一、实验内容
1.学号末尾为98,故采用98号系统调用
2.通过汇编指令触发系统调用
3.通过gdb跟踪该系统调用的内核处理过程
4.阅读分析系统调用入口的保存现场、恢复现场和系统调用返回,以及关注系统调用过程中内核堆栈状态的变化
二、环境准备
安装开发工具
sudo apt install build-essential
sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU
sudo apt install libncurses5-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
下载内核源代码
sudo apt install axel axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/ linux-5.4.34.tar.xz xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar cd linux-5.4.34
配置内核编译选项
make defconfig # Default configuration is based on 'x86_64_defconfig' make menuconfig # 打开debug相关选项 Kernel hacking ---> Compile-time checks and compiler options ---> [*] Compile the kernel with debug info [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging [*] Kernel debugging # 关闭KASLR,否则会导致打断点失败 Processor type and features ----> [] Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR)
编译内核
make -j$(nproc) # nproc gives the number of CPU cores/threads available
# 测试⼀下内核能不能正常加载运⾏,因为没有⽂件系统终会kernel panic
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage # 此时应该不能正常运行
制作根文件系统
#下载 axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 cd busybox-1.31.1 复制代码 #制作根文件系统 make menuconfig #记得要编译成静态链接,不⽤动态链接库。 Settings ---> [*] Build static binary (no shared libs) #然后编译安装,默认会安装到源码⽬录下的 _install ⽬录中。 make -j$(nproc) && make install
制作内存根文件系统镜像
mkdir rootfs cd rootfs cp ../busybox-1.31.1/_install/* ./ -rf mkdir dev proc sys home sudo cp -a /dev/{null,console,tty,tty1,tty2,tty3,tty4} dev/
准备init脚本文件放在根文件系统跟目录下(rootfs/init),添加如下内容到init文件。
#!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys echo "Wellcome TestOS!" echo "--------------------" cd home /bin/sh #给init脚本添加可执行权限 chmod +x init #打包成内存根文件系统镜像 find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz #测试挂载根文件系统,看内核启动完成后是否执行init脚本 qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz
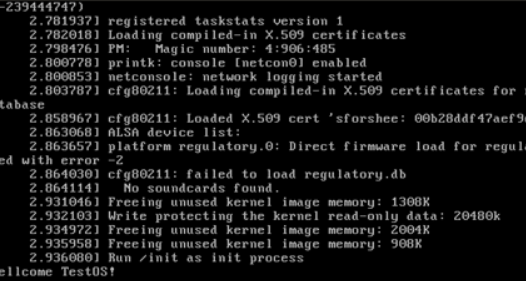
内存根文件系统制作完毕
三:查看系统调用,编写调用汇编代码
根据学号后两位在/arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl 中找到对应的系统调用函数__x64_sys_getrusage
![]()
查阅
struct rusage { struct timeval ru_utime; /* user time used 用户态使用的时间 */ struct timeval ru_stime; /* system time used 内核态使用的时间 */ long ru_maxrss; /* maximum resident set size */ long ru_ixrss; /* integral shared memory size */ long ru_idrss; /* integral unshared data size */ long ru_isrss; /* integral unshared stack size */ long ru_minflt; /* page reclaims */ long ru_majflt; /* page faults */ long ru_nswap; /* swaps */ long ru_inblock; /* block input operations */ long ru_oublock; /* block output operations */ long ru_msgsnd; /* messages sent */ long ru_msgrcv; /* messages received */ long ru_nsignals; /* signals received */ long ru_nvcsw; /* voluntary context switches */ long ru_nivcsw; /* involuntary context switches */ };
并且提供wait3,wait4和getrusage来获取该结构。
#include <sys/time.h> #include <sys/resource.h> int getrusage(int who, struct rusage usage);
汇编进行系统调用
写一个test.c的测试文件
int main() { asm volatile ( "movq $0x62, %rax " "syscall " ); return 0; }
使用下面命令将test.c进行静态编译
gcc -o test test.c -static
将形成的可执行文件放到rootfs/home/目录下,然后重新打包rootfs文件夹,由于我们对系统做了修改,需要重新打包成内存根文件系统镜像。因此要再次使用命令:
find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
这样,我们就完成了系统调用的准备,接下来使用gdb进行调试。
纯命令行启动qemu
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s -nographic -append "console=ttyS0"
在linux-5.4.34目录下启动gdb调试
cd linux-5.4.34/ gdb vmlinux target remote:1234 b __x64_sys_pwrite64
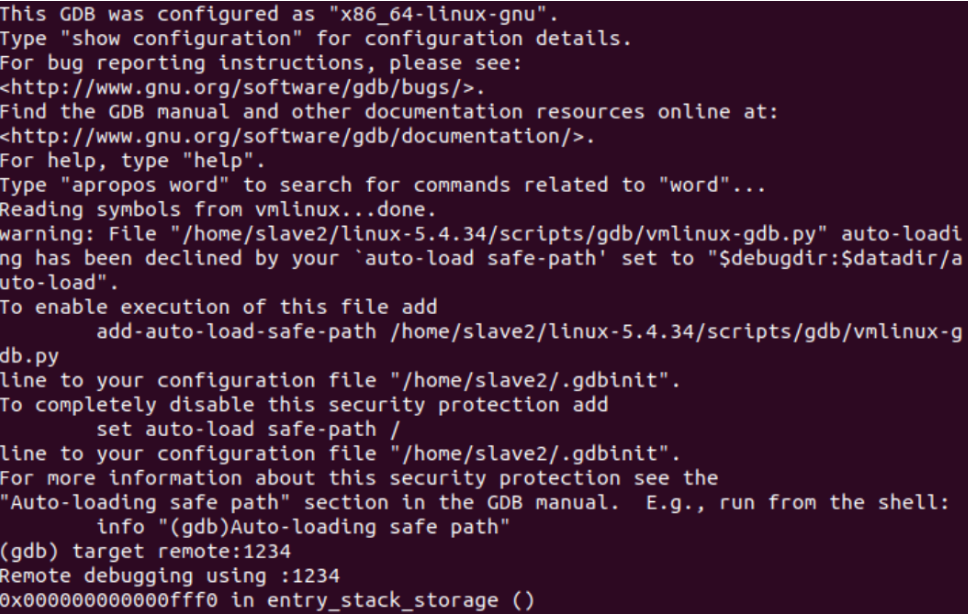

可以使用bt来观察方法的堆栈从而知道 entry_SYSCALL_64是系统调用的入口,它在系统调用之前已经初始化了该方法对应的内核堆栈
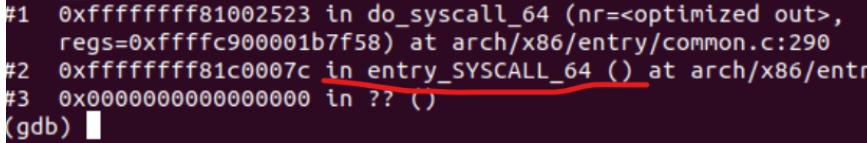
继续调试 直到最后结束,可以看到恢复现场以及系统调用返回,以及从内核态返回用户态的步骤:
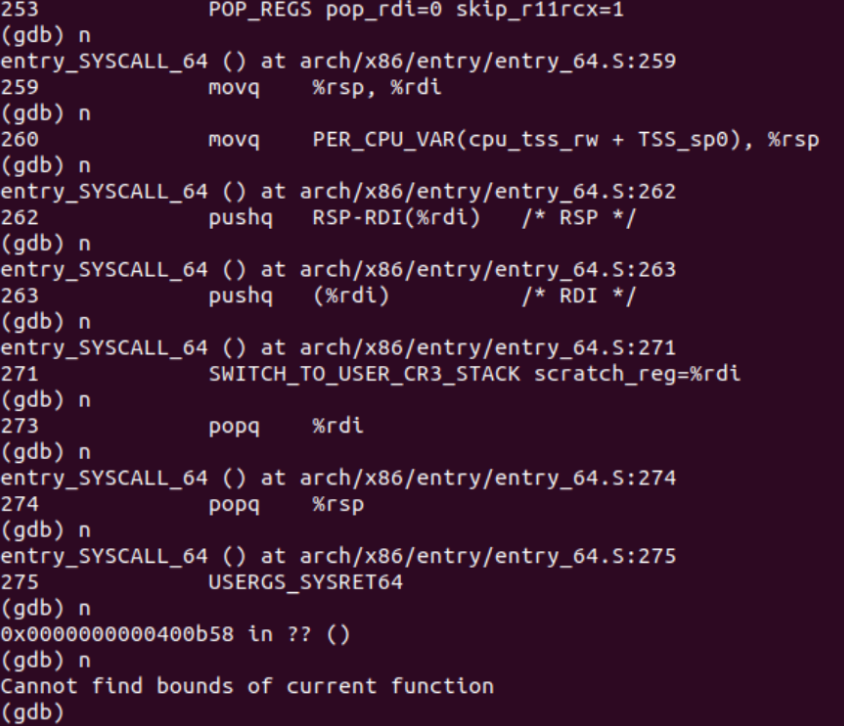
可以看到该系统调用涉及到do_syscall_64和entry_SYSCALL_64两个内核函数。
四、总结
本次实验中,使用gdb工具断点调试,查看了98号系统调用的调用过程,了解了系统调用的保存和恢复现场。
整个系统调用,保存和恢复现场过程:syscall指令触发系统调用,通过MSR寄存器找到了中断函数入口
然后进如 entry_SYSCALL_64( )执行现场保存
do_syscall_64( )查找调用入口并执行
准备恢复现场 调用entry_SYSCALL_64( )最后完成现场恢复