沉淀,再出发:XPath的理解和使用
一、前言
在很多查找的场合之下,我们需要使用正则表达式和其他的查找工具来进行内容的匹配和查找,特别是对于xml文件,我们可以使用xpath等工具来进行查找,通过树状结构我们可以很容易的对其中的元素,节点进行定位从而获取相应的内容,这样方便我们代码的规范性和可读性。
二、XPath的简介和使用
2.1、XPath简介
XPath 是一门在 XML 文档中查找信息的语言。XPath 是 XSLT 中的主要元素。XPath 于 1999 年 11 月 16 日 成为 W3C 标准。XQuery 和 XPointer 均构建于 XPath 表达式之上。XPath 使用路径表达式来选取 XML 文档中的节点或者节点集。这些路径表达式和我们在常规的电脑文件系统中看到的表达式非常相似。XPath 含有超过 100 个内建的函数(BIF)。这些函数用于字符串值、数值、日期和时间比较、节点和 QName 处理、序列处理、逻辑值等等。
2.2、XPath 术语
节点:在 XPath 中,有七种类型的节点:元素、属性、文本、命名空间、处理指令、注释以及文档(根)节点。XML 文档是被作为节点树来对待的。树的根被称为文档节点或者根节点。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> 2 <bookstore> 3 <book> 4 <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title> 5 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 6 <year>2005</year> 7 <price>29.99</price> 8 </book> 9 </bookstore>
上面的XML文档中的节点例子:
<bookstore> (文档节点) <author>J K. Rowling</author> (元素节点) lang="en" (属性节点) 基本值(或称原子值,Atomic value):基本值是无父或无子的节点。 基本值的例子: J K. Rowling "en" 项目(Item):项目是基本值或者节点。
节点关系:
1 父(Parent):每个元素以及属性都有一个父。 2 在下面的例子中,book 元素是 title、author、year 以及 price 元素的父: 3 <book> 4 <title>Harry Potter</title> 5 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 6 <year>2005</year> 7 <price>29.99</price> 8 </book> 9 子(Children):元素节点可有零个、一个或多个子。 10 在下面的例子中,title、author、year 以及 price 元素都是 book 元素的子: 11 <book> 12 <title>Harry Potter</title> 13 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 14 <year>2005</year> 15 <price>29.99</price> 16 </book> 17 同胞(Sibling):拥有相同的父的节点 18 在下面的例子中,title、author、year 以及 price 元素都是同胞: 19 <book> 20 <title>Harry Potter</title> 21 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 22 <year>2005</year> 23 <price>29.99</price> 24 </book> 25 先辈(Ancestor):某节点的父、父的父,等等。 26 在下面的例子中,title 元素的先辈是 book 元素和 bookstore 元素: 27 <bookstore> 28 <book> 29 <title>Harry Potter</title> 30 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 31 <year>2005</year> 32 <price>29.99</price> 33 </book> 34 </bookstore> 35 后代(Descendant):某个节点的子,子的子,等等。 36 在下面的例子中,bookstore 的后代是 book、title、author、year 以及 price 元素: 37 <bookstore> 38 <book> 39 <title>Harry Potter</title> 40 <author>J K. Rowling</author> 41 <year>2005</year> 42 <price>29.99</price> 43 </book> 44 </bookstore>
2.3、XPath 语法
XPath 使用路径表达式来选取 XML 文档中的节点或节点集。节点是通过沿着路径 (path) 或者步 (steps) 来选取的。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> 2 3 <bookstore> 4 5 <book> 6 <title lang="eng">Harry Potter</title> 7 <price>29.99</price> 8 </book> 9 10 <book> 11 <title lang="eng">Learning XML</title> 12 <price>39.95</price> 13 </book> 14 15 </bookstore>
选取节点:XPath 使用路径表达式在 XML 文档中选取节点。节点是通过沿着路径或者 step 来选取的。 下面列出了最有用的路径表达式:
1 表达式 描述 2 nodename 选取此节点的所有子节点。 3 / 从根节点选取。 4 // 从匹配选择的当前节点选择文档中的节点,而不考虑它们的位置。 5 . 选取当前节点。 6 .. 选取当前节点的父节点。 7 @ 选取属性。
1 路径表达式 结果 2 bookstore 选取 bookstore 元素的所有子节点。 3 /bookstore 选取根元素 bookstore。 4 注释:假如路径起始于正斜杠( / ),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径! 5 bookstore/book 选取属于 bookstore 的子元素的所有 book 元素。 6 //book 选取所有 book 子元素,而不管它们在文档中的位置。 7 bookstore//book 选择属于 bookstore 元素的后代的所有 book 元素,而不管它们位于 bookstore 之下的什么位置。 8 //@lang 选取名为 lang 的所有属性。
谓语(Predicates):谓语用来查找某个特定的节点或者包含某个指定的值的节点。谓语被嵌在方括号中。
1 路径表达式 结果 2 /bookstore/book[1] 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的第一个 book 元素。 3 /bookstore/book[last()] 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的最后一个 book 元素。 4 /bookstore/book[last()-1] 选取属于 bookstore 子元素的倒数第二个 book 元素。 5 /bookstore/book[position()<3] 选取最前面的两个属于 bookstore 元素的子元素的 book 元素。 6 //title[@lang] 选取所有拥有名为 lang 的属性的 title 元素。 7 //title[@lang='eng'] 选取所有 title 元素,且这些元素拥有值为 eng 的 lang 属性。 8 /bookstore/book[price>35.00] 选取 bookstore 元素的所有 book 元素,且其中的 price 元素的值须大于 35.00。 9 /bookstore/book[price>35.00]/title 选取 bookstore 元素中的 book 元素的所有 title 元素,且其中的 price 元素的值须大于 35.00。
选取未知节点:XPath 通配符可用来选取未知的 XML 元素。
1 通配符 描述 2 * 匹配任何元素节点。 3 @* 匹配任何属性节点。 4 node() 匹配任何类型的节点。
1 路径表达式 结果 2 /bookstore/* 选取 bookstore 元素的所有子元素。 3 //* 选取文档中的所有元素。 4 //title[@*] 选取所有带有属性的 title 元素。
选取若干路径:通过在路径表达式中使用"|"运算符,您可以选取若干个路径。
1 路径表达式 结果 2 //book/title | //book/price 选取 book 元素的所有 title 和 price 元素。 3 //title | //price 选取文档中的所有 title 和 price 元素。 4 /bookstore/book/title | //price 选取属于 bookstore 元素的 book 元素的所有 title 元素,以及文档中所有的 price 元素。
2.4、XPath 轴(Axes)
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> 2 3 <bookstore> 4 5 <book> 6 <title lang="eng">Harry Potter</title> 7 <price>29.99</price> 8 </book> 9 10 <book> 11 <title lang="eng">Learning XML</title> 12 <price>39.95</price> 13 </book> 14 15 </bookstore>
XPath 轴(Axes):轴可定义相对于当前节点的节点集。
1 轴名称 结果 2 ancestor 选取当前节点的所有先辈(父、祖父等)。 3 ancestor-or-self 选取当前节点的所有先辈(父、祖父等)以及当前节点本身。 4 attribute 选取当前节点的所有属性。 5 child 选取当前节点的所有子元素。 6 descendant 选取当前节点的所有后代元素(子、孙等)。 7 descendant-or-self 选取当前节点的所有后代元素(子、孙等)以及当前节点本身。 8 following 选取文档中当前节点的结束标签之后的所有节点。 9 namespace 选取当前节点的所有命名空间节点。 10 parent 选取当前节点的父节点。 11 preceding 选取文档中当前节点的开始标签之前的所有节点。 12 preceding-sibling 选取当前节点之前的所有同级节点。 13 self 选取当前节点。
2.5、XPath 运算符
1 运算符 描述 实例 返回值 2 | 计算两个节点集 //book | //cd 返回所有拥有 book 和 cd 元素的节点集 3 + 加法 6 + 4 10 4 - 减法 6 - 4 2 5 * 乘法 6 * 4 24 6 div 除法 8 div 4 2 7 = 等于 price=9.80 8 != 不等于 price!=9.80 9 < 小于 price<9.80 10 <= 小于或等于 price<=9.80 11 > 大于 price>9.80 12 >= 大于或等于 price>=9.80 13 or 或 price=9.80 or price=9.70 14 and 与 price>9.00 and price<9.90 15 mod 计算除法的余数 5 mod 2 1
2.6、XPath 实例

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <bookstore> <book category="COOKING"> <title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title> <author>Giada De Laurentiis</author> <year>2005</year> <price>30.00</price> </book> <book category="CHILDREN"> <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K. Rowling</author> <year>2005</year> <price>29.99</price> </book> <book category="WEB"> <title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title> <author>James McGovern</author> <author>Per Bothner</author> <author>Kurt Cagle</author> <author>James Linn</author> <author>Vaidyanathan Nagarajan</author> <year>2003</year> <price>49.99</price> </book> <book category="WEB"> <title lang="en">Learning XML</title> <author>Erik T. Ray</author> <year>2003</year> <price>39.95</price> </book> </bookstore>
加载 XML 文档:
所有现代浏览器都支持使用 XMLHttpRequest 来加载 XML 文档的方法。
针对大多数现代浏览器的代码:
var xmlhttp=new XMLHttpRequest()
针对古老的微软浏览器(IE 5 和 6)的代码:
var xmlhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP")
选取节点:Internet Explorer 和其他处理 XPath 的方式不同。
Internet Explorer 使用 selectNodes() 方法从 XML 文档中的选取节点:
xmlDoc.selectNodes(xpath);
Firefox、Chrome、Opera 以及 Safari 使用 evaluate() 方法从 XML 文档中选取节点:
xmlDoc.evaluate(xpath, xmlDoc, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE,null);
2.6.1、选取所有 title
/bookstore/book/title
1 <html> 2 3 <body> 4 <script> 5 function loadXMLDoc(dname) 6 { 7 if (window.XMLHttpRequest) 8 { 9 xhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); 10 } 11 else 12 { 13 xhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); 14 } 15 xhttp.open("GET",dname,false); 16 xhttp.send(""); 17 return xhttp.responseXML; 18 } 19 20 xml=loadXMLDoc("books.xml"); 21 path="/bookstore/book/title" 22 // code for IE 23 if (window.ActiveXObject) 24 { 25 var nodes=xml.selectNodes(path); 26 27 for (i=0;i<nodes.length;i++) 28 { 29 document.write(nodes[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue); 30 document.write("<br>"); 31 } 32 } 33 // code for Mozilla, Firefox, Opera, etc. 34 else if (document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument) 35 { 36 var nodes=xml.evaluate(path, xml, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE, null); 37 var result=nodes.iterateNext(); 38 39 while (result) 40 { 41 document.write(result.childNodes[0].nodeValue); 42 document.write("<br>"); 43 result=nodes.iterateNext(); 44 } 45 } 46 </script> 47 48 </body></html>
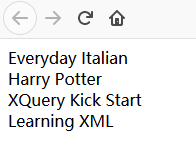
2.6.2、选取第一个 book 的 title
/bookstore/book[1]/title
1 <html> 2 3 <body> 4 <script> 5 function loadXMLDoc(dname) 6 { 7 if (window.XMLHttpRequest) 8 { 9 xhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); 10 } 11 else 12 { 13 xhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); 14 } 15 xhttp.open("GET",dname,false); 16 xhttp.send(""); 17 return xhttp.responseXML; 18 } 19 20 xml=loadXMLDoc("books.xml"); 21 path="/bookstore/book[1]/title"; 22 // code for IE 23 if (window.ActiveXObject) 24 { 25 var nodes=xml.selectNodes(path); 26 27 for (i=0;i<nodes.length;i++) 28 { 29 document.write(nodes[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue); 30 document.write("<br>"); 31 } 32 } 33 // code for Mozilla, Firefox, Opera, etc. 34 else if (document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument) 35 { 36 var nodes=xml.evaluate(path, xml, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE,null); 37 var result=nodes.iterateNext(); 38 39 while(result) 40 { 41 document.write(result.childNodes[0].nodeValue); 42 document.write("<br>"); 43 result=nodes.iterateNext(); 44 } 45 } 46 </script> 47 48 </body></html>
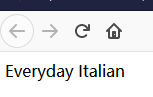
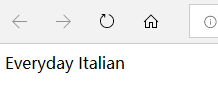
上面的例子IE5 以及更高版本将 [0] 视为第一个节点,而根据 W3C 的标准,应该是 [1]。为了解决 IE5+ 中 [0] 和 [1] 的问题,可以为 XPath 设置语言选择(SelectionLanguage)。
1 <html> 2 3 <body> 4 <script> 5 function loadXMLDoc(dname) 6 { 7 if (window.XMLHttpRequest) 8 { 9 xhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); 10 } 11 else 12 { 13 xhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); 14 } 15 xhttp.open("GET",dname,false); 16 xhttp.send(""); 17 return xhttp.responseXML; 18 } 19 20 xml=loadXMLDoc("books.xml"); 21 path="/bookstore/book[1]/title"; 22 // code for IE 23 if (window.ActiveXObject) 24 { 25 xml.setProperty("SelectionLanguage","XPath"); 26 var nodes=xml.selectNodes(path); 27 28 for (i=0;i<nodes.length;i++) 29 { 30 document.write(nodes[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue); 31 document.write("<br>"); 32 } 33 } 34 // code for Mozilla, Firefox, Opera, etc. 35 else if (document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument) 36 { 37 var nodes=xml.evaluate(path, xml, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE,null); 38 var result=nodes.iterateNext(); 39 40 while (result) 41 { 42 document.write(result.childNodes[0].nodeValue); 43 document.write("<br>"); 44 result=nodes.iterateNext(); 45 } 46 } 47 </script> 48 49 </body></html>
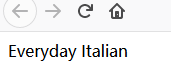
2.6.3、选取所有价格:选取 price 节点中的所有文本
/bookstore/book/price/text()

1 <html> 2 3 <body> 4 <script> 5 function loadXMLDoc(dname) 6 { 7 if (window.XMLHttpRequest) 8 { 9 xhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); 10 } 11 else 12 { 13 xhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); 14 } 15 xhttp.open("GET",dname,false); 16 xhttp.send(""); 17 return xhttp.responseXML; 18 } 19 20 xml=loadXMLDoc("books.xml"); 21 path="/bookstore/book/price/text()" 22 // code for IE 23 if (window.ActiveXObject) 24 { 25 var nodes=xml.selectNodes(path); 26 27 for (i=0;i<nodes.length;i++) 28 { 29 document.write(nodes[i].nodeValue); 30 document.write("<br>"); 31 } 32 } 33 // code for Mozilla, Firefox, Opera, etc. 34 else if (document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument) 35 { 36 var nodes=xml.evaluate(path, xml, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE,null); 37 var result=nodes.iterateNext(); 38 39 while (result) 40 { 41 document.write(result.nodeValue + "<br>"); 42 result=nodes.iterateNext(); 43 } 44 } 45 </script> 46 47 </body></html>

2.6.4、选取价格高于 35 的 price 节点
/bookstore/book[price>35]/price

1 <html> 2 3 <body> 4 <script> 5 function loadXMLDoc(dname) 6 { 7 if (window.XMLHttpRequest) 8 { 9 xhttp=new XMLHttpRequest(); 10 } 11 else 12 { 13 xhttp=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); 14 } 15 xhttp.open("GET",dname,false); 16 xhttp.send(""); 17 return xhttp.responseXML; 18 } 19 20 xml=loadXMLDoc("books.xml"); 21 path="/bookstore/book[price>35]/price"; 22 // code for IE 23 if (window.ActiveXObject) 24 { 25 var nodes=xml.selectNodes(path); 26 27 for (i=0;i<nodes.length;i++) 28 { 29 document.write(nodes[i].childNodes[0].nodeValue); 30 document.write("<br>"); 31 } 32 } 33 // code for Mozilla, Firefox, Opera, etc. 34 else if (document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument) 35 { 36 var nodes=xml.evaluate(path, xml, null, XPathResult.ANY_TYPE,null); 37 var result=nodes.iterateNext(); 38 39 while (result) 40 { 41 document.write(result.childNodes[0].nodeValue); 42 document.write("<br>"); 43 result=nodes.iterateNext(); 44 } 45 } 46 </script> 47 48 </body></html>

1 XSLT 是针对 XML 文件的样式表语言。通过 XSLT,可以把 XML 文件转换为其他的格式,比如 XHTML。 2 XQuery 和 XML 数据查询有关。XQuery 被设计用来查询任何可作为 XML 形态呈现的数据,包括数据库。 3 XLink 和 XPointer,XML 中的链接被分为两个部分:XLink 和 XPointer。XLink 和 XPointer 定义了在 XML 文档中创建超级链接的标准方法。
三、总结
通过对XPath的学习,我们可以更加深刻地理解xml这种树状结构,以及对这种结构的查找遍历方法,方便对网页的抓取和解析。
参考文献:https://code.ziqiangxuetang.com/xpath/xpath-tutorial.html
