给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
我们用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
示例 1:
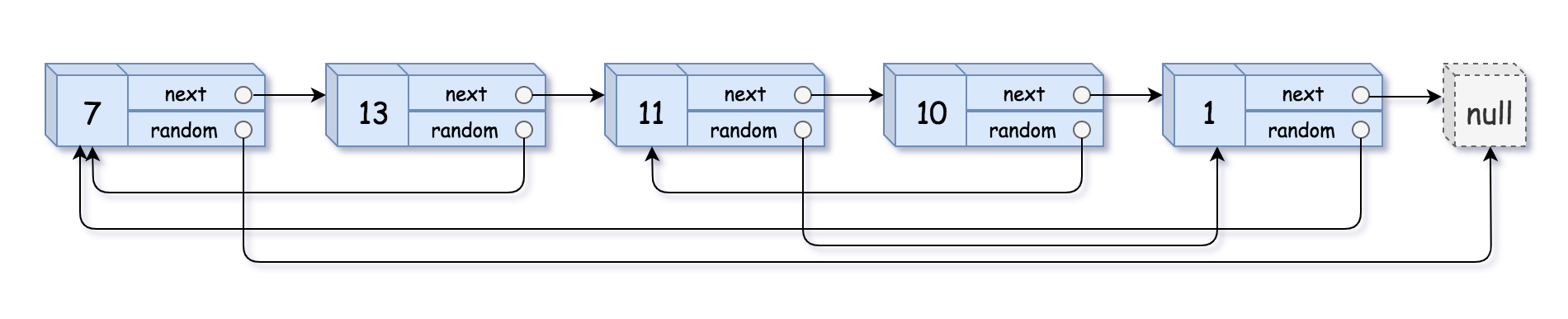
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
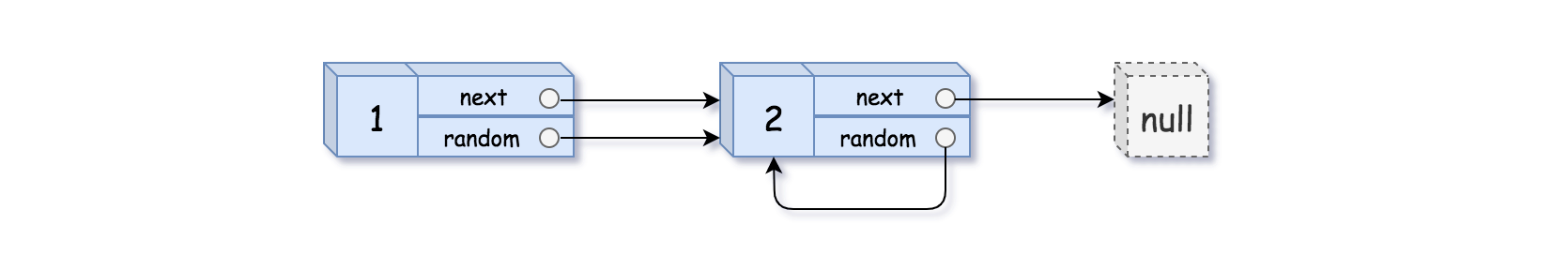
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
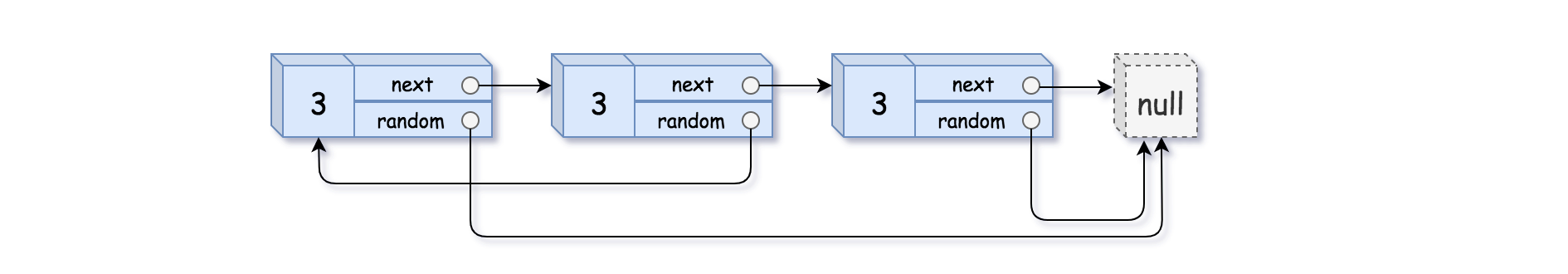
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] 输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = [] 输出:[] 解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。- 节点数目不超过 1000 。
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } */ class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { if(head == null) return head; copyNext(head); copyRandom(head); return link(head); } private void copyNext(Node head){ while(head != null){ Node cpnode = new Node(head.val); Node next = head.next; cpnode.next = next; head.next = cpnode; head = next; } } private void copyRandom(Node head){ while(head != null){ Node cpnode = head.next; if(head.random != null){ cpnode.random = head.random.next; } head = cpnode.next; } } private Node link(Node head){ Node newHead = head.next; Node cpnode = head.next; head.next = cpnode.next; head = head.next; while(head != null){ cpnode.next = head.next; head.next = head.next.next; cpnode = cpnode.next; head = head.next; } return newHead; } }