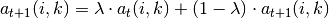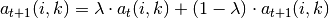1. 调用方法:
AffinityPropagation(damping=0.5, max_iter=200, convergence_iter=15, copy=True, preference=None, affinity=’euclidean’, verbose=False)
参数:
damping : float, optional, default: 0.5 防止更新过程中数值震荡
max_iter : int, optional, default: 200
convergence_iter : int, optional, default: 15
如果类簇数目在达到这么多次迭代以后仍然不变的话,就停止迭代。
copy : boolean, optional, default: True
Make a copy of input data.
preference : array-like, shape (n_samples,) or float, optional
每个points的preference。具有更大preference的点更可能被选为exemplar。类簇的数目受此值的影响,如果没有传递此参数,它们 会被设置成input similarities的中值。???
affinity : string, optional, default=``euclidean``
度量距离的方式,推荐precomputed and euclidean这两种,euclidean uses the negative squared euclidean distance between points.
verbose : boolean, optional, default: False
属性:
cluster_centers_indices_ : array, shape (n_clusters,)
类簇中心的索引
cluster_centers_ : array, shape (n_clusters, n_features)
类簇中心 (if affinity != precomputed)
labels_ : array, shape (n_samples,)
每个point的标签
affinity_matrix_ : array, shape (n_samples, n_samples)
Stores the affinity matrix used in fit.
n_iter_ : int
达到收敛需要的迭代次数。
2. scikit-learn介绍
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/clustering.html#affinity-propagation
3. 算法复杂性
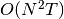 ,与样本数成正比。
,与样本数成正比。
4.算法描述
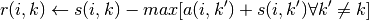
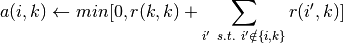
引入阻尼因子: