Optimum Receiver for the AWGN Channel
The optimum receiver for the AWGN channel consists of two building blocks.
One is either a signal correlator or a matched filter . The other is a detector.
Signal Correlator
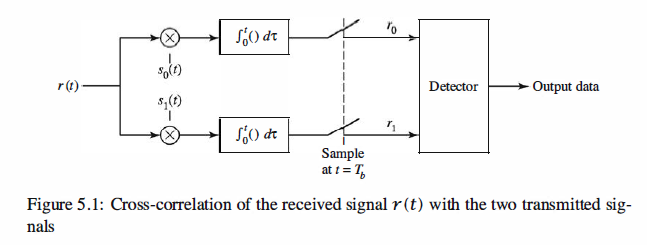
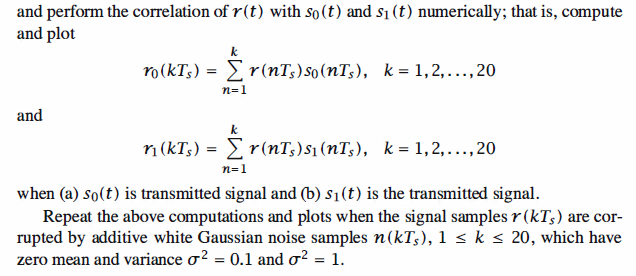
The signal correlator cross-correlates the received signal r ( t) with the two possible
transmitted signals s0 ( t) and s1( t), as illustrated in Figure 5 .1. That is, the signal
correlator computes the two outputs,
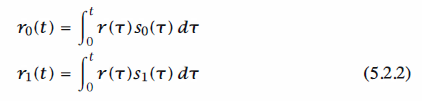
in the interval 0 <= t <= Tb, samples the two outputs at t = Tb, and feeds the sampled
outputs to the detector.
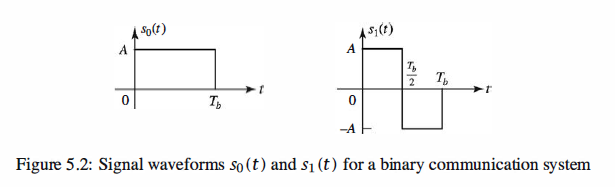
Suppose that
Matlab coding
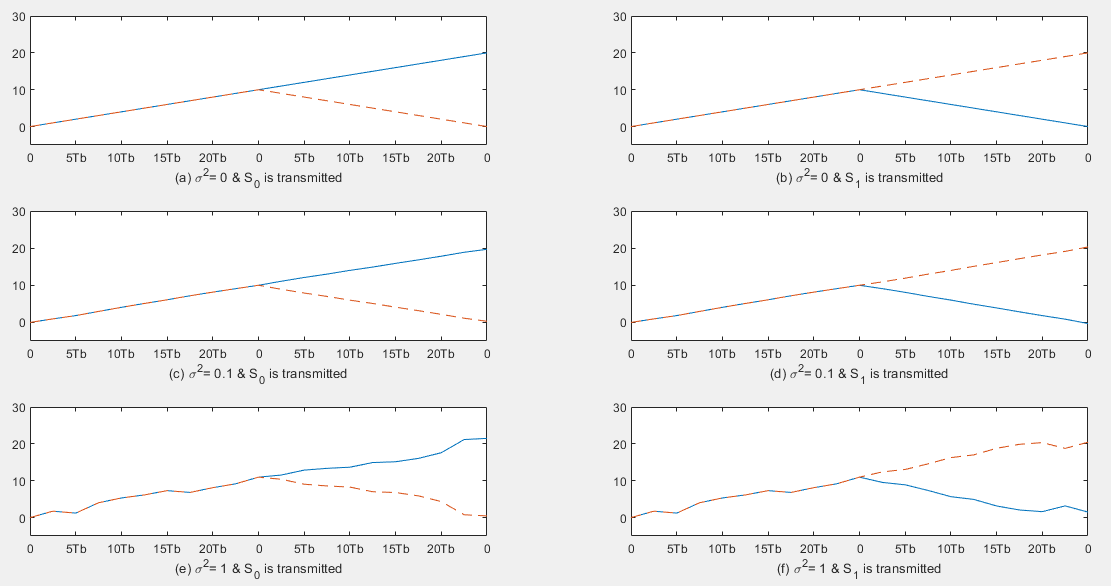
1 % MATLAB script 2 3 % Initialization: 4 K=20; % Number of samples 5 A=1; % Signal amplitude 6 l=0:K;
7 % Defining signal waveforms: 8 s_0=A*ones(1,K); 9 s_1=[A*ones(1,K/2) -A*ones(1,K/2)];
10 % Initializing output signals: 11 r_0=zeros(1,K); 12 r_1=zeros(1,K); 13 14 % Case 1: noise~N(0,0) sigma^2= 0 15 noise=random('Normal',0,0,1,K); 16 % Sub-case s = s_0: 17 s=s_0; 18 r=s+noise; % received signal 19 for n=1:K 20 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); % Signal Correlator 21 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 22 end 23 % Plotting the results: 24 subplot(3,2,1) 25 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 26 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 27 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 28 xlabel('(a) sigma^2= 0 & S_{0} is transmitted','fontsize',10) 29 % Sub-case s = s_1: 30 s=s_1; 31 r=s+noise; % received signal 32 for n=1:K 33 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); 34 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 35 end 36 % Plotting the results: 37 subplot(3,2,2) 38 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 39 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 40 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 41 xlabel('(b) sigma^2= 0 & S_{1} is transmitted','fontsize',10)
42 % Case 2: noise~N(0,0.1) sigma^2= 0.1 43 noise=random('Normal',0,0.1,1,K); 44 % Sub-case s = s_0: 45 s=s_0; 46 r=s+noise; % received signal 47 for n=1:K 48 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); 49 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 50 end 51 % Plotting the results: 52 subplot(3,2,3) 53 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 54 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 55 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 56 xlabel('(c) sigma^2= 0.1 & S_{0} is transmitted','fontsize',10) 57 % Sub-case s = s_1: 58 s=s_1; 59 r=s+noise; % received signal 60 for n=1:K 61 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); 62 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 63 end 64 % Plotting the results: 65 subplot(3,2,4) 66 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 67 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 68 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 69 xlabel('(d) sigma^2= 0.1 & S_{1} is transmitted','fontsize',10)
70 % Case 3: noise~N(0,1) sigma^2= 1 71 noise=random('Normal',0,1,1,K); 72 % Sub-case s = s_0: 73 s=s_0; 74 r=s+noise; % received signal 75 for n=1:K 76 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); 77 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 78 end 79 % Plotting the results: 80 subplot(3,2,5) 81 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 82 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 83 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 84 xlabel('(e) sigma^2= 1 & S_{0} is transmitted','fontsize',10) 85 % Sub-case s = s_1: 86 s=s_1; 87 r=s+noise; % received signal 88 for n=1:K 89 r_0(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_0(1:n)); 90 r_1(n)=sum(r(1:n).*s_1(1:n)); 91 end 92 % Plotting the results: 93 subplot(3,2,6) 94 plot(l,[0 r_0],'-',l,[0 r_1],'--') 95 set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'0','5Tb','10Tb','15Tb','20Tb'}) 96 axis([0 20 -5 30]) 97 xlabel('(f) sigma^2= 1 & S_{1} is transmitted','fontsize',10)
Simulation Results
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis