QT自定义图形项中的boundingRect()和shape()函数的理解
实现自定义图形项经常需要重绘的函数有boundingRect()、paint()、shape()。
针对霍亚飞的Qt creator中所说,boundingRect()函数具有以下特点:
1.paint绘制的图像必须在boundingRect()函数之中。
2.用来确定哪些区域需要重构(repaint)。
3.用来检测碰撞
其中第二个功能在帮助文档中没有看到(可能英语水平不过关),故而通过一次小测试借以理解以上函数:
对第一点和第二点的理解:为什么图像的绘制必须在boundingRect()函数所确定的Rect之中。
第一个测试:我们把图像画到boundingRect()的所设置的矩形外边,并且想办法观察到重绘的情况
项目建立之类的就不说了,自行参照书本。
首先搭建个测试的框架:
添加一个继承自QGraphicsItem的MyIetm和继承自QGraphicssView的MyView,两个类的内容如下:
//myitem.h内容如下 #ifndef MYITEM_H #define MYITEM_H #include <QGraphicsItem> class MyItem : public QGraphicsItem { public: MyItem(); QRectF boundingRect()const override; void paint(QPainter *painter,const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *option,QWidget *widget)override; private: void drawRectPath(QPainter *painter); }; #endif // MYITEM_H
//myitem.cpp内容如下: #include "myitem.h" #include <QPainter> MyItem::MyItem() { } QRectF MyItem::boundingRect()const { qreal penwidth=1; return QRectF(-50-penwidth/2,-50-penwidth/2,100+penwidth,100+penwidth); } void MyItem::drawRectPath(QPainter *painter){ QPainterPath rectPath; rectPath.moveTo(-50,-50); rectPath.lineTo(50,-50); rectPath.lineTo(50,50); rectPath.lineTo(-50,50); rectPath.closeSubpath();//返回绘图开始点 painter->setPen(QPen(Qt::red,20,Qt::SolidLine,Qt::SquareCap,Qt::MiterJoin));//pen参数别设置错了,要不不好看出来 painter->drawPath(rectPath); //在之前的绘图上我们绘制出QboundingRect的虚线方框 painter->setPen(QPen(Qt::black,1,Qt::DotLine,Qt::SquareCap,Qt::MiterJoin)); painter->drawRect(-50,-50,100,100); } void MyItem::paint(QPainter *painter ,const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *,QWidget *){ drawRectPath(painter); }
//myview.h什么也不需要改动 #ifndef MYVIEW_H #define MYVIEW_H #include <QGraphicsView> class MyView : public QGraphicsView { public: MyView(); }; #endif // MYVIEW_H
//myview.cpp内容如下: #include "myview.h" MyView::MyView() { }
//main.cpp文件 #include <QApplication> #include "myitem.h" #include <QGraphicsScene> #include "myview.h" int main(int argv,char* argc[]){ QApplication app(argv,argc); MyItem *item1=new MyItem; MyItem *item2=new MyItem; item1->setPos(0,0); item2->setPos(150,150); QGraphicsScene scene; scene.addItem(item1); scene.addItem(item2); MyView view; view.setScene(&scene); view.resize(600,600); view.show(); return app.exec(); }
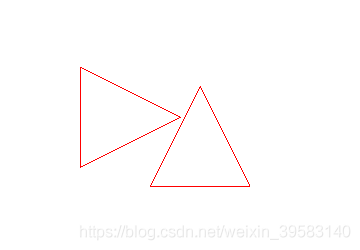
绘制的图形如下:
由上图,虽然我们绘制的图像和boundingRect返回的QRect是一样大的,但是因为我们的pen宽度,绘制的图形已经超出了boudingRect.
为了看到视图更新的效果,我们为图形项添加移动效果:
//在myitem.h中: //添加 protected: void keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event)override; void mousePressEvent(QGraphicsSceneMouseEvent *event)override;
//在myitem.cpp中: //更改MyItem()函数为: MyItem::MyItem() { //设置可以被移动以及获得焦点,缺一不可 setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsMovable); setFlag(QGraphicsItem::ItemIsFocusable); } //添加 //上下左右移动图形项 void MyItem::keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event){ switch (event->key()) { case Qt::Key_Left:{ moveBy(-1,0); break; } case Qt::Key_Up:{ moveBy(0,-1); break; } case Qt::Key_Right:{ moveBy(1,0); break; } case Qt::Key_Down:{ moveBy(0,1); break; } } } //鼠标点击获得焦点 void MyItem::mousePressEvent(QGraphicsSceneMouseEvent *){ setFocus(); }
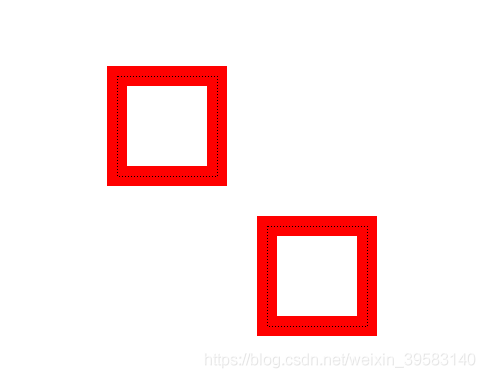
好了,点中方框图形(点击在虚线里边),就可以上下左右键移动了,试一试吧,也许我们已经可以猜到结果了:
理解这一点基础在于QGraphicsView的一个属性ViewportUpdateMode,可以通过
void setViewportUpdateMode(QGraphicsView::ViewportUpdateMode mode)
进行设定:
总共有五种模式,很容易理解:
QGraphicsView::FullViewportUpdate 全视口更新,整体都更新的意思啦
QGraphicsView::MinimalViewportUpdate 最小更新,哪里有变动更新哪里
QGraphicsView::SmartViewportUpdate 智能选择,它要自己选
QGraphicsView::BoundingRectViewportUpdate 来了,来了,它就是我们要注意的。
QGraphicsView::NoViewportUpdate 不更新
其中默认为QGraphicsView::MinimalViewportUpdate,也就是上例中我们没有进行设置的情况。事实上除了设置为FullViewportUpdate 其余四种皆会出现问题,不妨试一试。
我们可以通过在MyView的构造函数中设置为FullViewportUpdate 的全视口更新得到我们想要的结果,但是却是以牺牲性能为代价的。
理解第三点,用来检测碰撞
第二个测试:
在第一个测试基础上做以下更改:
MyItem.h中做添加
private: void drawRectPath(QPainter *painter);//绘制矩形不在使用 void drawtTriangle(QPainter *painter);//添加绘制三角形
在MyItem.cpp中更改三处
//第一处,实现drawtTriangle(QPainter *painter) void MyItem::drawtTriangle(QPainter *painter){ QPainterPath trianglePath; trianglePath.moveTo(0,-50); trianglePath.lineTo(50,50); trianglePath.lineTo(-50,50); trianglePath.closeSubpath(); painter->setPen(QPen(Qt::red,1,Qt::SolidLine,Qt::SquareCap,Qt::MiterJoin)); painter->drawPath(trianglePath); }
//第二处 重新实现paint void MyItem::paint(QPainter *painter ,const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *,QWidget *){ //绘制boundingRect的QRect以方便查看 painter->setPen(QPen(Qt::black,1,Qt::DotLine,Qt::SquareCap,Qt::MiterJoin)); painter->drawRect(-50,-50,100,100); if(hasFocus()&&!collidingItems().isEmpty()){ //判断是否有在获得焦点的同时有碰撞 painter->setBrush(QColor(Qt::black)); //若有碰撞则绘制的图形将以黑色作为画刷填充 } drawtTriangle(painter);//这次是三角形 }
//第三处:在keyPressEvent()函数中添加一个旋转的响应(按下R键) void MyItem::keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event){ switch (event->key()) { case Qt::Key_Left:{ moveBy(-1,0); break; } case Qt::Key_Up:{ moveBy(0,-1); break; } case Qt::Key_Right:{ moveBy(1,0); break; } case Qt::Key_Down:{ moveBy(0,1); break; } case Qt::Key_R:{ //按下R键旋转90度 setRotation(90); break; } } }
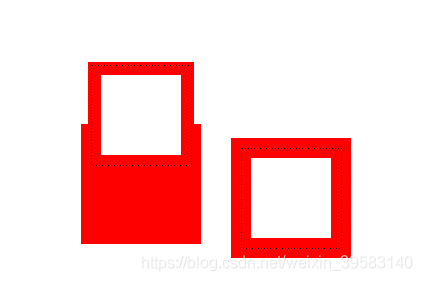
结果如下:
虚线接触时发生了碰撞,为了避免绘制的虚线对结果的影响,我们注释掉虚线部分
void MyItem::paint(QPainter *painter ,const QStyleOptionGraphicsItem *,QWidget *){ // painter->setPen(QPen(Qt::black,1,Qt::DotLine,Qt::SquareCap,Qt::MiterJoin)); // painter->drawRect(-50,-50,100,100); if(hasFocus()&&!collidingItems().isEmpty()){ painter->setBrush(QColor(Qt::black)); .............
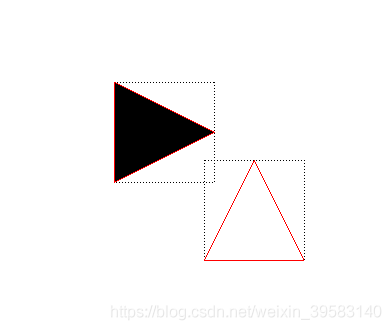
结果如下:
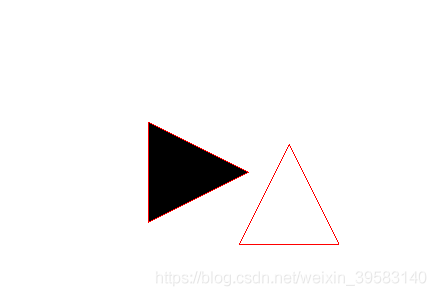
还没碰到呢,就已经变黑了(检测到碰撞了),可以得出结论了:
boundingRect与碰撞检测很明显是相关的 ;
但boundingRect返回的是矩形框,很明显不符合我们三角形碰撞的需求;
这就到了shape函数了,它返回的是QPainterPath故而可以是任何形状
myItem.h函数中添加新函数shape
//myitem.h ......... protected: void keyPressEvent(QKeyEvent *event)override; void mousePressEvent(QGraphicsSceneMouseEvent *event)override; QPainterPath shape()const override;//重写shape函数
shape函数的实现
//myitem.cpp ...... QPainterPath MyItem::shape()const{ //shape()函数返回一个一样的三角形路径 QPainterPath trianglePath; trianglePath.moveTo(0,-50); trianglePath.lineTo(50,50); trianglePath.lineTo(-50,50); trianglePath.closeSubpath(); return trianglePath; }
结果正如我们所需的: