6629 string matching
题意:给定一个字符串s,求s与自身所有前缀暴力匹配所需匹配次数
分析:每个前缀匹配次数即自身长度,exkmp的next数组记录的就是与自身最大匹配前缀的长度,加一遍就行,注意边界
代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<vector> #define fi first #define se second #define rep( i ,x ,y ) for( int i= x; i<= y ;i++ ) #define reb( i ,y ,x ) for( int i= y; i>= x ;i-- ) #define mem( a ,x ) memset( a ,x ,sizeof(a)) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int ,int> pii; typedef pair<ll ,ll> pll; typedef pair<string ,int> psi; char s[1005000]; int nxt[1005000]; void getnext( int l){ int a=0 ,p=0; nxt[0]=l; for( int i=1 ;i<l ;i++){ if( i>=p || i+nxt[i-a] >=p){ if( i>=p)p=i; while( p<l && s[p] == s[p-i])p++; nxt[i] = p-i; a=i; }else nxt[i] = nxt[i-a]; } } int main( ){ int t; scanf("%d" ,&t); while( t--){ scanf("%s" ,s); mem( nxt ,0 ); int l =strlen(s); getnext( l ); ll sum = 0; rep( i ,1 ,l-1 ){ if(nxt[i])sum+=min( l-1-i,nxt[i]); } printf("%lld " ,sum+l-1); } return 0; }
6630 permutation 2
题意:给定n,x,y,p[1~n]是1到n的一个全排列,求满足下列条件的全排列的个数:
分析:
1.转化成相似问题:有1~n的格子,每次可往左或右跳1或2步,起点为x,终点为y,求x到y走遍所有格子有几种走法
2.手动模拟一下就会注意到 x --> 1 -->x+1 和 y-1 --> n --> y 这两段路径走法是固定的,所以转化为x+1到y-1走遍其之间的格子有几种走法
在手动模拟一下,要想不遗漏又不至于无路可走,一次只能前进1或前进3,然后dp即可
3.dls直播中说他是直接打表找规律的,也许打表找规律比思维更快些
代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<vector> #define fi first #define se second #define rep( i ,x ,y ) for( int i= x; i<= y ;i++ ) #define reb( i ,y ,x ) for( int i= y; i>= x ;i-- ) #define mem( a ,x ) memset( a ,x ,sizeof(a)) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int ,int> pii; typedef pair<ll ,ll> pll; typedef pair<string ,int> psi; const int N = 100005; const ll mod = 998244353; int n ,x ,y ,t; ll dp[100050]; int main( ){ dp[1] = 1; dp[2] = 1; dp[3] = 1; rep( i ,4 ,N)dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-3])%mod; scanf("%d" ,&t); while( t-- ){ scanf("%d%d%d" ,&n ,&x ,&y); if( x>y )swap(x ,y); int k = y-x -1; if( x==1 )k++; if( y==n )k++; printf("%lld " ,dp[k]); } return 0; }
6628 permutation 1
题意:给定n,k,求1~n的全排列p[1~n]中,p[2]-p[1] ,p[3]-p[2] ,p[4]-p[3] ...... 的字典序第k小的全排列 ,其中n<=20 ,k<=10000
分析:
1.打表发现 ,当第一位是n时,后面1~n-1的全排列字典序和p[2]-p[1] ,p[3]-p[2] ,p[4]-p[3]的字典序是一样的,直接next_permutation枚举就行
当第一位变化时,规律就不明显了
2. 因为8! > 10000 ,所以n > 8 时 ,只管后面8位就行,而不管n是多少,对于相同k而言这8位的相对顺序是固定的,结合1直接预处理下1~8全排列的字典序就行
3.当n<8时,直接根据题意的判断条件sort一下1~n的所有全排列输出第k个即可
比赛时不会重载数组的比较运算符没写出来,要注意一下这个重载方式
暴力代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct P{ int a[10] ,b[10]; int l; bool operator < ( const P & s )const{ for( int i = 2 ;i<=l ;i++ ){ if( b[i] < s.b[i] )return 1; if( b[i] > s.b[i] )return 0; } return 0; } }p[50000]; int T ,k ,n; int p_pre[50000][10]; int main( ){ int a[25]; for( int i=1 ;i<=8 ;i++ ){ a[i] = i; } int cnt = 0; do{ cnt++; for( int i=1 ;i<=8 ;i++) p_pre[cnt][i] = a[i]; }while( next_permutation( a+1 ,a+9 ) ); scanf("%d" ,&T); while( T-- ){ scanf( "%d%d" ,&n ,&k ); if( n <=8 ){ for( int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++ )a[i] = i; cnt = 0; do{ cnt++; for( int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++){ p[cnt].l = n; p[cnt].a[i] = a[i]; p[cnt].b[i] = a[i]-a[i-1]; } }while( next_permutation( a+1 ,a+1+n )); sort( p+1 ,p+cnt+1 ); for( int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++ ){ if( i>1 )printf(" "); printf("%d" ,p[k].a[i] ); } } else{ a[1] = n; for( int i=2 ; i<=n-8 ;i++ ){ a[i] = i-1; } for( int i=n-8+1 ;i<=n ;i++ ){ a[i] = p_pre[k][i-n+8]+n-8-1; cout<<i<<" "<<a[i]<<endl; } for( int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++ ){ if( i>1 )printf(" "); printf("%d" ,a[i]); } } printf(" "); } return 0; }
但是这不是标准题解,由于next_permutation一次平均复杂度是O(n),所以n<8时时间复杂度是O(n!n*nlogn) ,这复杂度十分爆炸,只要k的范围扩大就100%会tle
标准题解是dfs构造第k小排列,复杂度是 O(kn^2) ,不是很懂 ,先码为敬
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define fi first #define se second #define mp make_pair #define pb push_back using namespace std; LL gcd(LL a,LL b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;} LL lcm(LL a,LL b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;} LL powmod(LL a,LL b,LL MOD){LL ans=1;while(b){if(b%2)ans=ans*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;b/=2;}return ans;} const int N = 503; int t,n,k; int vis[N],p[N]; bool dfs(int now,int pre,int l,int r){ if(now==n){ if(k==1){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cout<<p[i]-l+1; if(i<n-1)cout<<' '; else cout<<' '; } return 1; } k--; return 0; } for(int i=1-n;i<=n-1;i++){//枚举差异序列字典序最小 if(!vis[i+pre]){ vis[i+pre]=1; if(max(i+pre,r)-min(l,i+pre)<=n-1){ p[now]=i+pre; if(dfs(now+1,i+pre,min(i+pre,l),max(i+pre,r))){ vis[i+pre]=0; return 1; } } vis[i+pre]=0; } } return 0; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); for(cin>>t;t;t--){ cin>>n>>k;int sta=0; vis[n]=1; p[0]=n; dfs(1,n,n,n);//相对大小 vis[n]=0; } return 0; }
6627 equation
题意:给定数组a,b,解方程 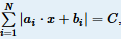
分析: 出现绝对值符号先去绝对值符号,发现分界点是x与 -bi/ai 的大小关系 ,对1~n个区间分类讨论即可 ,注意无数个解的情况
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define fi first #define se second #define rep( i ,x ,y ) for( int i= x; i<= y ;i++ ) #define reb( i ,y ,x ) for( int i= y; i>= x ;i-- ) #define mem( a ,x ) memset( a ,x ,sizeof(a)) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int ,int> pii; typedef pair<ll ,ll> pll; typedef pair<string ,int> psi; struct node{ ll a ,b; bool operator < (const node & s )const{ return b*s.a > a*s.b; } }p[100050]; ll sa[100050] ,sb[100050]; ll ansa[100050] ,ansb[100050]; ll t ,n ,c; int main( ){ scanf("%lld" ,&t ); while( t-- ){ scanf("%lld%lld" ,&n ,&c ); mem( sa ,0 ); mem( sb ,0 ); rep( i ,1 ,n ){ scanf("%lld%lld" ,&p[i].a ,&p[i].b); sa[i] = sa[i-1] + p[i].a; sb[i] = sb[i-1] + p[i].b; } sort( p+1 , p+1+n ); p[n+1].a = p[n+1].b = 0; int cnt = 0; ll xa ,xb ,g; reb( i ,n ,0 ){ xa = c-sb[n]; xb = sa[n]; //cout<<" now "<<p[i].a<<" "<<p[i].b<<endl; if( xb <0 )xa*=-1 ,xb*=-1; //cout<<sa[n]<<" "<<sb[n]<<endl; // cout<<"xa xb "<<xa<<" "<<xb<<endl; if( xa*p[i].a + xb*p[i].b >=0 && xa*p[i+1].a + xb*p[i+1].b <= 0 ){ if( xb !=0 ){ g = __gcd(abs(xa) ,abs(xb)); //cout<<g<<endl; ansa[++cnt] = xa/g; ansb[cnt] = xb/g; if( ansa[cnt] == ansa[cnt-1] && ansb[cnt] == ansb[cnt-1] )cnt--; } else if( xa == 0 ){ cnt = -1; break; } } sa[n] -= 2*p[i].a; sb[n] -= 2*p[i].b; } printf("%d" ,cnt); reb( i ,cnt ,1 )printf(" %lld/%lld" ,ansa[i] ,ansb[i] ); printf(" "); } return 0; }
|pi−pi+1|≤2
6625 three arrays
题意: 给定数组a,b,构造出ci = ai^bi 使得c数组字典序最小
分析:
1.将a,b各项以01串的形式存在字典树上
2.在字典树a,b上每次以尽量走相同的数字进行贪心,所得结果取异或就是c中结果,这里是用循环实现,用递归也可以
3.为什么这样贪心是可行的?
考虑:
1). a1与b中异或最小的配对项是b1,b1与b中异或最小的配对项是a1,则贪心的走肯定能在一次判断中同时确定a,b,取其异或值最优
2). a1与b中异或最小的配对项是b1,b1与b中异或最小的配对项是c1,则 a1^b1 == a1^c1(否则a1的最优匹配就是c1了),因为b1的最优匹配不是a1,所以b1^c1 < b1^a1 ,因为题目是求字典序最小,贪心的规则是靠前的尽量小,不考虑其他的东西,所以 取b1^c1更优,而b1^c1会在贪心过程中先被找到,所以这个贪心过程也是最优的
所以贪心的找的c1一定是字典序最小的
4.这个代码起初因为每次都memeset()字典树所以tle,只要delete()函数保证每次都将树上所有都清除干净了,就不用再mem()了。或者delete()每次最后只将父节点清除干净保证不会再进入其子树节点,然后下一次测试时在insert()时完成对子树节点的初始化也可以
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define fi first #define se second #define rep( i ,x ,y ) for( int i= x; i<= y ;i++ ) #define reb( i ,y ,x ) for( int i= y; i>= x ;i-- ) #define mem( a ,x ) memset( a ,x ,sizeof(a)) using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int ,int> pii; typedef pair<ll ,ll> pll; typedef pair<string ,int> psi; const int maxn = 100005; int cnt[2]; int trie[2][maxn*31][2] ; int sum[2][maxn*31][2] ; int t ,n ,ans[maxn]; inline void Insert(int id ,int x){ int root = 0 ,tmp; reb( i ,30 ,0 ){ tmp = (x>>i) & 1; if( !trie[id][root][tmp] )trie[id][root][tmp] = ++cnt[id]; sum[id][root][tmp] ++; root = trie[id][root][tmp]; } } inline void Delete(int id ,int x ){ int root = 0 ,tmp ,tot; reb( i ,30 ,0 ){ tmp = (x>>i) & 1; sum[id][root][tmp] --; if( !sum[id][root][tmp] ){ tot = root; root = trie[id][root][tmp]; trie[id][tot][tmp] = 0; } else root = trie[id][root][tmp]; if( !root )break; } } inline void init( ){ //mem( trie , 0 ); cnt[0] = cnt[1] = 0; } inline int Find( int x ,int y ){ x = y = 0; int root_a =0 , root_b = 0; reb( i ,30 ,0 ){
//这个贪心的顺序是关键 if( sum[0][root_a][0] && sum[1][root_b][0] ){ root_a = trie[0][root_a][0]; root_b = trie[1][root_b][0]; continue; } if( sum[0][root_a][1] && sum[1][root_b][1] ){ root_a = trie[0][root_a][1]; root_b = trie[1][root_b][1]; x |= (1<<i); y |= (1<<i); continue; } if( sum[0][root_a][0] && sum[1][root_b][1] ){ root_a = trie[0][root_a][0]; root_b = trie[1][root_b][1]; y |= (1<<i); continue; } if( sum[0][root_a][1] && sum[1][root_b][0] ){ root_a = trie[0][root_a][1]; root_b = trie[1][root_b][0]; x |= (1<<i); continue; } } //cout<<x<<" "<<y<<endl; Delete( 0 ,x ); Delete( 1 ,y ); return x^y; } int main( ){ //freopen( "out.txt" ,"w" ,stdout ); scanf("%d" ,&t ); while( t-- ){ scanf("%d" ,&n ); int now; init( ); rep( i ,1 ,n ){ scanf("%d" ,&now ); Insert(0 ,now ); } rep( i ,1 ,n ){ scanf("%d" ,&now ); Insert(1 ,now ); } rep( i ,1 ,n ){ ans[i] = Find( 0 ,0 ); } sort( ans+1 ,ans+1+n ); rep( i ,1 ,n ){ if(i!=1)printf(" "); printf("%d" ,ans[i]); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
官方题解也是贪心,先找配对再建图,由于上述3中贪心证明的2)也说明这个匹配的关系是偏序关系,所以建的图中不会有长度大于2的环,每次选个点将以其为起点路径上的点按顺序加入栈中,再两两消去即可。
但我觉得他说的出栈入栈操作方案中好像没提到下面这种情况怎么操作,从a1开始的话栈中有残留的点a1,栈不为空,a1也没有可匹配的点,就卡在这里了:
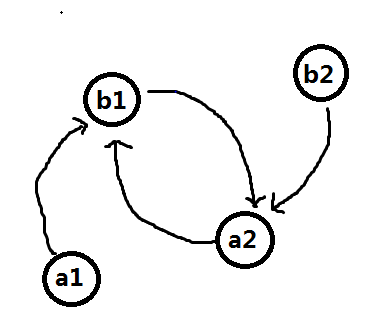
所以我觉得他的操作应该是 栈中残留有一个点或栈为空,都任意塞一个点进去,但这样好像不能保证残留点之间的配对最优?
可能是我理解错了,不懂,两种贪心的复杂度用该是一样的, 因为贪心的思路都一样
题解:
