一、函数基础
1、函数/方法:
非常抽象
独立完成某项功能的一个个体
2、函数的作用:
提高代码的重用性
提高功能开发的效率
提高程序代码的可维护性
3、分类
固定功能函数
高度抽象函数
4、函数四要素:
输入,输出,函数体,函数名。(函数体、函数名必须有,输入、输出不是必须有的!)
5、格式
public static 返回值类型 函数名(输入值类型参数,第二个,第三个,int a,string b)
{
return 上面的返回值类型
}
注:函数也是放在Main函数之外,在Class之内。花括号之内的为函数体。
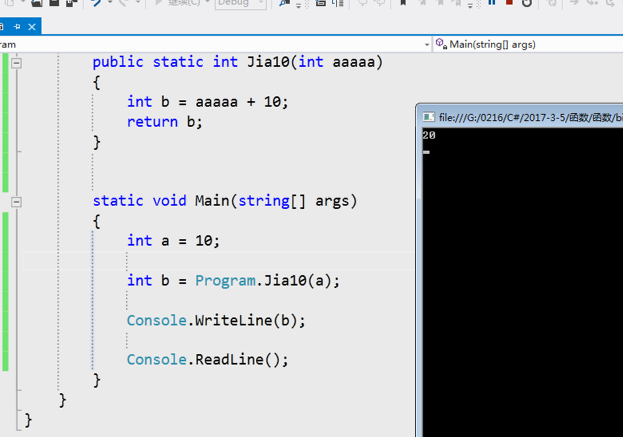

6、函数基础练习题
(1)
定义一个函数,需要用户输入一个姓名
输出 “xxx,你好啊!”
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 练习1 { class Program { public static string 你好(string a) { string b = a + "你好啊"; return b; } static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入您的姓名:"); string a = Console.ReadLine(); string c = Program.你好(a); Console.Write(c); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
(2)
定义一个函数,需要用户输入两个姓名
输出“xxx和xxx你们的缘分指数是(1-100),散了吧/缘分不错!”
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 练习2 { class Program { public static string yf(string a, string b) { Random r = new Random(); int c= r.Next(1, 101); string d; if (c < 50) d = a + "和" + b + "你们的缘分指数是" + c + ",不合适,散了吧!"; else d = a + "和" + b + "你们的缘分指数是" + c + ",凑合过吧!"; return d; } static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入第一个姓名:"); string a = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("请输入第二个姓名:"); string b = Console.ReadLine(); string d = Program.yf(a,b); Console.Write(d); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
(3)
定义一个函数,计算乘除,需要用户输入两个数和一个运算符
按照输入的运算符,对两个数进行相对的运算,输出结果
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 练习3 { class Program { public static double 计算(int a, int b, string c) { int d = 0; if (c == "*") d = a * b; else if (c == "/") d = a / b; return d; } static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入第一个数:"); int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); Console.Write("请输入第二个数:"); int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); Console.Write("请输入运算符*或/:"); string c = Console.ReadLine(); double d = Program.计算(a, b, c); Console.Write(d); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
(4)
猜拳方法
定义一个猜拳方法,返回比试结果,需要输入两个手势
手势可以是0 1 2
输出结果:“选手1的手势是石头,选手2的手势是包袱,选手2获胜!”
“手势有误!”
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace 练习4 { class Program { public static string 猜拳(int a, int b) { //0-剪刀,1-石头,2-布 string c = ""; string d = ""; string e = ""; if (a >= 0 && a <= 2 && b >= 0 && b <= 2) { if (a == 0) c = "剪刀"; else if (a == 1) c = "石头"; else if (a == 2) c = "布"; if (b == 0) d = "剪刀"; else if (b == 1) d = "石头"; else if (b == 2) d = "布"; if ((a - b == 1) || (a - b == -2)) e = "选手1的手势是" + c + "选手二的手势是" + d + "选手一获胜!"; else if ((b - 1 == 1) || (b - a == -2)) e = "选手1的手势是" + c + "选手二的手势是" + d + "选手二获胜!"; } else e = "输入有误!"; return e; } static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入第一个手势(0、1、2):"); int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); Console.Write("请输入第二个手势(0、1、2):"); int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); string f = Program.猜拳(a, b); Console.Write(f); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
函数的多种形态:
1、有参数,有返回值(上文的例子)
2、无参数,无返回值

3、有参数,无返回值

4、无参数,有返回值
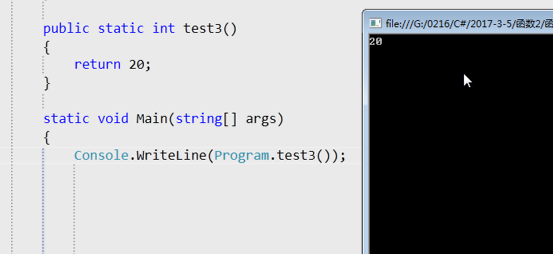
函数返回多个值的办法:
ref - 可出可进 ref 调用外部变量

out - 只出不进

递归:
递进去,归还回来的一个过程
使用的方法:
函数调用它本身
函数一遇到return就会立即停止后面代码的执行,跳出函数,执行调用本身后面归还的代码。
