1.有理数类的设计
package rati;
public class Rational {
private int num;//分子
private int den;//分母
public Rational (int num,int den)//构造函数
{
this.num = num;
this.den = den;
}
public int getNumerator()//获取分子
{
return this.num;
}
public int getDenominator()//获取分母
{
return this.den;
}
public Rational add(Rational first, Rational second)//加法
{
int n = first.num * second.den + second.num * first.den;
int d = first.den * second.den;
return new Rational(n,d);
}
public Rational subtract(Rational first,Rational second)//减法
{
int n = first.num * second.den - second.num * first.den;
int d = first.den * second.den;
return new Rational(n,d);
}
public Rational multiply(Rational first,Rational second)//乘法
{
int n = first.num * second.num;
int d = first.den * second.den;
return new Rational(n,d);
}
public Rational divide(Rational first,Rational second)//除法
{
int n = first.num * second.den;
int d = first.den * second.num;
return new Rational(n,d);
}
public boolean equal(Rational first,Rational second) //判断是否相等
{
if ((first.num == second.num)&(first.den == second.den)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public int intValue()//返回整数
{
return this.num / this.den;
}
public String toString()//返回字符串
{
return this.num + "/" + this.den;
}
}
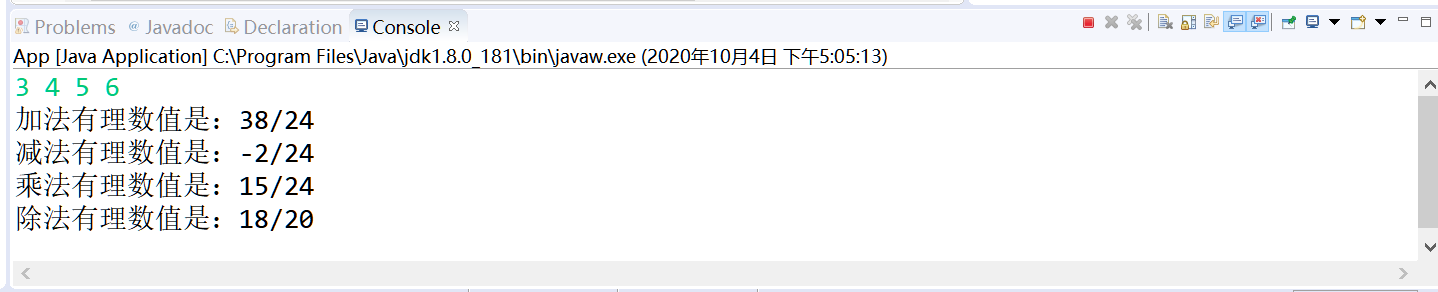
2.测试代码
package rati;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext())
{
int a=sc.nextInt(),b=sc.nextInt(),c=sc.nextInt(),d=sc.nextInt();
Rational R1= new Rational(a,b),R2=new Rational(c,d);
Rational R;
R= R1.add(R1, R2);
System.out.println("加法有理数值是:"+R);
R=R1.subtract(R1, R2);
System.out.println("减法有理数值是:"+R);
R=R1.multiply(R1, R2);
System.out.println("乘法有理数值是:"+R);
R=R1.divide(R1, R2);
System.out.println("除法有理数值是:"+R);
}
}
}
3.尝试描述怎么与c语言的有理数代码相比较,为什么你设计的类更加面向对象?
C语言是面向过程编程,所以如果是C语言,我会用各种函数来完成各种功能。
JAVA语言是面向对象编程语言,我会把每个类的属性、方法进行封装。
4.别人如何复用你的代码?
适用我的有理数包就可以。
5.别人的代码是否依赖你的有理数类的属性?当你的有理数类的属性修改时,是否会影响他人调用你有理数类的代码?
会依赖,会影响。
6.有理数类的public方法是否设置合适?为什么有的方法设置为private?
合适。有些类只是为了在自己的类中修改,别的类无法修改,保证安全性。