辑结构
2. 内存池操作
2.1 创建内存池
2.2 销毁内存池
2.3 重置内存池
2.4 分配内存
2.4.1 ngx_palloc()函数分析
2.4.2 ngx_palloc_block()函数分析
2.5 释放内存
2.6 注册cleanup
2.7 内存池的物理结构
3. 一个例子
3.1 代码
3.2 如何编译
3.3 运行结果
4. 小结
5. 致谢
0. 序
nginx对内存的管理由其自己实现的内存池结构ngx_pool_t来完成,本文重点叙述nginx的内存管理。
nginx内存管理相关文件:
(1) ./src/os/unix/ngx_alloc.h/.c
- 内存相关的操作,封装了最基本的内存分配函数
- 如free/malloc/memalign/posix_memalign,分别被封装为ngx_free,ngx_alloc/ngx_calloc, ngx_memalign
- ngx_alloc:封装malloc分配内存
- ngx_calloc:封装malloc分配内存,并初始化空间内容为0
- ngx_memalign:返回基于一个指定alignment的大小为size的内存空间,且其地址为alignment的整数倍,alignment为2的幂。
(2) ./src/core/ngx_palloc.h/.c
- 封装创建/销毁内存池,从内存池分配空间等函数
.表示nginx-1.0.4代码目录,本文为/usr/src/nginx-1.0.4。
1. 内存池结构
nginx对内存的管理均统一完成,例如,在特定的生命周期统一建立内存池(如main函数系统启动初期即分配1024B大小的内存池),需要内存时统一分配内存池中的内存,在适当的时候释放内存池的内存(如关闭http链接时调用ngx_destroy_pool进行销毁)。
因此,开发者只需在需要内存时进行申请即可,不用过多考虑内存的释放等问题,大大提高了开发的效率。先看一下内存池结构。
1.1 ngx_pool_t结构
此处统一一下概念,内存池的数据块:即分配内存在这些数据块中进行,一个内存池可以有多一个内存池数据块。nginx的内存池结构如下。
- 00048: typedef struct {
- 00049: u_char *last; //当前内存池分配到此处,即下一次分配从此处开始
- 00050: u_char *end; //内存池结束位置
- 00051: ngx_pool_t *next; //内存池里面有很多块内存,这些内存块就是通过该指针连成链表的
- 00052: ngx_uint_t failed; //内存池分配失败次数
- 00053: } ngx_pool_data_t; //内存池的数据块位置信息
- 00054:
- 00055:
- 00056: struct ngx_pool_s{ //内存池头部结构
- 00057: ngx_pool_data_t d; //内存池的数据块
- 00058: size_t max; //内存池数据块的最大值
- 00059: ngx_pool_t *current; //指向当前内存池
- 00060: ngx_chain_t *chain; //该指针挂接一个ngx_chain_t结构
- 00061: ngx_pool_large_t *large; //大块内存链表,即分配空间超过max的内存
- 00062: ngx_pool_cleanup_t *cleanup; //释放内存池的callback
- 00063: ngx_log_t *log; //日志信息
- 00064: };
其中,sizeof(ngx_pool_data_t)=16B,sizeof(ngx_pool_t)=40B。
nginx将几乎所有的结构体放在ngx_core.h文件中重新进行了申明,如下。
- typedef struct ngx_module_s ngx_module_t;
- typedef struct ngx_conf_s ngx_conf_t;
- typedef struct ngx_cycle_s ngx_cycle_t;
- typedef struct ngx_pool_s ngx_pool_t;
- typedef struct ngx_chain_s ngx_chain_t;
- typedef struct ngx_log_s ngx_log_t;
- typedef struct ngx_array_s ngx_array_t;
- typedef struct ngx_open_file_s ngx_open_file_t;
- typedef struct ngx_command_s ngx_command_t;
- typedef struct ngx_file_s ngx_file_t;
- typedef struct ngx_event_s ngx_event_t;
- typedef struct ngx_event_aio_s ngx_event_aio_t;
- typedef struct ngx_connection_s ngx_connection_t;
1.2 其他相关结构
其他与内存池相干的数据结构,如清除资源的cleanup链表,分配的大块内存链表等,如下。
- 00015: /*
- 00016: * NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL should be (ngx_pagesize - 1), i.e. 4095 on x86.
- 00017: * On Windows NT it decreases a number of locked pages in a kernel.
- 00018: */
- 00019: #define NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL (ngx_pagesize - 1) //在x86体系结构下,该值一般为4096B,即4K
- 00020:
- 00021: #define NGX_DEFAULT_POOL_SIZE (16* 1024)
- 00022:
- 00023: #define NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT 16
- 00024: #define NGX_MIN_POOL_SIZE
- 00025: ngx_align((sizeof(ngx_pool_t) + 2 * sizeof(ngx_pool_large_t)),
- 00026: NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT)
- 00027:
- 00028:
- 00029: typedef void (*ngx_pool_cleanup_pt)(void *data); //cleanup的callback类型
- 00030:
- 00031: typedef struct ngx_pool_cleanup_s ngx_pool_cleanup_t;
- 00032:
- 00033: struct ngx_pool_cleanup_s{
- 00034: ngx_pool_cleanup_pt handler;
- 00035: void *data; //指向要清除的数据
- 00036: ngx_pool_cleanup_t *next; //下一个cleanup callback
- 00037: };
- 00038:
- 00039:
- 00040: typedef struct ngx_pool_large_s ngx_pool_large_t;
- 00041:
- 00042: struct ngx_pool_large_s{
- 00043: ngx_pool_large_t *next; //指向下一块大块内存
- 00044: void *alloc; //指向分配的大块内存
- 00045: };
- ...
- ...
- 00067: typedef struct {
- 00068: ngx_fd_t fd;
- 00069: u_char *name;
- 00070: ngx_log_t *log;
- 00071: } ngx_pool_cleanup_file_t;
- 00072:
(gdb) p getpagesize()
$18 = 4096
全局变量ngx_pagesize的初始化是在如下函数中完成的。./src/os/unix/ngx_posix_init.c
- ngx_int_t
- ngx_os_init(ngx_log_t *log)
- {
- ngx_uint_t n;
- #if (NGX_HAVE_OS_SPECIFIC_INIT)
- if (ngx_os_specific_init(log) != NGX_OK) {
- return NGX_ERROR;
- }
- #endif
- ngx_init_setproctitle(log);
- /** 该函数为glibc的库函数,由系统调用实现,返回内核中的PAGE_SIZE,该值依赖体系结构*/
- ngx_pagesize = getpagesize();
- ngx_cacheline_size = NGX_CPU_CACHE_LINE;
- ...
- }
这些数据结构之间的关系,请参考后面的图。
1.3 ngx_pool_t的逻辑结构
这些数据结构逻辑结构图如下。注:本文采用UML的方式画出该图。

2. 内存池操作
2.1 创建内存池
创建内存池有ngx_create_pool()函数完成,代码如下。
- 00015: ngx_pool_t *
- 00016: ngx_create_pool(size_t size, ngx_log_t *log)
- 00017: {
- 00018: ngx_pool_t *p;
- 00019:
- 00020: p = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, size, log);
- 00021: if (p == NULL) {
- 00022: return NULL;
- 00023: }
- 00024:
- 00025: p->d.last = (u_char *) p + sizeof(ngx_pool_t); //last指向ngx_pool_t结构体之后数据取起始位置
- 00026: p->d.end = (u_char *) p + size; //end指向分配的整个size大小的内存的末尾
- 00027: p->d.next = NULL;
- 00028: p->d.failed = 0;
- 00029:
- 00030: size = size - sizeof(ngx_pool_t);
- 00031: p->max = (size < NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL) ? size : NGX_MAX_ALLOC_FROM_POOL; //最大不超过4095B
- 00032:
- 00033: p->current = p;
- 00034: p->chain = NULL;
- 00035: p->large = NULL;
- 00036: p->cleanup = NULL;
- 00037: p->log = log;
- 00038:
- 00039: return p;
- 00040: }
例如,调用ngx_create_pool(1024, 0x80d1c4c)后,创建的内存池物理结构如下图。

2.2 销毁内存池
销毁内存池由如下函数完成。
void ngx_destroy_pool(ngx_pool_t *pool)
该函数将遍历内存池链表,所有释放内存,如果注册了clenup(也是一个链表结构),亦将遍历该cleanup链表结构依次调用clenup的handler清理。同时,还将遍历large链表,释放大块内存。
2.3 重置内存池
重置内存池由下面的函数完成。
void ngx_reset_pool(ngx_pool_t *pool);
该函数将释放所有large内存,并且将d->last指针重新指向ngx_pool_t结构之后数据区的开始位置,同刚创建后的位置相同。
2.4 分配内存
内存分配的函数如下。
void *ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pnalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pcalloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size);
void *ngx_pmemalign(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size, size_t alignment);
返回值为分配的内存起始地址。选择其中的两个函数进行分析,其他的也很好理解,省略。
2.4.1 ngx_palloc()函数分析
ngx_palloc()代码如下,分析请参考笔者所加的注释。
- 00115: void *
- 00116: ngx_palloc(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
- 00117: {
- 00118: u_char *m;
- 00119: ngx_pool_t *p;
- 00120:
- 00121: if (size <= pool->max) {//判断待分配内存与max值
- 00122:
- 00123: p = pool->current; //小于max值,则从current节点开始遍历pool链表
- 00124:
- 00125: do {
- 00126: m = ngx_align_ptr(p->d.last, NGX_ALIGNMENT);
- 00127:
- 00128: if ((size_t) (p->d.end - m) >= size) {
- 00129: p->d.last = m + size; //在该节点指向的内存块中分配size大小的内存
- 00130:
- 00131: return m;
- 00132: }
- 00133:
- 00134: p = p->d.next;
- 00135:
- 00136: } while (p);
- 00137:
- 00138: return ngx_palloc_block(pool, size); //链表里没有能分配size大小内存的节点,则生成一个新的节点并在其中分配内存
- 00139: }
- 00140:
- 00141: return ngx_palloc_large(pool, size); //大于max值,则在large链表里分配内存
- 00142: }
例如,在2.1节中创建的内存池中分配200B的内存,调用ngx_palloc(pool, 200)后,该内存池物理结构如下图。

2.4.2 ngx_palloc_block()函数分析
ngx_palloc_block函数代码如下,分析请参考笔者所加的注释。
- 00175: static void *
- 00176: ngx_palloc_block(ngx_pool_t *pool, size_t size)
- 00177: {
- 00178: u_char *m;
- 00179: size_t psize;
- 00180: ngx_pool_t *p, *new, *current;
- 00181:
- 00182: psize = (size_t) (pool->d.end - (u_char *) pool); //计算pool的大小
- 00183:
- 00184: m = ngx_memalign(NGX_POOL_ALIGNMENT, psize, pool->log);//分配一块与pool大小相同的内存
- 00185: if (m == NULL) {
- 00186: return NULL;
- 00187: }
- 00188:
- 00189: new = (ngx_pool_t *) m;
- 00190:
- 00191: new->d.end = m + psize; //设置end指针
- 00192: new->d.next = NULL;
- 00193: new->d.failed = 0;
- 00194:
- 00195: m += sizeof(ngx_pool_data_t); //让m指向该块内存ngx_pool_data_t结构体之后数据区起始位置
- 00196: m = ngx_align_ptr(m, NGX_ALIGNMENT); //按4字节对齐
- 00197: new->d.last = m + size; //在数据区分配size大小的内存并设置last指针
- 00198:
- 00199: current = pool->current;
- 00200:
- 00201: for (p = current; p->d.next; p = p->d.next) {
- 00202: if (p->d.failed++ > 4) { //failed的值只在此处被修改
- 00203: current = p->d.next; //失败4次以上移动current指针
- 00204: }
- 00205: }
- 00206:
- 00207: p->d.next = new; //将这次分配的内存块new加入该内存池
- 00208:
- 00209: pool->current = current ? current : new;
- 00210:
- 00211: return m;
- 00212: }
注意:该函数分配一块内存后,last指针指向的是ngx_pool_data_t结构体(大小16B)之后数据区的起始位置。而创建内存池时时,last指针指向的是ngx_pool_t结构体(大小40B)之后数据区的起始位置。
结合2.7节的内存池的物理结构,更容易理解。
2.5 释放内存
请参考如下函数,不再赘述。
ngx_int_t ngx_pfree(ngx_pool_t *pool, void *p)
需要注意的是该函数只释放large链表中注册的内存,普通内存在ngx_destroy_pool中统一释放。
2.6 注册cleanup
请参考如下函数,该函数实现也很简单,此处不再赘述。
ngx_pool_cleanup_t *ngx_pool_cleanup_add(ngx_pool_t *p, size_t size)
2.7 内存池的物理结构
针对本文第3节的例子,画出的内存池的物理结构如下图。

从该图也能看出2.4节的结论,即内存池第一块内存前40字节为ngx_pool_t结构,后续加入的内存块前16个字节为ngx_pool_data_t结构,这两个结构之后便是真正可以分配内存区域。
因此,本文Reference中的内存分配相关中的图是有一点点小问题的,并不是每一个节点的前面都是ngx_pool_t结构。
3. 一个例子
理解并掌握开源软件的最好方式莫过于自己写一些测试代码,或者改写软件本身,并进行调试来进一步理解开源软件的原理和设计方法。本节给出一个创建内存池并从中分配内存的简单例子。
3.1 代码
- /**
- * ngx_pool_t test, to test ngx_palloc, ngx_palloc_block, ngx_palloc_large
- */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include "ngx_config.h"
- #include "ngx_conf_file.h"
- #include "nginx.h"
- #include "ngx_core.h"
- #include "ngx_string.h"
- #include "ngx_palloc.h"
- volatile ngx_cycle_t *ngx_cycle;
- void ngx_log_error_core(ngx_uint_t level, ngx_log_t *log, ngx_err_t err,
- const char *fmt, ...)
- {
- }
- void dump_pool(ngx_pool_t* pool)
- {
- while (pool)
- {
- printf("pool = 0x%x ", pool);
- printf(" .d ");
- printf(" .last = 0x%x ", pool->d.last);
- printf(" .end = 0x%x ", pool->d.end);
- printf(" .next = 0x%x ", pool->d.next);
- printf(" .failed = %d ", pool->d.failed);
- printf(" .max = %d ", pool->max);
- printf(" .current = 0x%x ", pool->current);
- printf(" .chain = 0x%x ", pool->chain);
- printf(" .large = 0x%x ", pool->large);
- printf(" .cleanup = 0x%x ", pool->cleanup);
- printf(" .log = 0x%x ", pool->log);
- printf("available pool memory = %d ", pool->d.end - pool->d.last);
- pool = pool->d.next;
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- ngx_pool_t *pool;
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("create a new pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- pool = ngx_create_pool(1024, NULL);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 1 from the pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 2 from the pool: ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- printf("alloc block 3 from the pool : ");
- printf("-------------------------------- ");
- ngx_palloc(pool, 512);
- dump_pool(pool);
- ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
- return 0;
- }
3.2 如何编译
这个问题是编写测试代码或者改写软件本身最迫切需要解决的问题,否则,编写的代码无从编译或运行,那也无从进行调试并理解软件了。
如何对自己编写的测试代码进行编译,可参考Linux平台代码覆盖率测试-编译过程自动化及对链接的解释、Linux平台如何编译使用Google test写的单元测试?。我们要做的是学习这种编译工程的方法,针对该例子,笔者编写的makefile文件如下。——这便是本节的主要目的。
- CXX = gcc
- CXXFLAGS += -g -Wall -Wextra
- NGX_ROOT = /usr/src/nginx-1.0.4
- TARGETS = ngx_pool_t_test
- TARGETS_C_FILE = $(TARGETS).c
- CLEANUP = rm -f $(TARGETS) *.o
- all: $(TARGETS)
- clean:
- $(CLEANUP)
- CORE_INCS = -I.
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/core
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/event
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/event/modules
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/src/os/unix
- -I$(NGX_ROOT)/objs
- NGX_PALLOC = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/core/ngx_palloc.o
- NGX_STRING = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/core/ngx_string.o
- NGX_ALLOC = $(NGX_ROOT)/objs/src/os/unix/ngx_alloc.o
- $(TARGETS): $(TARGETS_C_FILE)
- $(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $(CORE_INCS) $(NGX_PALLOC) $(NGX_STRING) $(NGX_ALLOC) $^ -o $@
3.3 运行运行结果
- # ./ngx_pool_t_test
- --------------------------------
- create a new pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922048
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 984
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 1 from the pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 2 from the pool:
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x8922450
- .failed = 0
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- pool = 0x8922450
- .d
- .last = 0x8922660
- .end = 0x8922850
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
- --------------------------------
- alloc block 3 from the pool :
- --------------------------------
- pool = 0x8922020
- .d
- .last = 0x8922248
- .end = 0x8922420
- .next = 0x8922450
- .failed = 1
- .max = 984
- .current = 0x8922020
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 472
- pool = 0x8922450
- .d
- .last = 0x8922660
- .end = 0x8922850
- .next = 0x8922880
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
- pool = 0x8922880
- .d
- .last = 0x8922a90
- .end = 0x8922c80
- .next = 0x0
- .failed = 0
- .max = 0
- .current = 0x0
- .chain = 0x0
- .large = 0x0
- .cleanup = 0x0
- .log = 0x0
- available pool memory = 496
4. 小结
本文针对nginx-1.0.4的内存管理进行了较为全面的分析,包括相关内存池数据结构,内存池的创建、销毁,以及从内存池中分配内存等。最后通过一个简单例子向读者展示nginx内存池的创建和分配操作,同时借此向读者展示编译测试代码的方法。
分析完nginx的内存管理,你一定惊叹于nginx作者的聪明才智。这种内存管理的设计方法小巧、快捷,值得借鉴!