实验目的
根据给出的文法编制LR(1)分析程序,以便对任意输入的符号串进行分析。本次实验的目的主要是加深对LR(1)分析法的理解。
实验环境
①开发语言:java
②开发环境:jdk1.8
功能描述
利用LR(1)分析表,对输入符号串自底而上的分析过程。输入要分析的字符串,输出解析结果到结果文件。如果成功输出success,如果失败输出错误信息
分析表构造过程
closure和goto函数

文法
Algol,为算法语言(ALGOrithmic Language)的缩写,是计算机发展史上首批产生的高级程式语言家族。当时还是晶体管计算机流行的时代,由于ALGOL语句和普通语言表达式接近,更适于数值计算,所以ALGOL多用于科学计算机。
我用的是类Algol文法
program → block
block → { stmts }
stmts → stmt stmts | e
stmt → id= expr ;
| if ( bool ) stmt
| if ( bool) stmt else stmt
| while (bool) stmt
| do stmt while (bool ) ;
| break ;
| block
bool → expr < expr
| expr <= expr
| expr > expr
| expr >= expr
| expr
expr → expr + term
| expr - term
| term
term → term * factor
| term / factor
| factor
factor → ( expr ) | id| num
程序设计思路
1.手动画出LR(1)表。其实我已经写出来得到first集的函数,但是构造LR(1)的算法逻辑好复杂啊。因为这个实验是针对特定的文法,就没有专门去写构造LR(1)表的函数。但是这个58个状态画的真的累,以后考虑下写写构造LR(1)表的算法。
2.定义一个用于描述规则的类type,用于规约的时候查询。有三个属性right,left,pop
- right:String存放规则的左边
- left:String存放规则的右边
- pop:int规约时要弹出几个状态
3.定义一个Map全局变量存放规则的集合rule
定义存放action表的MapMaction和存放goto表的MapMgoto,key是状态,value是输入非终结符或终结符对应的操作。
如当前状态2,遇到'>'跳到状态15,则Map<2,Map<">",15>>
定义状态栈和符号栈的全局变量
用list存放非终结符和终结符,方便查询
static Map<Integer,type> rule=new HashMap<>();//规则
static Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();//状态栈
static Stack<String> stack1=new Stack<>();//符号栈
static List<String> NFinal=new ArrayList<String>();//非终结符
static List<String> Final=new ArrayList<String>();//终结符
static Map<Integer,Map<String,String>> Maction=new HashMap<>();//LRaction表
static Map<Integer,Map<String,String>> Mgoto=new HashMap<>();//LRgoto表
4.程序结构描述:函数调用格式、参数含义、返回值描述、函数功能
- getActionMap()
参数:无
返回值:无
功能:初始化action表 - getGotoMap()
参数:无
返回值:无
功能:初始化goto表 - newrule()
参数:无
返回值:无
功能:初始化规则集合 - newtype(String right,String left,int pop,int key)
参数:right,left,pop用来new一个type,将参数key作为rule的key,type作为value
返回值:无
功能:初始化一条规则 - isFinal(String a)
参数:a输入串
返回值:一个终结符/NULL
功能:得到当前句子的第一个终结符,若有返回第一个终结符,若无返回NULL - isNFinal(String a)
参数:a输入串
返回值:一个非终结符/NULL
功能:得到当前句子的第一个非终结符,若有返回第一个终结符,若无返回NULL - getTag()
参数:无
返回值:无
功能:初始化终结符和非终结符list - cifa(String s1)
参数:s1为待分析的字符串
返回值:无
功能:进行对s1的词法分析 - print(int step,String stack,String stack1,String s1,String AorG,int i)
参数:step当前步骤,stack状态栈,stack1符号栈,s1输入串,AorG操作,i是action还是goto操作
返回值:无
功能:将分析结果输出到输出文件 - getinput()
参数:无
返回值:String
功能:输入要分析的字符串
5.流程图
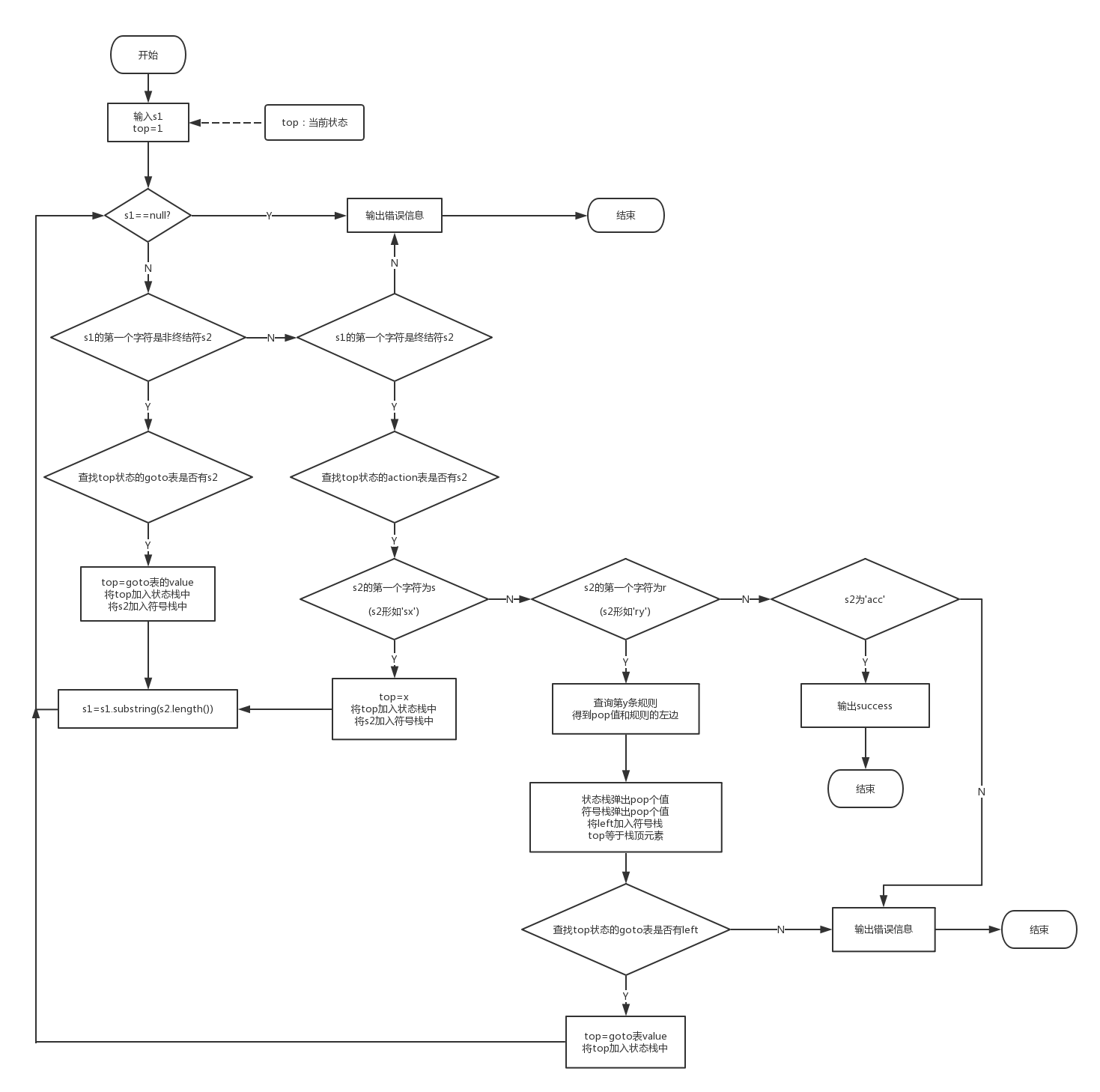
程序结构描写
(1)初始化action表(部分)
public static void getActionMap()//初始化action
{
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("{", "s4");
Maction.put(1, map);
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("$","acc");
Maction.put(2, map);
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("$","r1");
Maction.put(3, map);
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("{","s4");
map.put("id","s7");
map.put("if","s8");
map.put("while","s9");
map.put("do","s10");
map.put("break","s11");
Maction.put(4, map);
}
(2)初始化goto表(部分)
public static void getGotoMap()//初始化goto
{
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("program","2");
map.put("block","2");
Mgoto.put(1, map);
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("block","12");
map.put("stst","5");
map.put("stmt","6");
Mgoto.put(4, map);
map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("block","12");
map.put("stst","14");
map.put("stmt","6");
Mgoto.put(6, map);
}
(3)初始化规则集
public static void newrule()//初始化规则
{
newtype("program","block",1,1);
newtype("block","{stst}",3,2);
newtype("stst","stmtstst",2,3);
newtype("stmt","id=expr;",4,4);
newtype("stmt","if(bool)stmt",5,5);
newtype("stmt","if(bool)elsestmt",6,6);
newtype("stmt","while(bool)stmt",5,7);
newtype("stmt","dostmtwhile(bool);",7,8);
newtype("stmt","break;",2,9);
newtype("stmt","block",1,10);
newtype("bool","expr<expr",3,11);
newtype("bool","expr<=expr",4,12);
newtype("bool","expr>expr",3,13);
newtype("bool","expr>=expr",4,14);
newtype("bool","expr",1,15);
newtype("expr","expr+term",3,16);
newtype("expr","expr-term",3,17);
newtype("expr","term",1,18);
newtype("term","term*term",3,19);
newtype("term","term/term",3,20);
newtype("term","factor",1,21);
newtype("factor","(expr)",3,22);
newtype("factor","id",1,23);
newtype("factor","num",1,24);
newtype("stst","stmt",1,25);
}
(1)初始化一条规则
public static void newtype(String right,String left,int pop,int key)
{
type type=new type();
type.right=right;
type.left=left;
type.pop=pop;
rule.put(key, type);
}
(5)查找非终结符
public static String isFinal(String a)//查找终结符
{
//找出first
StringBuffer a1=new StringBuffer();
boolean flag=false;
String a2=null;
for(int i=0;i<a.length();i++)
{
a1.append(a.charAt(i));
if(Final.contains(a1.toString()))
{
flag=true;
a2=a1.toString();
break;
}
}
if(flag)
return a2;
else
return null;
}
(6)初始化各种符号(部分)
public static void getTag()//初始化各种符号
{
Final.add("{");
Final.add("}");
Final.add("id");
Final.add("=");
Final.add("if");
Final.add("(");
Final.add(")");
Final.add("else");
Final.add("while");
Final.add("do");
}
(7)词法分析过程
public static void cifa(String s1) throws IOException//开始语法分析
{
stack.push(1);
stack1.push("$");
System.out.println("步骤 "+"状态栈 "+"符号栈 输入串 "+"action "+"goto ");
int step=1;
int top=1;
while(s1!=null)
{
if(isFinal(s1)!=null)//查找action表
{
Map<String,String> map1=new HashMap<>();
map1=Maction.get(top);//gai
if(map1!=null)
{
if(map1.containsKey(isFinal(s1)))//终结符action
{
String s2=map1.get(isFinal(s1));//操作
if(s2.charAt(0)=='r')//规约
{
String s3=s2.substring(1);
int i=Integer.parseInt(s3);//按照第几条规则规约
type type=new type();
type=rule.get(i);
int popnum=type.pop;//要弹出几条
print(step,stack.toString(),stack1.toString(),s1,"按照"+type.right+"->"+type.left+"的规则进行规约",0);
for(int flag=0;flag<popnum;flag++)
{
stack.pop();//状态栈弹出
stack1.pop();//符号栈弹出
}
top=stack.peek();//顶端
stack1.push(type.right);
Map<String,String> map2=new HashMap<>();
map2=Mgoto.get(top);//非终结符用goto
if(map2.containsKey(type.right))
{
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(map2.get(type.right)));
top=Integer.parseInt(map2.get(type.right));
}
else
{
System.out.println("error sen!");
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 :"+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1).getBytes());
break;
}
}
else if(s2.charAt(0)=='s')//移入
{
String s3=s2.substring(1);
print(step, stack.toString(), stack1.toString(),s1, s2, 1);
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s3));
top=Integer.parseInt(s3);//现在那个状态
stack1.push(isFinal(s1));
s1=s1.substring(isFinal(s1).length());
}
else if(s2.equals("acc"))
{
//归约成功
print(step, stack.toString(),stack1.toString(), s1, s2, 1);
p.write(("success!").getBytes());
System.out.println("
success!");
break;
}
}
else
{
//没有这个操作,出错
System.out.println("error");
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 : "+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1+"
").getBytes());
break;
}
}
else
{
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 : "+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1+"
").getBytes());
break;
}
}
else if (isNFinal(s1)!=null)//查找goto表
{
Map<String,String> map2=new HashMap<>();
map2=Mgoto.get(top);//非终结符用goto
if(map2!=null)
{
if(map2.containsKey(isNFinal(s1)))//非终结符有跳转
{
String s2=map2.get(isNFinal(s1));//跳转到哪
print(step,stack.toString(),stack1.toString(),s1,s2,0);
top=Integer.parseInt(s2);
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s2));
s1=s1.substring(isNFinal(s1).length());
}
else
{
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 :"+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1+"
").getBytes());
System.out.println("error sentence!");
break;
}
}
else
{
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 :"+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1+"
").getBytes());
break;
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("error!can not identify the word!");
p.write(("
语法错误!
当前状态 :"+top+"
无法解析符号 :"+s1+"
").getBytes());
break;
}
step+=1;//步骤加一
}
}
(8)main函数
public static void main(String []arg) throws IOException
{
getActionMap();
getGotoMap();
newrule();
getTag();
p=new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\Users\Mac\Desktop\result.txt"));
String str=input.getinput();
p.write(("分析代码
"+str+"
").getBytes());
cifa(str);
p.close();
}
函数调用图
测试数据
(1)
- 输入
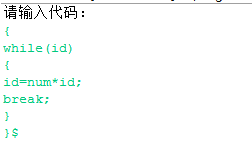
- 输出

(2) - 输入
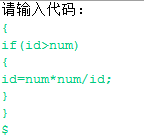
+输出

(3) - 输入
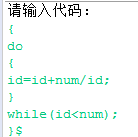
- 输出

(4)错误 - 输入

+输出

错误原因:将变量赋值给常量
总结
在这次实验之前,我只知道LR(1)求向前看符的方法,但是并不知道为什么要用first求。经过这次实验,我才知道规约的话要在下一个输入为规约后式子的规约符号下一个符号的first集中才规约,这样可以缩小规约范围,及时排错。
这次实验最大的困难就是递归求LR(1)表,但是我不太会递归就只能手动画LR(1)表了,也算为理论考试做准备。然后就出来了58个状态,最大的问题就是容易忘记在状态中加入新的规则,这一点在理论考试的时候要多加注意。