参考文献:极客时间傅健老师的《Netty源码剖析与实战》Talk is cheap.show me the code!
三种I/O模式
BIO:Block I/O,即同步并阻塞的IO;BIO就是传统的java.io包下的代码实现
NIO:New IO(non-blocking IO):同步非阻塞的IO,jdk1.4及以上版本提供
AIO:Async IO: 异步非阻塞IO,jdk1.7
阻塞和非阻塞
阻塞:没有数据传输过来时,读会阻塞直到有数据;缓冲区满时,写操作也会阻塞。
非阻塞: 非阻塞遇到这些情况都是直接返回。
同步和异步
同步:数据就绪后需要自己去读是同步。
异步:数据就绪后直接读好再回调给程序是异步。
Netty对三种IO的支持
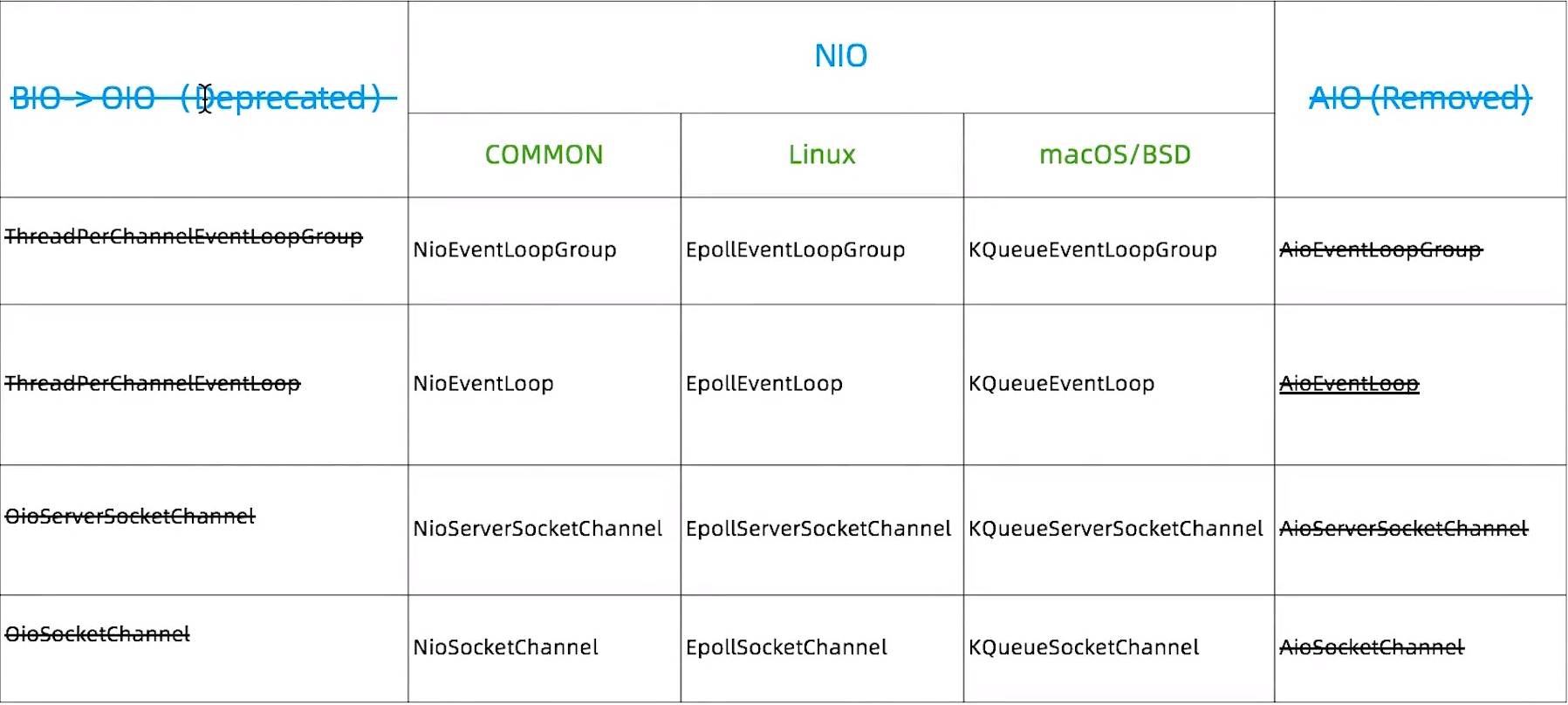
首先Netty是都支持三种IO模式的,准确的来说是曾经都支持过,因为BIO的被Netty给过期了,AIO被Netty给删除了,具体原因这就不多赘述;知道BIO在Netty被称为OIO,NIO在多平台下都有对应的支持,有人会问为啥有common的支持了还有Linux等其他的意义吗,这好比全栈和后端前端之分一样,一个通用一个专用的区别。
Netty切换IO模式
如上图所示,对应的实现类都差不多,甚至可以看出都是头不一样,如果NIO的通用是NioEventLoopGroup,而OIO的实现则是OioEventLoopGroup,先看之前的一个demo
public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap sb = new ServerBootstrap(); sb.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)); p.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture f = sb.bind(8090).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
图上标粗的就是切换的模式的关键点。现在看看切换成OIO的代码
public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new OioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new OioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap sb = new ServerBootstrap(); sb.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(OioServerSocketChannel.class) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)); p.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture f = sb.bind(8090).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
上面代码改动也就是标粗的那些。运行起来是完全没问题的。
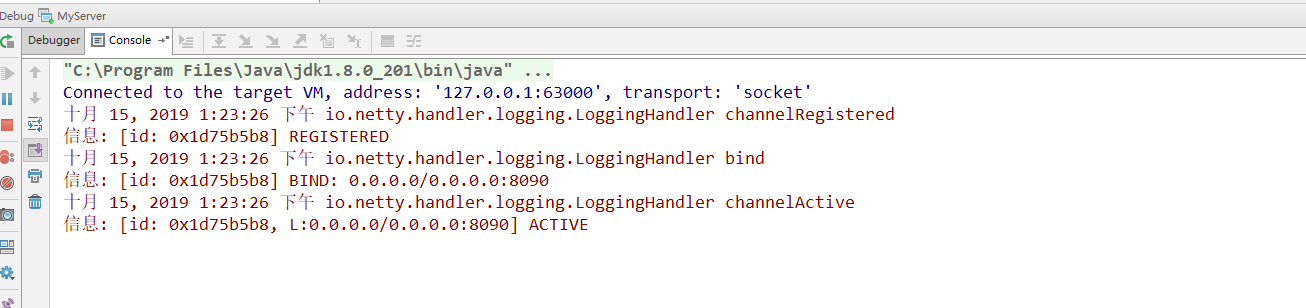
那么具体是怎么做的呢,我们看看源码就知道了;
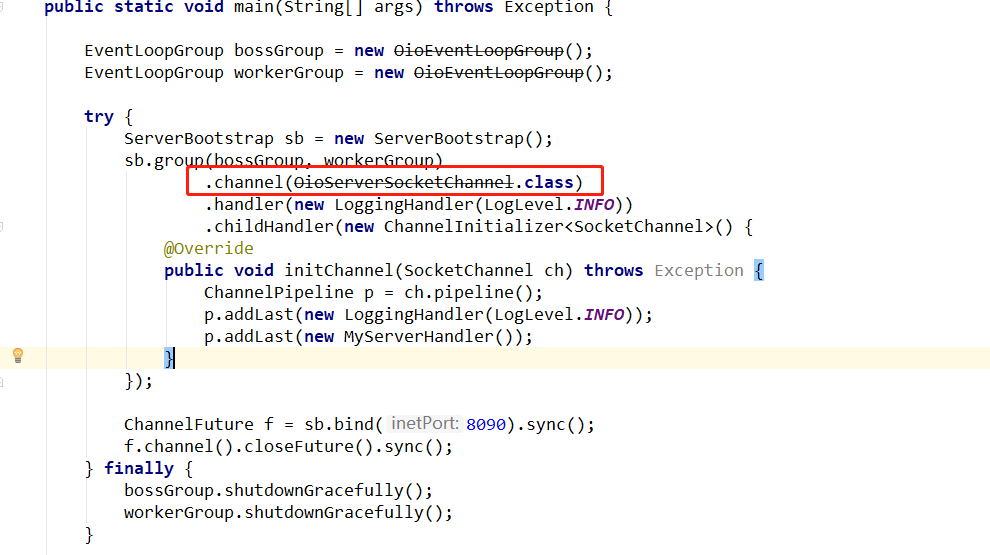
点进channel()方法里,核心步骤在此:
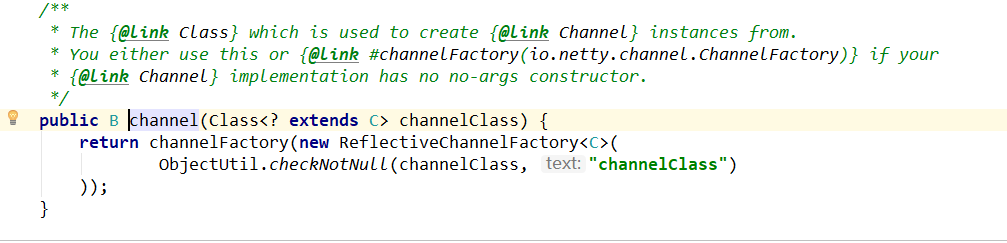
不难发现传入的是OioServerSocketChannel.class,由channelFactory工厂创建返回,进入ReflectiveChannelFactory();
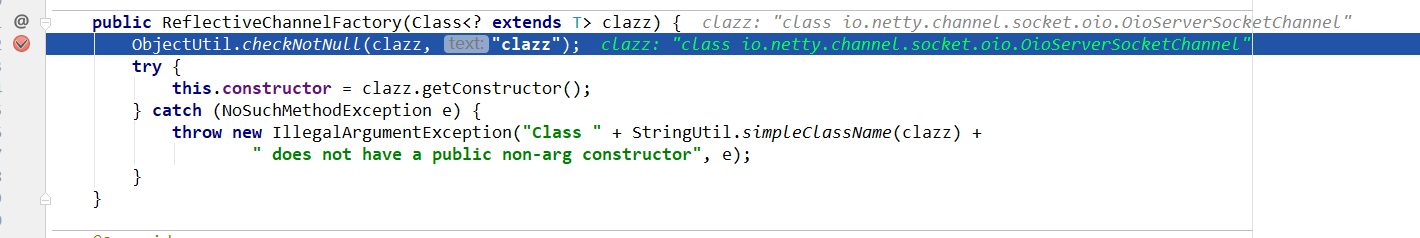
上图的代码中有“this.constructor = clazz.getConstructor();”获取无参构造;
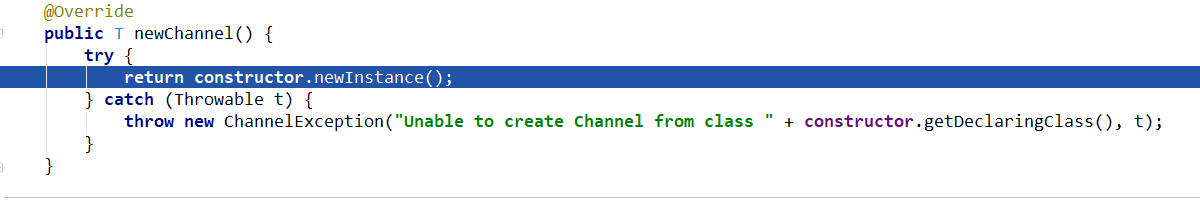
可以看出“return constructor.newInstance();”返回泛型“T” 就是要使用的IO模式。
总结来说:Netty实现IO模式的切换就是泛型+反射+工厂实现的。
除此之外,还有一点,"EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();";实际上,它就相当于一个死循环,在“NioEventLoop.java”中,有个run(),如下图源码,可以看出它是个死循环(for (;;) {}),现在可以简单的理解它就是循环监听、处理事件的。
@Override protected void run() { for (;;) { try { try { switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) { case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE: continue; case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT: // fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIO case SelectStrategy.SELECT: select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); // 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' is always evaluated // before calling 'selector.wakeup()' to reduce the wake-up // overhead. (Selector.wakeup() is an expensive operation.) // // However, there is a race condition in this approach. // The race condition is triggered when 'wakenUp' is set to // true too early. // // 'wakenUp' is set to true too early if: // 1) Selector is waken up between 'wakenUp.set(false)' and // 'selector.select(...)'. (BAD) // 2) Selector is waken up between 'selector.select(...)' and // 'if (wakenUp.get()) { ... }'. (OK) // // In the first case, 'wakenUp' is set to true and the // following 'selector.select(...)' will wake up immediately. // Until 'wakenUp' is set to false again in the next round, // 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' will fail, and therefore // any attempt to wake up the Selector will fail, too, causing // the following 'selector.select(...)' call to block // unnecessarily. // // To fix this problem, we wake up the selector again if wakenUp // is true immediately after selector.select(...). // It is inefficient in that it wakes up the selector for both // the first case (BAD - wake-up required) and the second case // (OK - no wake-up required). if (wakenUp.get()) { selector.wakeup(); } // fall through default: } } catch (IOException e) { // If we receive an IOException here its because the Selector is messed up. Let's rebuild // the selector and retry. https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566 rebuildSelector0(); handleLoopException(e); continue; } cancelledKeys = 0; needsToSelectAgain = false; final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio; if (ioRatio == 100) { try { processSelectedKeys(); } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. runAllTasks(); } } else { final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); try { processSelectedKeys(); } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime; runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); } } } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } // Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception. try { if (isShuttingDown()) { closeAll(); if (confirmShutdown()) { return; } } } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } } }
我只想做的更好,仅此而已