通常ESP8266的闪存文件系统大小是4Mb,其中有1Mb的空间是程序存储大小,剩下的3Mb是文件存储,但是其中有一部分是存储系统文件的,所以用户可用的文件存储空间是小于3Mb的。
更多信息详见https://arduino-esp8266.readthedocs.io/en/latest/filesystem.html
所使用的FS.h
/*FS.h - file system wrapper
Copyright (c) 2015 Ivan Grokhotkov. All rights reserved.
This file is part of the esp8266 core for Arduino environment.
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
#ifndef FS_H
#define FS_H
#include <memory>
#include <Arduino.h>
namespace fs {
class File;
class Dir;
class FileImpl;
typedef std::shared_ptr<FileImpl> FileImplPtr;
class FSImpl;
typedef std::shared_ptr<FSImpl> FSImplPtr;
class DirImpl;
typedef std::shared_ptr<DirImpl> DirImplPtr;
template <typename Tfs>
bool mount(Tfs& fs, const char* mountPoint);
enum SeekMode {
SeekSet = 0,
SeekCur = 1,
SeekEnd = 2
};
class File : public Stream
{
public:
File(FileImplPtr p = FileImplPtr()) : _p(p) {}
// Print methods:
size_t write(uint8_t) override;
size_t write(const uint8_t *buf, size_t size) override;
// Stream methods:
int available() override;
int read() override;
int peek() override;
void flush() override;
size_t readBytes(char *buffer, size_t length) override {
return read((uint8_t*)buffer, length);
}
size_t read(uint8_t* buf, size_t size);
bool seek(uint32_t pos, SeekMode mode);
bool seek(uint32_t pos) {
return seek(pos, SeekSet);
}
size_t position() const;
size_t size() const;
void close();
operator bool() const;
const char* name() const;
String readString() override;
protected:
FileImplPtr _p;
};
class Dir {
public:
Dir(DirImplPtr impl = DirImplPtr()): _impl(impl) { }
File openFile(const char* mode);
String fileName();
size_t fileSize();
bool next();
protected:
DirImplPtr _impl;
};
struct FSInfo {
size_t totalBytes;
size_t usedBytes;
size_t blockSize;
size_t pageSize;
size_t maxOpenFiles;
size_t maxPathLength;
};
class FS
{
public:
FS(FSImplPtr impl) : _impl(impl) { }
bool begin();
void end();
bool format();
bool info(FSInfo& info);
File open(const char* path, const char* mode);
File open(const String& path, const char* mode);
bool exists(const char* path);
bool exists(const String& path);
Dir openDir(const char* path);
Dir openDir(const String& path);
bool remove(const char* path);
bool remove(const String& path);
bool rename(const char* pathFrom, const char* pathTo);
bool rename(const String& pathFrom, const String& pathTo);
protected:
FSImplPtr _impl;
};
} // namespace fs
#ifndef FS_NO_GLOBALS
using fs::FS;
using fs::File;
using fs::Dir;
using fs::SeekMode;
using fs::SeekSet;
using fs::SeekCur;
using fs::SeekEnd;
using fs::FSInfo;
#endif //FS_NO_GLOBALS
#if !defined(NO_GLOBAL_INSTANCES) && !defined(NO_GLOBAL_SPIFFS)
extern fs::FS SPIFFS;
#endif
#endif //FS_H
一、通过程序向闪存文件系统写入信息
需要注意的是,在使用闪存文件系统的时候,在工具--Flash Size----4M(1M SPIFFS)不可以选择(no SPIFFS)的,如图1
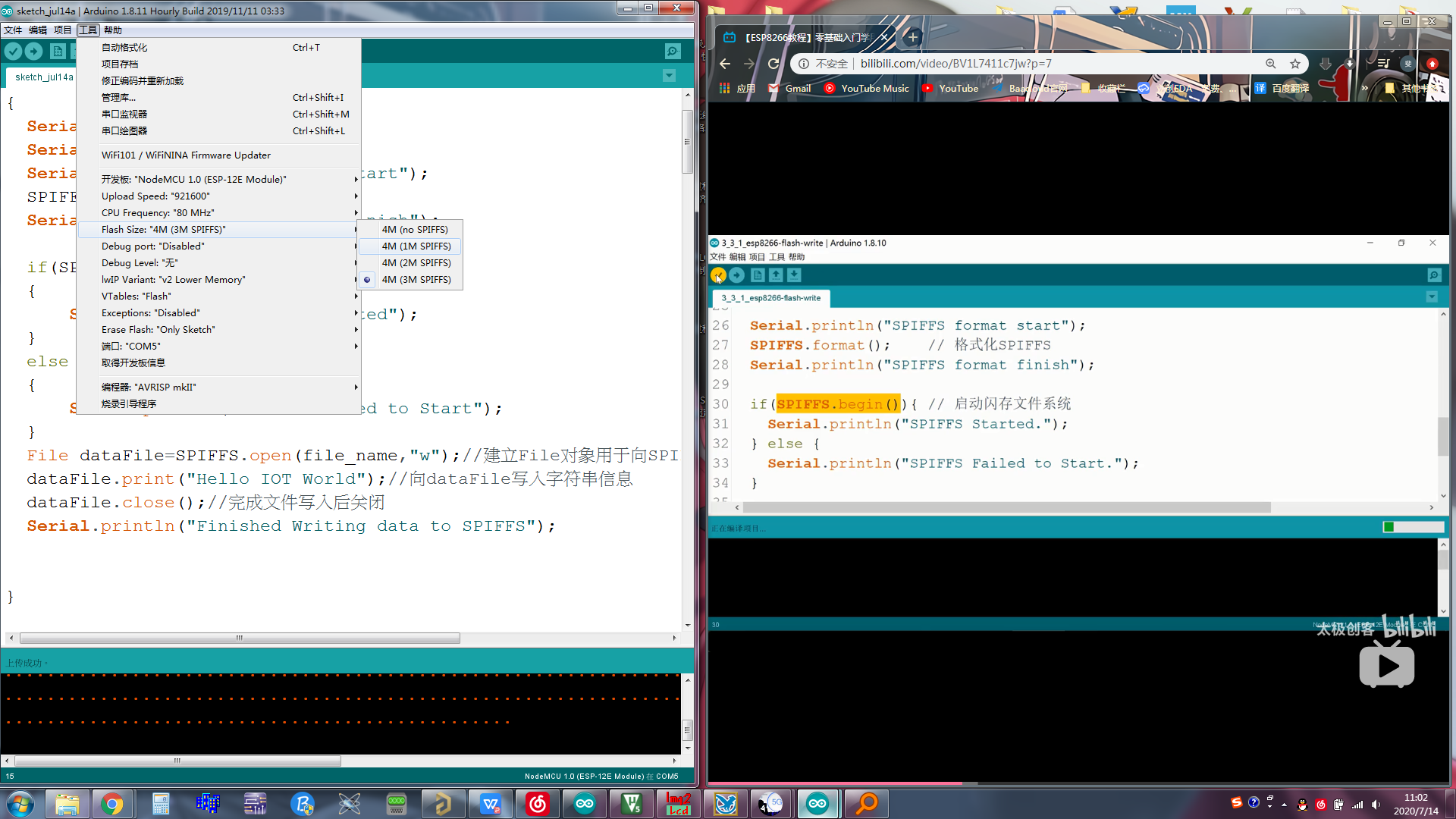
图1
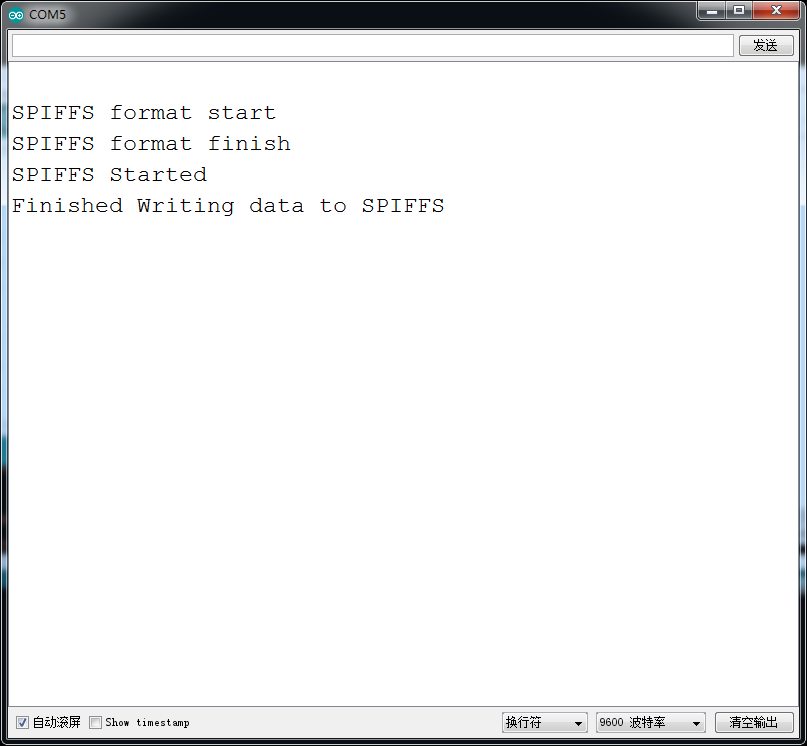
图2
二、通过程序从闪存文件系统中读取信息
代码:
代码部分将写和读都包括在内,格式化结束后,向文件系统写入信息(注,写入操作是从文件系统最开始写入信息和添加信息有所不同),之后在通过读,读出内容,在用串口发送到串口监视器上。
#include <FS.h>
String file_name="/taichi-maker/notes.txt";//被读取的文件位置和名称
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("SPIFFS format start");
SPIFFS.format();//格式化SPIFFS
Serial.println("SPIFFS format finish");
if(SPIFFS.begin())
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Started");
}
else
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Failed to Start");
}
File dataFile=SPIFFS.open(file_name,"w");//建立File对象用于向SPIFFS中的file对象,“w”,就是写的意思
dataFile.print("Hello IOT World ,Second Time");//向dataFile写入字符串信息
dataFile.close();//完成文件写入后关闭
Serial.println("Finished Writing data to SPIFFS");
//读取文件系统中的内容
if (SPIFFS.exists(file_name))
{
Serial.print(file_name);
Serial.print(" FOUND");
}
else
{
Serial.print(file_name);
Serial.print(" NOT FOUND");
}
dataFile=SPIFFS.open(file_name,"r");//读取文件内容且通过串口监视器打印出来
for(int i=0;i<dataFile.size();i++)
{
Serial.print((char)dataFile.read());
}
dataFile.close();//完成文件写入后关闭
}
void loop()
{
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}

图3
三、向文件系统添加信息
添加信息和写入信息不同的地方就是,写入信息不管你之前有没有入过信息,他都直接从第一个空间开始写入,而添加呢,则就是在你之前写过信息的基础上,也就是在之前信息的结尾,加上需要添加的信息。
1 #include <FS.h>
2 String file_name="/taichi-maker/notes.txt";//被读取的文件位置和名称
3 void setup()
4 {
5 Serial.begin(9600);
6 Serial.println("");
7 Serial.println("SPIFFS format start");
8 //SPIFFS.format();//格式化SPIFFS
9 //Serial.println("SPIFFS format finish");
10
11 if(SPIFFS.begin())
12 {
13 Serial.println("SPIFFS Started");
14 }
15 else
16 {
17 Serial.println("SPIFFS Failed to Start");
18 }
19 File dataFile=SPIFFS.open(file_name,"a");//建立File对象用于向SPIFFS中的file对象,“a”,就是添加的意思
20 dataFile.println("This is Appended Info.");//向dataFile的结尾添加字符串信息
21 dataFile.close();//完成文件写入后关闭
22 Serial.println("Finished Appended data to SPIFFS");
23
24 if (SPIFFS.exists(file_name))
25 {
26 Serial.print(file_name);
27 Serial.print(" FOUND");
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 Serial.print(file_name);
32 Serial.println(" NOT FOUND");
33 }
34 dataFile=SPIFFS.open(file_name,"r");//读取文件内容且通过串口监视器打印出来
35 for(int i=0;i<dataFile.size();i++)
36 {
37 Serial.print((char)dataFile.read());
38 }
39 dataFile.close();//完成文件写入后关闭
40
41 }
42
43 void loop()
44 {
45 // put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
46
47 }

图4
四、查看闪存文件系统的目录下的文件
代码:
#include <FS.h>
String file_name="/taichi-maker/myFile.txt";//被读取的文件位置和名称
String folder_name="/taichi-maker";//被读取的文件夹名称
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("SPIFFS format start");
//SPIFFS.format();//格式化SPIFFS
//Serial.println("SPIFFS format finish");
if(SPIFFS.begin())
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Started");
}
else
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Failed to Start");
}
File dataFile=SPIFFS.open(file_name,"w");//建立File对象用于向SPIFFS中的file对象,“w”,就是写入的意思
dataFile.println("Hello Taichi-maker");//向myfile.txt写入数据
dataFile.close();//完成文件写入后关闭
Serial.println("Finished Appended data to SPIFFS");
//显示目录中文件内容以及文件大小
Dir dir =SPIFFS.openDir(folder_name);//建立“目录对象”dir
while(dir.next())//dir.next()用于检查目录中是否还有”下一个文件“
{
Serial.println(dir.fileName());//输出文件名
}
}
void loop()
{
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}
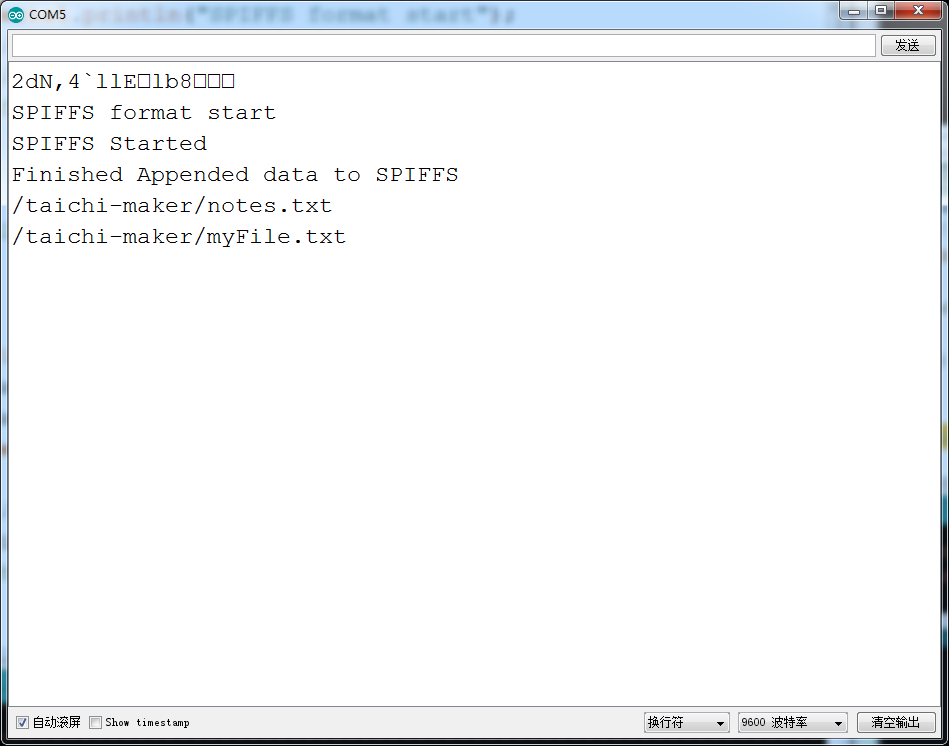
图5
五、从闪存文件系统中删除文件
代码
#include <FS.h>
String file_name="/taichi-maker/notes.txt";//被读取的文件位置和名称
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("SPIFFS format start");
//SPIFFS.format();//格式化SPIFFS
//Serial.println("SPIFFS format finish");
if(SPIFFS.begin())
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Started");
}
else
{
Serial.println("SPIFFS Failed to Start");
}
if (SPIFFS.remove(file_name))//remove 函数删除note.txt文件,同时返回值
{
Serial.print(file_name);
Serial.println ("remove sucess");
}
else
{
Serial.print(file_name);
Serial.println ("remove fail");
}
}
void loop()
{
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}
可以看到我们打印的消息显示失败了如图6,因为在我们让串口监视器显示之前,我们是按过一次复位键了,也就是说,按复位之前程序已经执行过了,所以我们再次删除一个不存在的文件是不可能成功的。为了验证我们是否成功,可以将之前读取文件夹内容的程序烧进NODEMCU。

图6
可以看到如图7所示,这说明我们成功的删除了note.txt文件了。

图7