在windows下,一个文件有:创建时间、修改时间、访问时间。
在Linux下,一个文件有:状态改动时间、修改时间、访问时间。
1)查看文件(或文件夹)的三种时间标记 (stat 命令)

Access 访问时间(access time) atime
Modify 修改时间(modifytime) mtime
Change 状态改动时间(change time) ctime
ls -lc filename # 列出文件的ctime ls -lu filename # 列出文件的atime ls -l filename # 列出文件的mtime
2)3种时间标记的含义
访问时间:读一次文件的内容,atime就会更新
修改时间:文件内容做后一次被修改的时间
状态改动时间:文件的i节点最后一次被修改的时间,通过chmod、chown修改文件属性时,ctime会更新
3)修改文件的时间
使用 touch 命令对文件的时间进行修改
修改文件的访问时间 atime
touch -a -d "指定时间" 文件名
修改文件的修改时间 mtime
touch -m -d "指定时间" 文件名
修改文件的状态改动时间 ctime
一起修改文件的访问时间和修改时间
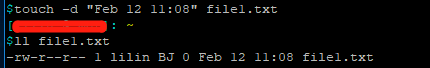
touch -d "指定时间" 文件名 # -d date 的意思 touch --date="指定时间" 文件名
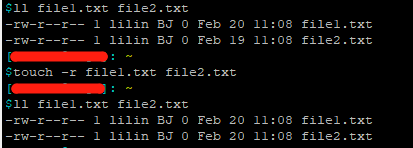
将 文件2 的时间设置为 文件1 的时间
touch -r 文件1 文件2 # -r reference 的意思 touch --reference=file1.txt file2.txt
将文件的时间设置为当前时间
touch file

遍历修改时间戳
for i in `ls fastq_*.fastq`; do num=`echo $i | awk 'BEGIN{FS="_"}{print $NF}' | awk 'BEGIN{FS="."}{print $1}'`; time=`head -n 1 $i | awk '{print $5}' | awk 'BEGIN{FS="="}{print $NF}'` ; touch -d "$time" $i; touch -d "$time" sequencing_summary_$num.txt; done 遍历fastq文件 从fastq的文件命中获取文件编号 从fastq文件的第一行中获取时间 将文件的时间戳修改为从文件中获取的时间