0x01、Spring
1什么是Spring
Spring 是一个开源框架,是为了解决企业应用程序开发复杂性而创建的(解耦)。
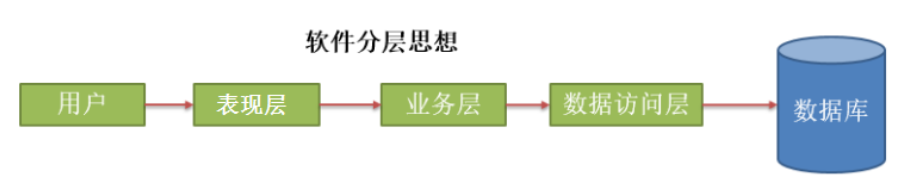
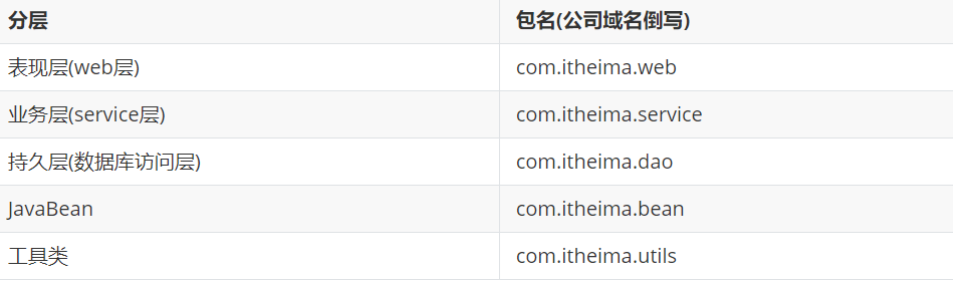
框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许您选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。
简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
一站式:Spring提供了三层解决方案.
0x02、IOC
它的核心思想就是:
1、通过Bean工厂读取配置文件使用反射创建对象。
2、把创建出来的对象都存起来,当使用者需要对象的时候,不再自己创建对象,而是调用Bean工厂的方法从容器中获取对象
这里面要解释两个问题:
第一个:存哪去?
分析:由于我们是很多对象,肯定要找个集合来存。这时候有 Map 和 List 供选择。
到底选 Map 还是 List 就看我们有没有查找需求。有查找需求,选 Map。
所以我们的答案就是:在应用加载时,创建一个 Map,用于存放三层对象。我们把这个 map 称之为容器。
第二个: 什么是工厂?
工厂就是负责给我们从容器中获取指定对象的类。这时候我们获取对象的方式发生了改变。
原来:我们在获取对象时,都是采用 new 的方式。 是主动的。
1、Spring的IOC入门案例
步骤:
1. 创建Maven工程, 添加坐标
2. 准备好接口和实现类
3. 创建spring的配置文件 (applicationContext.xml), 配置bean标签
4. 创建工厂对象 获得bean 调用
- 1.1、引入spring的依赖(使用5.0.2版本)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
-
1.2、接口和实现类
- UserServiceImpl.java
public interface UserService { String getName(); }-
UserServiceImpl.java
```java
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
public void init(){
System.out.println("UserServiceImpl对象创建了...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("UserServiceImpl对象销毁了...");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "周杰棍";
}
}
```
- 1.3、在类的根路径下创建spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
每一个实现类就对应一个bean标签
id属性: 对象的唯一标识,根据这个唯一标识,就可以从核心容器中获取对象
class属性: 对象所属的实现类的全限定名
-->
<bean class="org.example.Impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService"></bean>
</beans>
- 1.4、测试代码
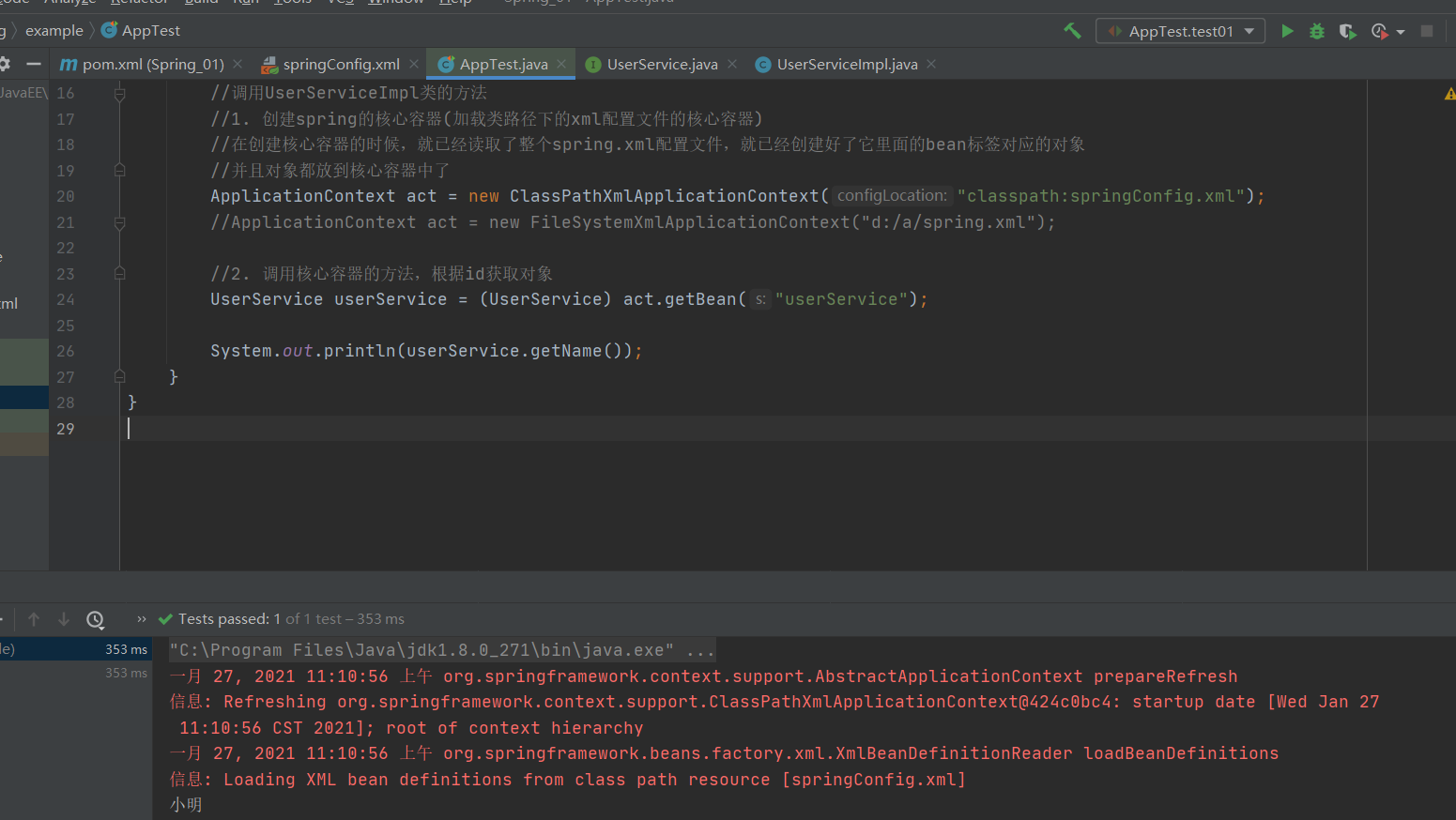
public class AppTest
{
@Test
public void test01(){
//调用UserServiceImpl类的方法
//1. 创建spring的核心容器(加载类路径下的xml配置文件的核心容器)
//在创建核心容器的时候,就已经读取了整个spring.xml配置文件,就已经创建好了它里面的bean标签对应的对象
//并且对象都放到核心容器中了
ApplicationContext act = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:springConfig.xml");
//ApplicationContext act = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("d:/a/spring.xml");
//2. 调用核心容器的方法,根据id获取对象
UserService userService = (UserService) act.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService.getName());
}
}
2、Spring配置文件下的Bean标签 配置
- 配置文件详解(Bean标签)
- bean的作用范围和生命周期
(一)、配置文件详解(Bean标签)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
每一个实现类就对应一个bean标签
id属性: 对象的唯一标识,根据这个唯一标识,就可以从核心容器中获取对象
class属性: 对象所属的实现类的全限定名
scope属性: 对象的范围
1. singleton 单例(默认)
2. prototype 多例
lazy-init: 配置懒加载,核心容器创建的时候是否创建出该类对象
init-method: 配置类的对象初始化的时候,要调用哪个方法
destroy-method: 配置这个类的对象销毁的时候,要调用哪个方法
单例模式下(默认没有开启懒加载),由核心容器进行管理的对象什么时候创建什么时候销毁?
1. 核心容器创建的时候,会创建出它所配置的所有类的对象
2. 核心容器销毁的时候,它里面的对象才会被销毁
多例模式下,由spring管理的对象什么时候创建什么时候销毁
1. 当核心容器调用getBean(id)的时候,创建对象
2. 垃圾回收机制才能销毁这个对象
-->
<bean class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
id="userService"
scope="prototype" lazy-init="false"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>
-
id或者name属性
用于标识bean , 其实id 和 name都必须具备唯一标识 ,两种用哪一种都可以。但是一定要唯一、 一般开发中使用id来声明.
-
class属性: 用来配置要实现化类的全限定名
-
scope属性: 用来描述bean的作用范围
singleton: 默认值,单例模式。spring创建bean对象时会以单例方式创建。(默认)
prototype: 多例模式。spring创建bean对象时会以多例模式创建。
request: 针对Web应用。spring创建对象时,会将此对象存储到request作用域。(不用管)
session: 针对Web应用。spring创建对象时,会将此对象存储到session作用域。(不用管)
-
init-method属性:spring为bean初始化提供的回调方法
-
destroy-method属性:spring为bean销毁时提供的回调方法. 销毁方法针对的都是单例bean , 如果想销毁bean , 可以关闭工厂
(二)、bean的作用范围和生命周期
- 单例对象: scope="singleton",一个应用只有一个对象的实例。它的作用范围就是整个引用。
- 核心容器创建的时候,会创建出它所配置的所有类的对象
- 核心容器销毁的时候,它里面的对象才会被销毁
- 多例对象: scope="prototype",每次访问对象时,都会重新创建对象实例。
- 当核心容器调用getBean(id)的时候,创建对象
- 垃圾回收机制才能销毁这个对象
3、Spring的工厂模式
ApplicationContext接口的三种实现类
1、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:它是从类的根路径下加载配置文件
2、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:它是从磁盘路径上加载配置文件,配置文件可以在磁盘的任意位置。
3、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:当我们使用注解配置容器对象时,需要使用此类来创建 spring 容器。它用来读取注解。
继承自 ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext加载方式是框架启动时就开始创建所有单例的bean,存到了容器里面
- 非懒加载: 在核心容器创建的时候,创建出所有的bean对象,存到核心容器中
- 懒加载: 第一次调用getBean()的时候,创建出bean对象,存到核心容器中
4、实例化Bean
需要实例化的类,提供无参构造方法
配置代码
<bean class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" id="userService"></bean>
0x03、依赖注入
依赖注入全称是 dependency Injection 翻译过来是依赖注入.其实就是如果我们托管的某一个类中存在属性,需要spring在创建该类实例的时候,顺便给这个对象里面的属性进行赋值。 这就是依赖注入。
现在, Bean的创建交给Spring了, 需要在xml里面进行注册
我们交给Spring创建的Bean里面可能有一些属性(字段), Spring帮我创建的同时也把Bean的一些属性(字段)给赋值, 这个赋值就是注入.
简单的来说如下:
- 注册: 把bean的创建交给Spring
- 依赖注入: bean创建的同时, bean里面可能有一些字段需要赋值, 这个赋值交给Spring, 这个过程就是依赖注入
测试代码(环境):

- Controller.UserController
import com.idea.service.UserService;
public class UserController{
private UserService userService;
public String getName(){
return userService.getName();
}
}
- service.UserService
public interface UserService {
String getName();
}
- service.Impl.UserServiceImpl
import com.idea.dao.UserDao;
import com.idea.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public String getName() {
return userDao.getName();
}
}
- dao.UserDao:
public interface UserDao {
String getName();
}
- dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl
import com.idea.dao.UserDao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
//模拟数据库执行语句,并得到名字为王五
@Override
public String getName(){
return "王五";
}
}
然后我们创建springConfig.xml的配置文件,我们需要把实现类放进来
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="UserController" class="com.idea.controller.UserController"></bean>
<bean id="UserService" class="com.idea.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="UserDao" class="com.idea.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
- 测试代码:(最外层的Controller不用解耦)
import com.idea.controller.UserController;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class demo {
@Test
public void test01(){
//创建容器
ApplicationContext act = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:springConfig.xml");
//1. 创建UserController对象
UserController userController = (UserController) act.getBean("UserController");
//2. 调用UserController对象的getName()方法
String name = userController.getName();
System.out.println("获取到的name为:" + name);
}
}
1、构造方法方式注入
通过上面的环境搭建,我们执行一下
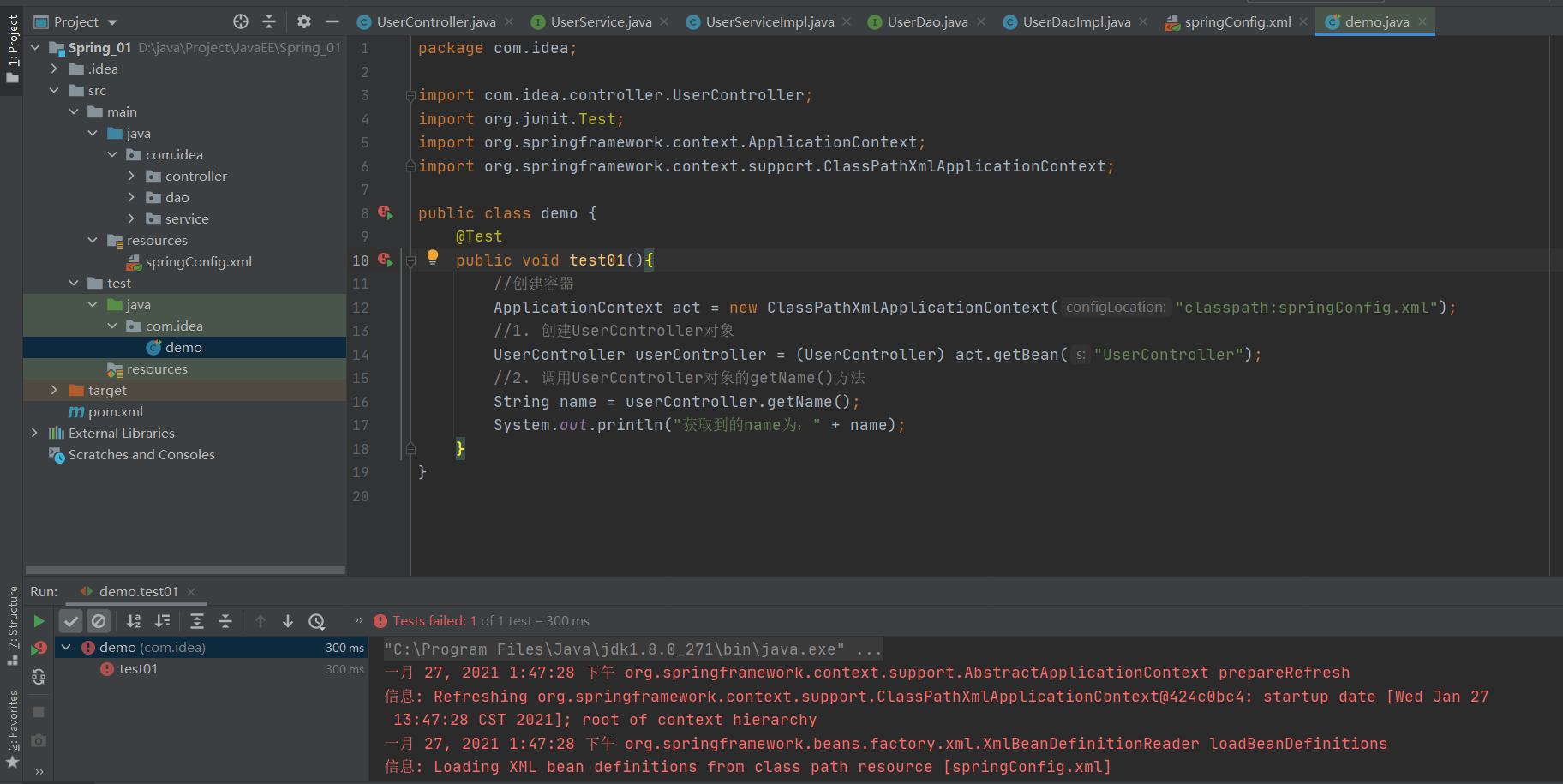
发现调用失败了;UserService和UserDao还没有赋值。但是我们不能直接在里面赋值,这样就耦合了,这时候就用到了依赖注入
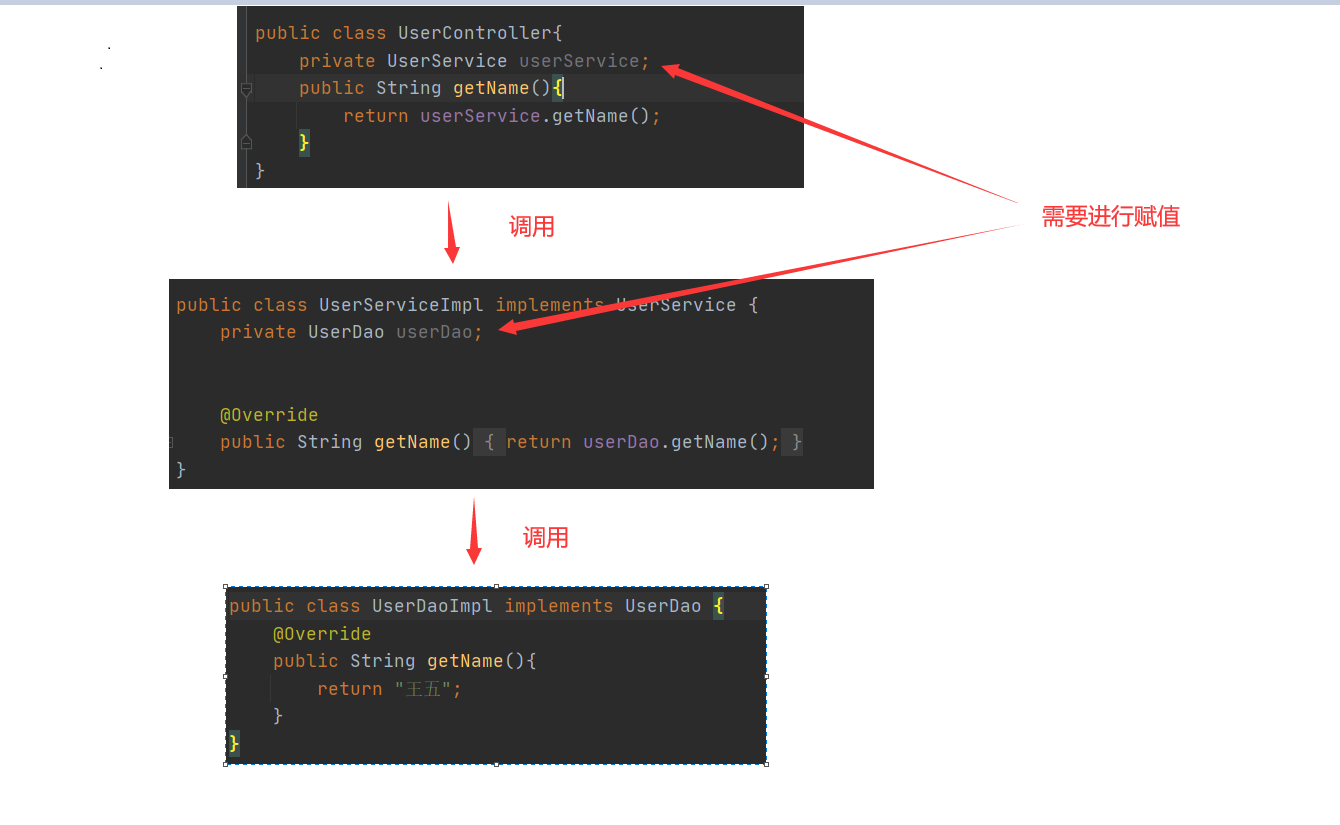
1、构造方法赋值
有参构造方法赋值的时候,就必须要有无参构造方法,不然会报错
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
它里面的UserService属性要进行赋值
使用有参构造进行属性的注入,使用<constructor-arg>标签
-->
<bean id="UserController" class="com.idea.controller.UserController">
<constructor-arg name="userService" ref="UserService"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--
它里面的UserDao属性需要赋值
-->
<bean id="UserService" class="com.idea.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="UserDao" class="com.idea.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
-
1、bean是实例化出对象,id就是对象名,
ref="UserService"就是获取UserService对象,要传进去的内容 -
2、
name="userService"是属性名,也就是要传的参数
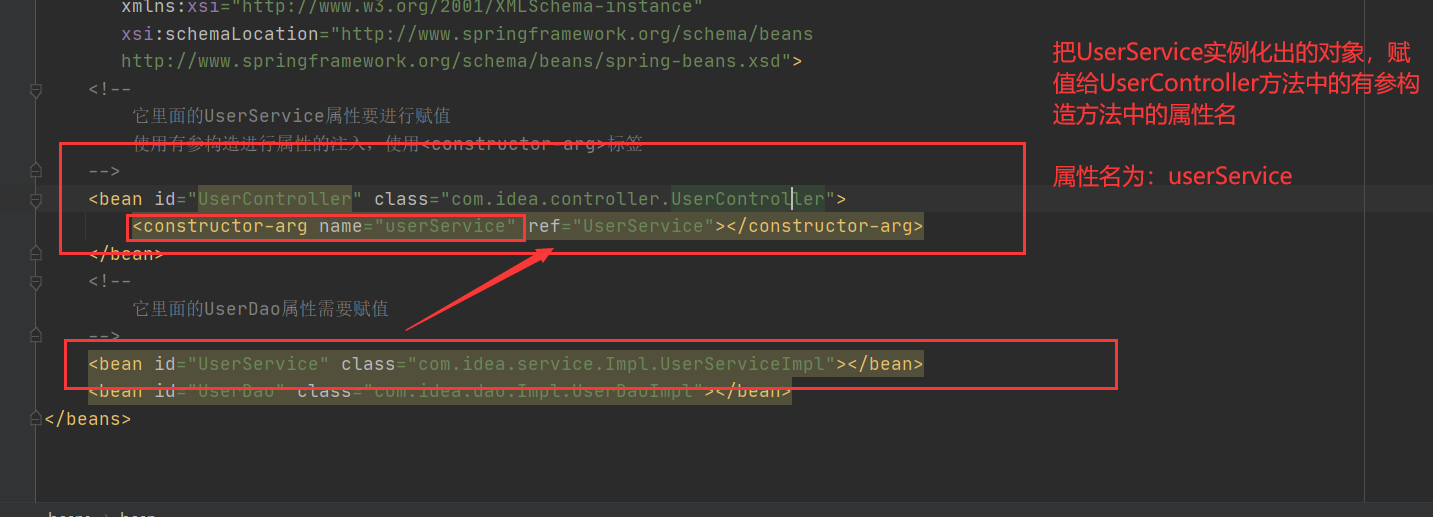
完整代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
它里面的UserService属性要进行赋值
使用有参构造进行属性的注入,使用<constructor-arg>标签
-->
<bean id="UserController" class="com.idea.controller.UserController">
<constructor-arg name="userService" ref="UserService"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--
它里面的UserDao属性需要赋值
-->
<bean id="UserService" class="com.idea.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="UserDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="UserDao" class="com.idea.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
2、set方法方式的注入
要通过set方法注入,那就得有setter
- springConfig.xml
name:就是setter设置的参数名
ref: 对象UserService赋值给name标签的userService
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
它里面的UserService属性要进行赋值
使用set方法进行属性的注入
-->
<bean id="UserController" class="com.idea.controller.UserController">
<property name="userService" ref="UserService"></property>
</bean>
<!--
它里面的UserDao属性需要赋值
-->
<bean id="UserService" class="com.idea.service.Impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="UserDao"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="UserDao" class="com.idea.dao.Impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>
- UserController
import com.idea.service.UserService;
public class UserController{
private UserService userService;
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public String getName(){
return userService.getName();
}
}
- UserServiceImpl
import com.idea.dao.UserDao;
import com.idea.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return userDao.getName();
}
}
3.2.2 注入数组类型(了解一下)
-
java代码
package com.itheima.dao.impl; import com.itheima.dao.UserDao; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Map; /** * 包名:com.itheima.dao.impl * * @author Leevi * 日期2020-08-09 12:05 */ public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ private String[] stringArray; public void setStringArray(String[] stringArray) { this.stringArray = stringArray; } @Override public String getName() { System.out.println("数组stringArray:" + Arrays.toString(stringArray)); //模拟调用数据库方法获取name return "奥巴马"; } } -
配置文件
<bean id="userDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"> <!--注入数组--> <property name="stringArray"> <array> <value>hello1</value> <value>hello2</value> <value>hello3</value> <value>hello4</value> </array> </property> </bean>
3.2.3 注入Map类型(了解)
-
Java代码
package com.itheima.dao.impl; import com.itheima.dao.UserDao; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Map; /** * 包名:com.itheima.dao.impl * * @author Leevi * 日期2020-08-09 12:05 */ public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ private Map map; public void setMap(Map map) { this.map = map; } @Override public String getName() { System.out.println("map的值为:" + map); //模拟调用数据库方法获取name return "奥巴马"; } } -
配置文件
<bean id="userDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl""> <!--注入map--> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="username" value="aobama"></entry> <entry key="pwd" value="123456"></entry> <entry key="address" value="召唤师峡谷"></entry> </map> </property> </bean>
3.2.4 注入简单类型数据(掌握)
- Java代码
package com.itheima.dao.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.UserDao;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 包名:com.itheima.dao.impl
*
* @author Leevi
* 日期2020-08-09 12:05
*/
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
private String username;
private Integer age;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
System.out.println("年龄是:" + age);
//模拟调用数据库方法获取name
return username;
}
}
-
配置文件
<!-- 它里面的userDao属性要进行赋值 --> <bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" p:userDao-ref="userDao"> <!--构造函数方式注入--> <!--<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>--> <!--set方法注入--> <!--<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property>--> </bean> <bean id="userDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"> <!--set方法注入--> <property name="age" value="28"></property> <property name="username" value="奥巴马"></property> </bean>
0x04、番外&总结
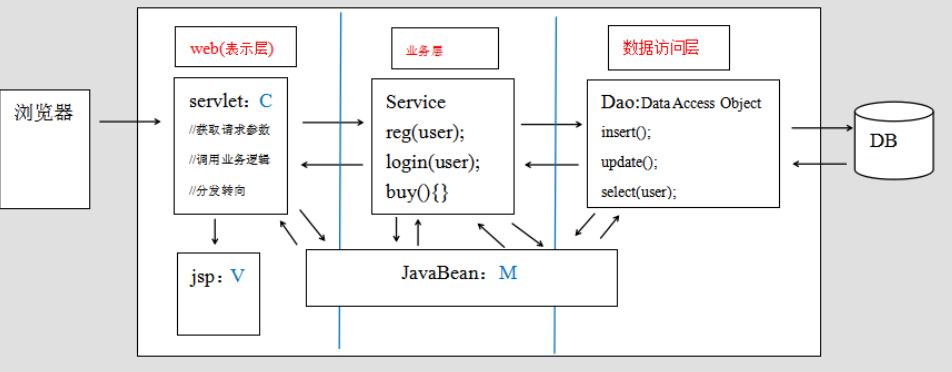
今天内容有IOC,和依赖注入
1、IOC是什么?
IOC就是spring.xml中bean标签:让我们不用去new对象,让spring实例化对象,进行解耦