Spread Spectrum Communication Systems
Spread spectrum signals for digital communications were originally developed and
used for military communications for the following reasons: (1) to provide resistance
to hostile jamming, (2) to hide the signal by transmitting it at low power and, thus,
make it difficult for an unintended listener to detect its presence in noise; and (3) to
make it possible for multiple users to communicate through the same channel. Today,
however, spread spectrum signals are being used to provide reliable communications in
a variety of commercial applications, including mobile vehicular communications and
interoffice wireless communications.
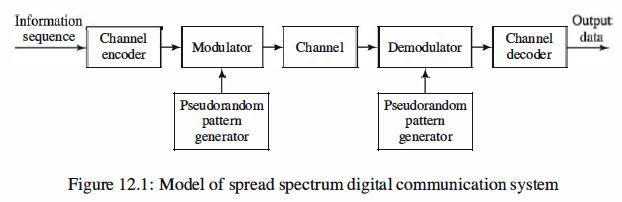
The basic elements of a spread spectrum digital communication system are illustrated
in Figure 12.1. We observe that the channel encoder and decoder and the modulator
and demodulator are the basic elements of a conventional digital communication
system. In addition to these elements, a spread spectrum system employs two identical
pseudorandom sequence generators, one of which interfaces with the modulator at
the transmitting end and the second of which interfaces with the demodulator at the
receiving end. These two generators produce a pseudorandom or pseudonoise (PN)
binary-valued sequence that is used to spread the transmitted signal in frequency at the
modulator and to despread the received signal at the demodulator.
Time synchronization of the PN sequence generated at the receiver, with the PN
sequence contained in the received signal, is required to properly despread the received
spread spectrum signal. In a practical system, synchronization is established prior to
the transmission of information by transmitting a fixed PN bit pattern that is designed
so that the receiver will detect it with high probability in the presence of interference.
After time synchronization of the PN sequence generators is established, the transmission
of information commences. In the data mode, the communication system usually
tracks the timing of the incoming received signal and keeps the PN sequence generator
in synchronism.
Two basic types of spread spectrum signals for digital communications:
namely, direct-sequence (DS) spread spectrum and frequencyhopped (FH) spread spectrum.
Two types of digital modulation are considered in conjunction with spread spectrum,
namely: PSK and FSK. PSK modulation is generally used with DS spread
spectrum and is appropriate for applications where phase coherence between the transmitted
signal and the received signal can be maintained over a time interval that spans
several symbol (or bit) intervals. On the other hand, FSK modulation is commonly
used with FH spread spectrum and is appropriate in applications where phase coherence
of the carrier cannot be maintained due to time variations in the transmission
characteristics of the communications channel.
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis
