Each month Blake gets the report containing main economic indicators of the company "Blake Technologies". There are n commodities produced by the company. For each of them there is exactly one integer in the final report, that denotes corresponding revenue. Before the report gets to Blake, it passes through the hands of m managers. Each of them may reorder the elements in some order. Namely, thei-th manager either sorts first ri numbers in non-descending or non-ascending order and then passes the report to the manager i + 1, or directly to Blake (if this manager has number i = m).
Employees of the "Blake Technologies" are preparing the report right now. You know the initial sequence ai of length n and the description of each manager, that is value ri and his favourite order. You are asked to speed up the process and determine how the final report will look like.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200 000) — the number of commodities in the report and the number of managers, respectively.
The second line contains n integers ai (|ai| ≤ 109) — the initial report before it gets to the first manager.
Then follow m lines with the descriptions of the operations managers are going to perform. The i-th of these lines contains two integers tiand ri (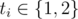 , 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
, 1 ≤ ri ≤ n), meaning that the i-th manager sorts the first ri numbers either in the non-descending (if ti = 1) or non-ascending (if ti = 2) order.
Print n integers — the final report, which will be passed to Blake by manager number m.
3 1
1 2 3
2 2
2 1 3
4 2
1 2 4 3
2 3
1 2
2 4 1 3
In the first sample, the initial report looked like: 1 2 3. After the first manager the first two numbers were transposed: 2 1 3. The report got to Blake in this form.
In the second sample the original report was like this: 1 2 4 3. After the first manager the report changed to: 4 2 1 3. After the second manager the report changed to: 2 4 1 3. This report was handed over to Blake.
思路:首先由于每次排序都是重第一个排到指定的位置,那么由于对每一段排序是有先后顺序的,如果前面的排序范围为[1,b];假如后面有范围[1,c];
如果c>=b前面的[1,b]的排序是不是可以忽略了,并且如果c<b&&(a[i-1]==a[i])(a表示的是升序或降序),那么后面的这段变化也可以省略掉,所以经过筛选后可以得到需要排序的那些段,假如段为[1,a],[1,b],....[1,x];那么可以得到a>b>c>...x;那么首先我们先把第一段排完,那么在排完第一段后,假设数组个数为n,[b+1,n],这段就不会再改变了,那么可以取出来,同时因为a[i]!=a[i-1],并且[1,b]要么升序要么降序,因为当操作[1,b]时肯定要将[1,b]翻过来,就是升序变降序,降序变升序,那么当在下一个操做[1,c]执行后可以知道此时变化后的数组[c+1,b]可以确定而且我们知道[c+1,b]=原数组[1,k](k-1==b-c-1);

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<queue> 7 #include<stack> 8 using namespace std; 9 int num[2000003]; 10 int a[2000003],b[2000003]; 11 int kk[2000003]; 12 int cmp1(const void *p,const void*q); 13 int cmp2(const void *p,const void*q); 14 typedef pair<int,int>P; 15 stack<P>sac; 16 stack<P>sac1; 17 int main(void) 18 { 19 int i,j,k,p,q; 20 scanf("%d %d",&p,&q); 21 for(i=0; i<p; i++) 22 { 23 scanf("%d",&num[i]); 24 } 25 for(i=0; i<q; i++) 26 { 27 scanf("%d %d",&a[i],&b[i]); 28 } 29 for(i=0; i<q; i++) 30 {P N; 31 while(!sac.empty()) 32 { 33 N=sac.top(); 34 if(N.second<=b[i]) 35 sac.pop(); 36 else break; 37 }if(sac.empty()) 38 sac.push(P(a[i],b[i])); 39 else if(a[i]!=N.first) 40 { 41 sac.push(P(a[i],b[i])); 42 } 43 } 44 while(!sac.empty()) 45 { 46 P L=sac.top(); 47 sac.pop(); 48 sac1.push(L); 49 }P rt;int flag=0;int t=0;int y=p-1;int ans=p-1;int rns=0; 50 int qian;P L; 51 while(!sac1.empty()) 52 { 53 L=sac1.top(); 54 sac1.pop(); 55 if(flag==0) 56 { 57 flag=1;qian=p; 58 if(L.first==1) 59 qsort(num,L.second,sizeof(int),cmp1); 60 else qsort(num,L.second,sizeof(int),cmp2); 61 } 62 else { 63 if(t%2==1) 64 { t++; 65 for(i=rns;i<rns+(qian-L.second)&&y>=0;i++) 66 { 67 kk[y--]=num[i]; 68 } 69 rns=i; 70 qian=L.second; 71 } 72 else if(t%2==0) 73 {t++; 74 for(i=ans;i>ans-(qian-L.second)&&y>=0;i--) 75 { 76 kk[y--]=num[i]; 77 }qian=L.second;ans=i; 78 } 79 }} if(t%2==1) 80 { t++; 81 for(i=rns;y>=0;i++) 82 { 83 kk[y--]=num[i]; 84 } 85 86 } 87 else if(t%2==0) 88 {t++; 89 for(i=ans;y>=0;i--) 90 { 91 kk[y--]=num[i]; 92 } 93 } 94 printf("%d",kk[0]); 95 for(i=1; i<p; i++) 96 printf(" %d",kk[i]); 97 return 0; 98 } 99 100 int cmp1(const void *p,const void*q) 101 { 102 int *n=(int*)p; 103 int *m=(int*)q; 104 return *n-*m; 105 } 106 int cmp2(const void *p,const void*q) 107 { 108 int *n=(int*)p; 109 int *m=(int*)q; 110 return *m-*n; 111 }
复杂度为(O(n));