Demodulation of OFDM Signals
As we have observed above, the modulator in an OFDM system can be implemented by
computing the IDFT. The demodulator that recovers the information
symbols {Xk} from the received signal samples is implemented by computing the DFT.
The detector is described below. When the number of subcarriers is
large, say K > 30, the modulator and demodulator in the OFDM system are efficiently
implemented by using the fast Fourier transform algorithm (FFT algorithm) to compute the DFT and IDFT.
Matlab Coding
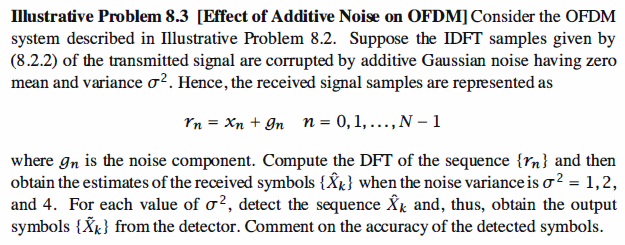
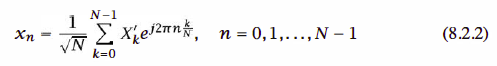
1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 8.3. 2 echo on 3 clear; 4 K=10;N=2*K;T=100; 5 variance=1 or 4; 6 noise=sqrt(variance)*randn(1,N); 7 a=rand(1,36); 8 a=sign(a-0.5); 9 b=reshape(a,9,4);
10 % Generate the 16QAM points 11 XXX=2*b(:,1)+b(:,2)+j*(2*b(:,3)+b(:,4)); 12 XX=XXX'; 13 X=[0 XX 0 conj(XX(9:-1:1))]; 14 x=zeros(1,N); 15 for n=0:N-1 16 for k=0:N-1 17 x(n+1)=x(n+1)+1/sqrt(N)*X(k+1)*exp(j*2*pi*n*k/N); 18 echo off 19 end 20 end 21 echo on 22 r=x+noise; 23 Y=zeros(1,10); 24 for k=1:9 25 for n=0:N-1 26 Y(1,k+1)=Y(1,k+1)+1/sqrt(N)*r(n+1)*exp(-j*2*pi*k*n/N); 27 echo off 28 end 29 end 30 echo on
31 % Detect the nearest neighbor in the 16QAM constellation 32 for k=1:9 33 if real(Y(1,k+1))>0 34 if real(Y(1,k+1))>2 35 Z(1,k+1)=3; 36 else 37 Z(1,k+1)=1; 38 end 39 else 40 if real(Y(1,k+1))<-2 41 Z(1,k+1)=-3; 42 else 43 Z(1,k+1)=-1; 44 end 45 end 46 if imag(Y(1,k+1))>0 47 if imag(Y(1,k+1))>2 48 Z(1,k+1)=Z(1,k+1)+3*j; 49 else 50 Z(1,k+1)=Z(1,k+1)+j; 51 end 52 else 53 if imag(Y(1,k+1))<-2 54 Z(1,k+1)=Z(1,k+1)-3*j; 55 else 56 Z(1,k+1)=Z(1,k+1)-j; 57 end 58 end 59 echo off 60 end 61 echo on 62 error=max(size(find(Z(1,2:10)-X(1,2:10))));
Result
>> variance
variance =
4
>> XX
XX =
Columns 1 through 6
-3.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 + 3.0000i 1.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 + 1.0000i -3.0000 - 3.0000i
Columns 7 through 9
-1.0000 + 1.0000i 1.0000 - 3.0000i -1.0000 + 3.0000i
>> Y
Y =
Columns 1 through 6
0.0000 + 0.0000i -4.1333 + 1.2388i -2.4657 + 3.6617i -0.0808 + 3.1247i -0.8439 + 0.0408i -1.1949 + 2.4617i
Columns 7 through 10
-4.4393 - 4.6753i -3.7024 + 1.2707i 3.0362 - 1.2516i -3.7607 + 2.1932i
>> Z
Z =
Columns 1 through 6
0.0000 + 0.0000i -3.0000 + 1.0000i -3.0000 + 3.0000i -1.0000 + 3.0000i -1.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 + 3.0000i
Columns 7 through 10
-3.0000 - 3.0000i -3.0000 + 1.0000i 3.0000 - 1.0000i -3.0000 + 3.0000i
>> variance
variance =
1
>> XX
XX =
Columns 1 through 6
1.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 - 3.0000i 3.0000 + 1.0000i 3.0000 - 3.0000i -3.0000 - 3.0000i 3.0000 - 1.0000i
Columns 7 through 9
1.0000 + 1.0000i -3.0000 - 1.0000i -1.0000 + 1.0000i
>> Y
Y =
Columns 1 through 6
0.0000 + 0.0000i 1.2252 + 1.8573i -1.0852 - 3.9203i 4.2954 - 0.5971i 3.0646 - 2.2739i -1.8358 - 2.4102i
Columns 7 through 10
3.5648 - 0.1429i 2.1387 + 1.1687i -2.4536 + 0.0122i 0.4438 + 1.5946i
>> Z
Z =
Columns 1 through 6
0.0000 + 0.0000i 1.0000 + 1.0000i -1.0000 - 3.0000i 3.0000 - 1.0000i 3.0000 - 3.0000i -1.0000 - 3.0000i
Columns 7 through 10
3.0000 - 1.0000i 3.0000 + 1.0000i -3.0000 + 1.0000i 1.0000 + 1.0000i
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis