策略模式是一种行为设计模式, 它能让你定义一系列算法, 并将每种算法分别放入独立的类中, 以使算法的对象能够相互替换。
Java 8 开始支持 lambda 方法, 它可作为一种替代策略模式的简单方式。
这里有一些核心 Java 程序库中策略模式的示例:
- 对 java.util.Comparator#compare() 的调用来自
Collections#sort(). - javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet:
service()方法, 还有所有接受HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象作为参数的doXXX()方法。 - javax.servlet.Filter#doFilter()
识别方法: 策略模式可以通过允许嵌套对象完成实际工作的方法以及允许将该对象替换为不同对象的设置器来识别。
策略模式结构
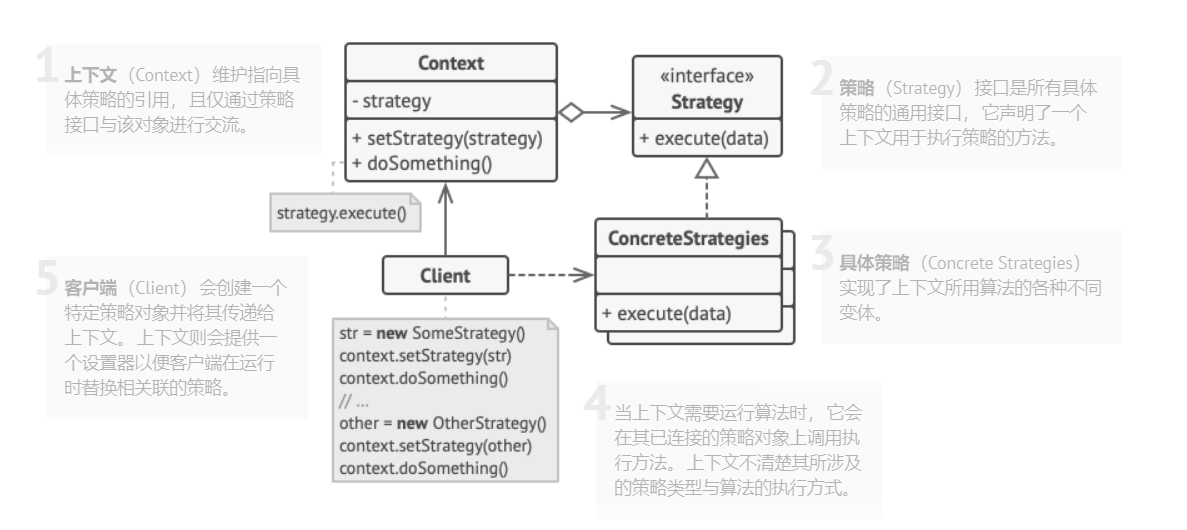
样例
策略模式被用于在电子商务应用中实现各种支付方法。 客户选中希望购买的商品后需要选择一种支付方式: Paypal 或者信用卡。
具体策略不仅会完成实际的支付工作, 还会改变支付表单的行为, 并在表单中提供相应的字段来记录支付信息。
通用的支付方法接口
package behavioral.strategy;
public interface PayStrategy {
boolean pay(int paymentAmount);
void collectPaymentDetails();
}
使用 PayPal 支付
package behavioral.strategy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PayByPayPal implements PayStrategy {
private static final Map<String, String> DATA_BASE = new HashMap<>();
private final BufferedReader READER = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
private String email;
private String password;
private boolean signedIn;
static {
DATA_BASE.put("hua", "hua@qq.com");
DATA_BASE.put("user", "user@qq.com");
}
@Override
public boolean pay(int paymentAmount) {
if (signedIn) {
System.out.println("Paying " + paymentAmount + " using PayPal.");
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void collectPaymentDetails() {
try {
while (!signedIn) {
System.out.println("Enter the user's email:");
email = READER.readLine();
System.out.println("Enter the password:");
password = READER.readLine();
if (verify()) {
System.out.println("Data verification has been successful.");
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong email or password!");
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private boolean verify() {
setSignedIn(email.equals(DATA_BASE.get(password)));
return signedIn;
}
private void setSignedIn(boolean signedIn) {
this.signedIn = signedIn;
}
}
使用信用卡支付
package behavioral.strategy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class PayByCreditCard implements PayStrategy {
private final BufferedReader READER = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
private CreditCard card;
@Override
public boolean pay(int paymentAmount) {
if (cardIsPresent()) {
System.out.println("Paying " + paymentAmount + " using Credit Card.");
card.setAmount(card.getAmount() - paymentAmount);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void collectPaymentDetails() {
try {
System.out.print("Enter the card number: ");
String number = READER.readLine();
System.out.print("Enter the card expiration date 'mm/yy': ");
String date = READER.readLine();
System.out.print("Enter the CVV code: ");
String cvv = READER.readLine();
card = new CreditCard(number, date, cvv);
//credit card 有效性检查
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private boolean cardIsPresent() {
return card != null;
}
}
信用卡类
package behavioral.strategy;
public class CreditCard {
private int amount;
private String number;
private String date;
private String cvv;
public CreditCard(String number, String date, String cvv) {
this.amount = 100_000;
this.number = number;
this.date = date;
this.cvv = cvv;
}
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
}
订单类
package behavioral.strategy;
/**
* 订单类。
* 不知道用户选择的具体付款方式(策略)。
* 它使用公共策略接口将采集的支付数据委托给策略对象。
* 它可以用来保存订单到数据库。
*/
public class Order {
private int totalCost = 0;
private boolean isClosed = false;
public void processOrder(PayStrategy strategy) {
strategy.collectPaymentDetails();
}
public int getTotalCost() {
return totalCost;
}
public void setTotalCost(int totalCost) {
this.totalCost = totalCost;
}
public boolean isClosed() {
return isClosed;
}
public void setClosed() {
isClosed = true;
}
}
测试代码
package behavioral.strategy;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Demo {
private static Map<Integer, Integer> priceOnProducts = new HashMap<>();
private static BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
private static Order order = new Order();
private static PayStrategy strategy;
static {
priceOnProducts.put(1, 2200);
priceOnProducts.put(2, 1850);
priceOnProducts.put(3, 1100);
priceOnProducts.put(4, 890);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
while (!order.isClosed()) {
int cost;
String continueChoice;
do {
System.out.print("Please, select a product:" + "
" +
"1 - Mother board" + "
" +
"2 - CPU" + "
" +
"3 - HDD" + "
" +
"4 - Memory" + "
");
int choice = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
cost = priceOnProducts.get(choice);
System.out.print("Count: ");
int count = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
order.setTotalCost(cost * count);
System.out.print("Do you wish to continue selecting products? Y/N: ");
continueChoice = reader.readLine();
} while (continueChoice.equalsIgnoreCase("Y"));
if (strategy == null) {
System.out.println("Please, select a payment method:" + "
" +
"1 - PalPay" + "
" +
"2 - Credit Card");
String paymentMethod = reader.readLine();
// Client creates different strategies based on input from user,
// application configuration, etc.
if (paymentMethod.equals("1")) {
strategy = new PayByPayPal();
} else {
strategy = new PayByCreditCard();
}
}
// Order object delegates gathering payment data to strategy object,
// since only strategies know what data they need to process a
// payment.
order.processOrder(strategy);
System.out.print("Pay " + order.getTotalCost() + " units or Continue shopping? P/C: ");
String proceed = reader.readLine();
if (proceed.equalsIgnoreCase("P")) {
// Finally, strategy handles the payment.
if (strategy.pay(order.getTotalCost())) {
System.out.println("Payment has been successful.");
} else {
System.out.println("FAIL! Please, check your data.");
}
order.setClosed();
}
}
}
}
/**
*Please, select a product:
* 1 - Mother board
* 2 - CPU
* 3 - HDD
* 4 - Memory
* 1
* Count: 3
* Do you wish to continue selecting products? Y/N:
* N
* Please, select a payment method:
* 1 - PalPay
* 2 - Credit Card
* 1
* Enter the user's email:
* hua@qq.com
* Enter the password:
* hua
* Data verification has been successful.
* Pay 6600 units or Continue shopping? P/C:
* P
* Paying 6600 using PayPal.
* Payment has been successful.
*
* Process finished with exit code 0
*/
适用场景
-
当你想使用对象中各种不同的算法变体, 并希望能在运行时切换算法时, 可使用策略模式。
策略模式让你能够将对象关联至可以不同方式执行特定子任务的不同子对象, 从而以间接方式在运行时更改对象行为。
-
当你有许多仅在执行某些行为时略有不同的相似类时, 可使用策略模式。
策略模式让你能将不同行为抽取到一个独立类层次结构中, 并将原始类组合成同一个,从而减少重复代码。
-
如果算法在上下文的逻辑中不是特别重要, 使用该模式能将类的业务逻辑与其算法实现细节隔离开来。
策略模式让你能将各种算法的代码、 内部数据和依赖关系与其他代码隔离开来。 不同客户端可通过一个简单接口执行算法, 并能在运行时进行切换。
-
当类中使用了复杂条件运算符以在同一算法的不同变体中切换时, 可使用该模式。
策略模式将所有继承自同样接口的算法抽取到独立类中, 因此不再需要条件语句。 原始对象并不实现所有算法的变体, 而是将执行工作委派给其中的一个独立算法对象。
实现方式
- 从上下文类中找出修改频率较高的算法 (也可能是用于在运行时选择某个算法变体的复杂条件运算符)。
- 声明该算法所有变体的通用策略接口。
- 将算法逐一抽取到各自的类中, 它们都必须实现策略接口。
- 在上下文类中添加一个成员变量用于保存对于策略对象的引用。 然后提供设置器以修改该成员变量。 上下文仅可通过策略接口同策略对象进行交互, 如有需要还可定义一个接口来让策略访问其数据。
- 客户端必须将上下文类与相应策略进行关联, 使上下文可以预期的方式完成其主要工作。
策略模式优点
- 你可以在运行时切换对象内的算法。
- 你可以将算法的实现和使用算法的代码隔离开来。
- 你可以使用组合来代替继承。
- 开闭原则。 你无需对上下文进行修改就能够引入新的策略。
策略模式缺点
- 如果你的算法极少发生改变, 那么没有任何理由引入新的类和接口。 使用该模式只会让程序过于复杂。
- 客户端必须知晓策略间的不同——它需要选择合适的策略。
- 许多现代编程语言支持函数类型功能,允许你在一组匿名函数中实现不同版本的算法。 这样, 你使用这些函数的方式就和使用策略对象时完全相同, 无需借助额外的类和接口来保持代码简洁。