转载: http://www.codingsoho.com/zh/course/5/article/194
版权声明: 转载请注明出处 http://www.codingsoho.com/
做外贸的朋友有个需求,打算去亚马逊网站上爬取一点信息用于商业,利用学到的爬虫技术,小帮忙一下
需求:按指定链接(品种)爬虫相应的图片和介绍,避免一个个点进去看耗费时间
定义类和初始化
在这一节我们将爬虫功能进行类封装
定义类amazon_dynamic,实现构造函数如下
class amazon_dynamic():
def __init__(self, result_path, img_path):
self.result_path = result_path
self.img_path = img_path
self.driver = chrome()
self.next_page_flag = ""
- result_path : 访问路径
- img_path : 图片存储路径
- next_page_flag:是否为下一页
打开网页
def open_web(self, url):
try:
self.driver.get(url)
WebDriverWait(self.driver, 60).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "pagnNextString")))
except:
print "open page failure"
两个函数解释一下,这个再前一节中都已用到
driver.get获取网页内容WebDriverWait,等待指定的内容出现,设置超时时间60秒
访问下一页
这也是个基本功能,往往一页是不能列出所有产品的
同样,等待指定的内容出现之后,模拟点击“下一页”按钮
def next_page(self):
try:
WebDriverWait(self.driver, 60).until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, "pagnNextString")))
self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//span[@class="srSprite pagnNextArrow"]').click()
except:
print "open the next page failure %s" %self.driver.current_url
关闭页面
任务完成后,关闭页面
def page_close(self):
self.driver.close()
爬取页面信息
def get_info(self, max_num_to_extract):
# extacted result
product_pic_url_lst = []
product_info_lst = []
# find the product infor
while True:
info_of_all = self.driver.find_elements_by_xpath('//ul[@id="s-results-list-atf"]/li')
if len(info_of_all) >= max_num_to_extract:
break
sleep(1)
# get the specific information
for info in info_of_all[0:10]:
li_ID = info.get_attribute('id')
try:
product_pic = self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//li[@id="%s"]//img[@class="s-access-image cfMarker"]' % li_ID)
product_infos = self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//li[@id="%s"]//div[1]/div[3]/div[1]/a' % li_ID)
product_price = self.driver.find_elements_by_xpath('//li[@id="%s"]//div[1]/div[3]/div[3]/a/span[@class="a-offscreen"]' % li_ID)
except Exception as e:
print "get_info error {}".format(e)
continue
# src
pic_url = product_pic.get_attribute('src')
# title
product_name = product_infos.get_attribute('title')
# href
product_url = product_infos.get_attribute('href')
# price
if len(product_price) == 1:
product_price = product_price[0].get_attribute('aria-label')
elif len(product_price) >= 2:
product_price = product_price[1].text
else:
product_price = "No price"
# save to list
if pic_url and product_name and product_url:
product_pic_url_lst.append(pic_url)
product_info_lst.append([product_name, product_price, product_url])
else:
print now_time(), "ERROR:couldn't get all information of it, and will skip"
return product_info_lst, product_pic_url_lst
上面这段程序主要是从获取的网页内容中查找指定内容,官方网站的布局一直是变化的,所以这段代码在实际过程中也一直要更新。
上面的代码更新到2018/10/8,大部分内容都适配了,除了价格部分。这个大家自己去练习吧。
- 首先通过
self.driver.find_elements_by_xpath('//ul[@id="s-results-list-atf"]/li')获取搜索结果的整段内容,对应的结构如下,这里我们用到了find_elements_by_xpath方法,通过id定位ul
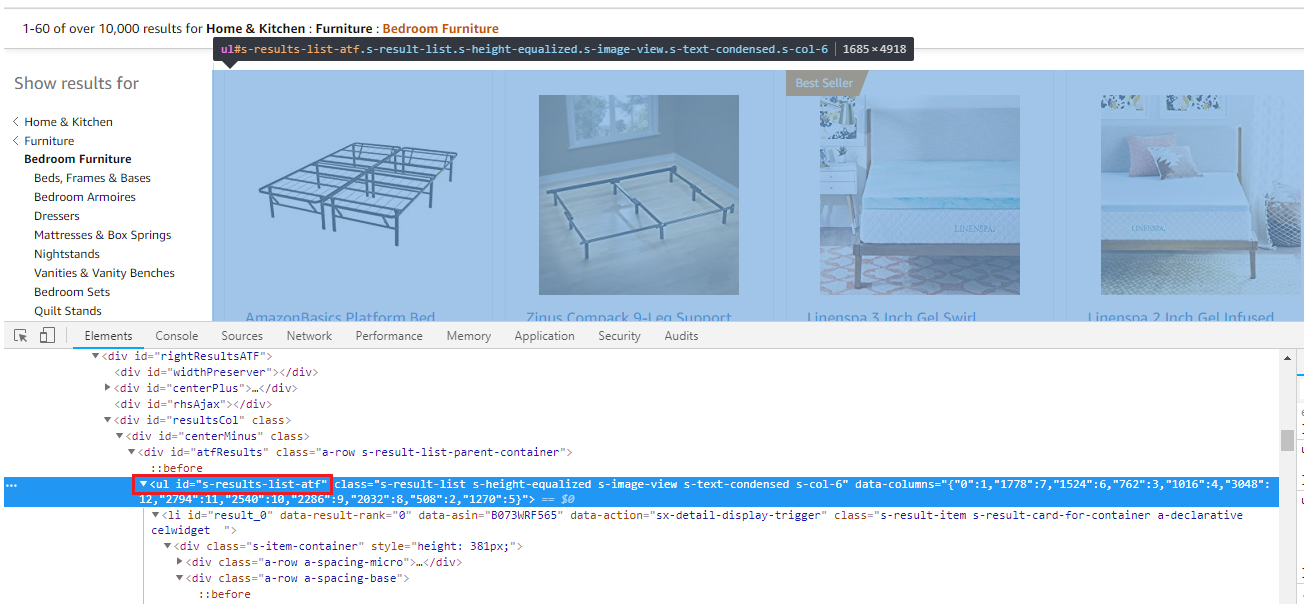
- 找到产品区域后,轮询各个图片,每个图片对应一个
li,获取这个li的ID用于进一步定位各个图片 - 在单个图片块内容里,查找我们想要的内容,比如搜索图片
self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//li[@id="%s"]//img[@class="s-access-image cfMarker"]' % li_ID),它是通过img的class来定位的 - 获取它的标题等信息,我们用的是
self.driver.find_element_by_xpath('//li[@id="%s"]//div[1]/div[3]/div[1]/a' % li_ID),得到的是<a>,然后进一步通过get_attribute('title')获取它的标题
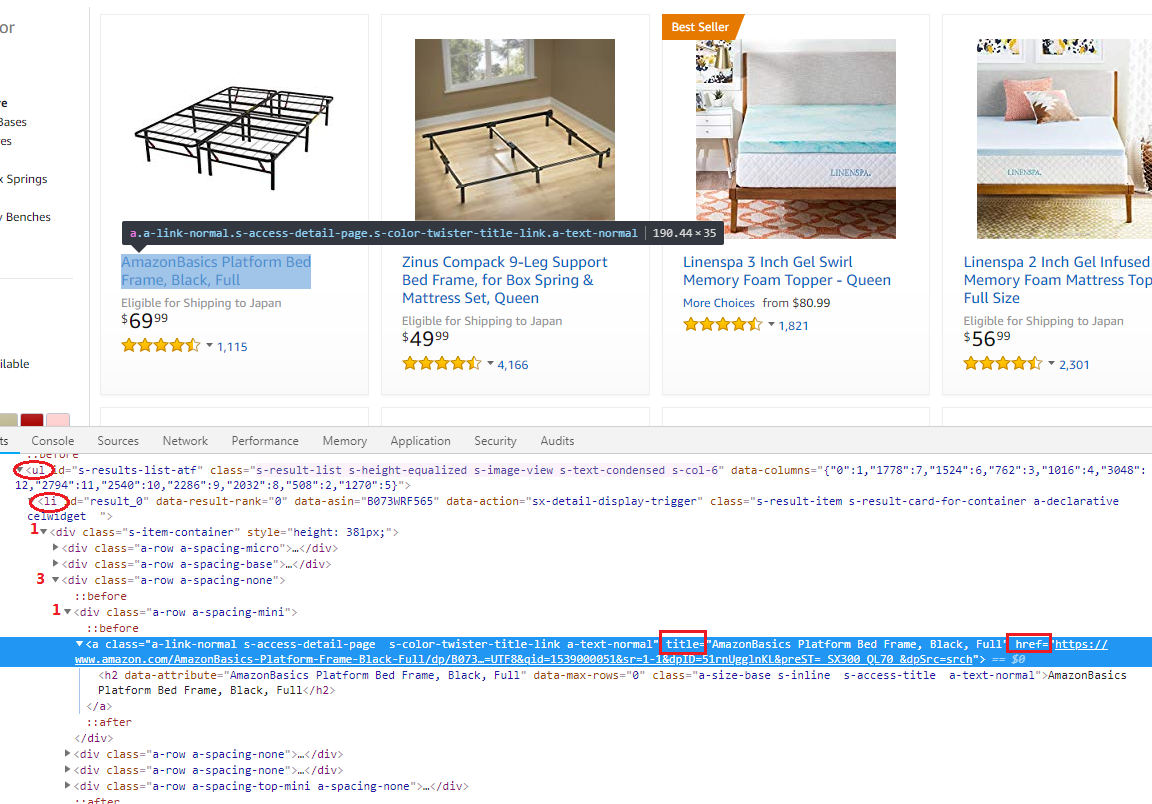
- 获取它的价格可以用类似方法,根据下图的html结构定义相应的搜索规则
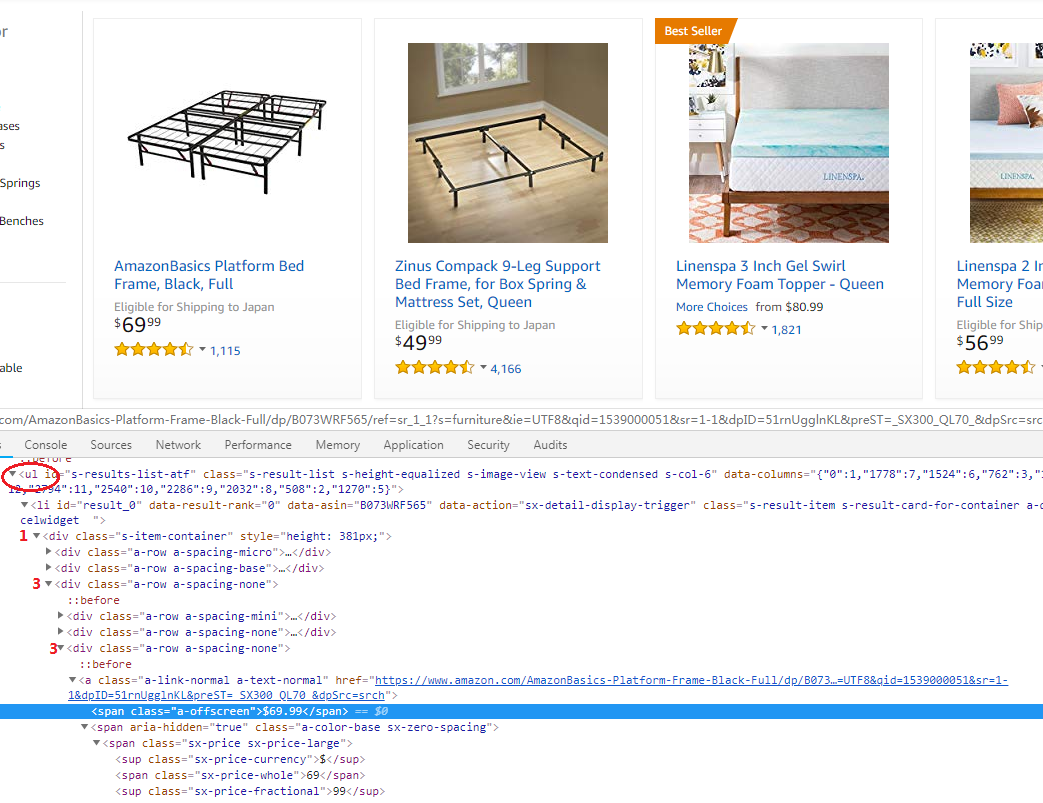
- 全部内容筛选完成后,存储这些内容到列表里返回
存储图片
上一步中,我们仅仅获取了图片的链接,有的时候我们需要存储图片,可以通过下面代码实现
def web_static(url):
try:
return requests.get(url, proxies=proxies, stream=True)
except Exception as e:
print "web_static :: url request get failure {} for url {}".format(e, url)
return False
def saveImg_sub(name, url, path):
img = web_static(url.strip())
try:
with open(name, 'wb') as p:
shutil.copyfileobj(img.raw, p)
del img
except:
img = os.path.join(path,"downloadfailure.jpg")
os.system('cp %s %s' % (img, name))
def saveImg(product_pic_url, path):
pics_path = []
len_lst = len(product_pic_url)
for pic_url in product_pic_url:
len_lst -= 1
name = os.path.join(path, pic_url.split('/')[-1])
pics_path.append(name)
if os.path.exists(name):
continue
t = Thread(target=saveImg_sub,args=(name, pic_url, path))
t.start()
return pics_path
web_static用于获取网页内容,这里用requests实现的,你可以用你熟悉的方法- 图片存储函数
saveImg根据图片的链接生成本地文件的名字和路径,然后保存到本地,为了提高效率,使用了多线程技术。页面获取和存储过程通过子线程saveImg_sub来实现 - 存储子线程里,获取页面内容,然后存储到本地,如果文件获取失败,则用一个预定义的图片代替。
- 文件的打开用
with方法,这样你不需要自己去操心文件关闭 - 文件的拷贝用
shutil.copyfileobj,有的时候也可以用write函数 os.system('cp %s %s' % (img, name))这条语句可以调用系统命令
- 文件的打开用
保存到文件
这些内容我们可以把它写道一个文件里,前面介绍过写道txt文件的方式,本节我们介绍如何写到excel里
首先安装XlsxWriter
pip install XlsxWriter
代码如下
from xlsxwriter import Workbook
def write_data_excel(data1, data2, path):
name = path.split('/')[-1]
create_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M', time.localtime(time.time()))
pure_name = '%s_%s.xlsx' % (name, create_time)
file_name = os.path.join(path , pure_name)
new_f = Workbook(file_name)
sheet1 = new_f.add_worksheet(create_time)
sheet1_format = new_f.add_format({})
sheet1_format.set_text_wrap()
sheet1.set_column(0, 0, 25)
sheet1.set_column(1, 4, 60)
for i in range(len(data1)):
if i:
sheet1.set_row(i, 125)
sheet1.insert_image(i, 0, data2[i])
for j in range(len(data1[i])):
if i == 0:
sheet1.set_row(0, 18)
headers = ['PRODUCE NAME', 'PRODUCE PRICE', 'THE LINK']
sheet1.write(0, j + 1, headers[j])
else:
try:
sheet1.write(i, (j + 1), data1[i][j], sheet1_format)
except:
pass
new_f.close()
return file_name
几个命令介绍
- 初始化命令
Workbook - 插入工作页使用命令
add_worksheet - 图片插入使用
insert_image
效果图如下
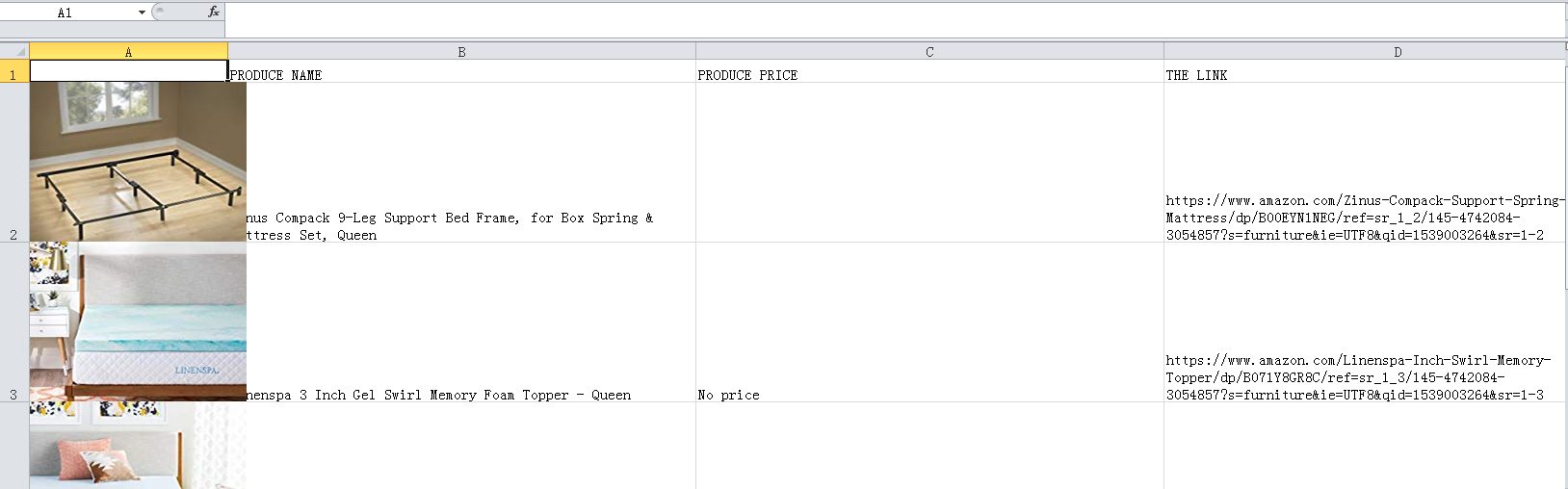
上传到百度云
最后,我们可以将生成的文件直接上传到百度云
import subprocess
subprocess.call(['bypy', 'upload', str(result_file), "/upload/to/"])
这个不是本文重点,不做详细解释,可参考文档https://github.com/houtianze/bypy