201871010135 张玉晶《面向对象程序设计(java)》第6-7周学习总结
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11605051.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
1.深入理解程序设计中算法与程序的关系; 2.深入理解java程序设计中类与对象的关系; 3.理解OO程序设计的第2个特征:继承、多态; 4.学会采用继承定义类设计程序(重点、难点); 5.能够分析与设计至少包含3个自定义类的程序; 6.掌握利用父类定义子类的语法规则及对象使用要求。 |
第一部分:总结第五章理论知识
一 .继承:
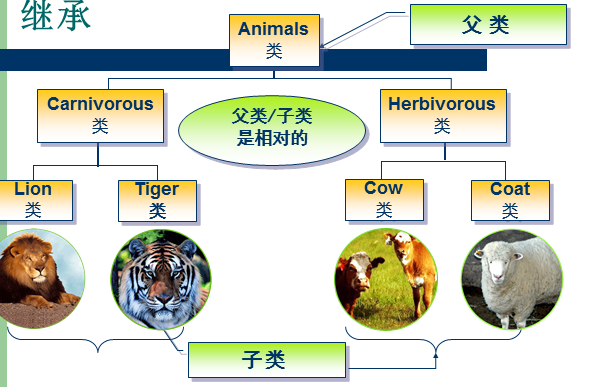
1. 继承:用已有的类来构建新类的一种机制。子类继承了父类的域和方法,同时也添加新的域和方法以适应新情况。
2. 类继承的格式:
class 新类名(子类) extends 已有类名(父类,超类)
a) 子类的构造器不能直接访问超类的私有域,必须调用超类构造器,而且必须是第一条语句。 super();
b) 子类不能直接访问超类的私有域,必须和其它方法一样,使用公共接口。 super.方法名();
c) 父类对象可以引用子类对象。
d) 多态性质。(在程序中同一个符号在不同情况下具有不同解释的想象)
e) 子类可增加父类的域的方法或覆盖,但不可以删除父类的任何方法及域。 方法覆盖只在不同的类中完成。
3. 继承层次:从一个超类扩展而来的类集合称为继承层次。
a)java 只支持单继承。(只有一个父类,可由多个子类)
b) 继承层次结构中,每个子类对象也可视作是超类对象,因此,可以将子类对象赋给超类变量。
4. 抽象类 abstract方法,只能声明,不能实现。
a) 包含一个或多个抽象方法的类本身必须被声明为抽象类;
b) 抽象方法充当着占位的角色,它们的具体实现在子类中;
c) 抽象类不能被实例化,既不能创建对象,只能产生子类。
5. 动态绑定 : 又称为运行时绑定,即程序在运行时会自动选择调用哪个方法。
6. 阻止继承: final类的方法 不允许继承的类称为 final 类。
7. 强制类型转换 : 把一个超类对象赋给一个子类变量,就必须进行强制类型转换。
8. 访问修饰符: public private protected 默认。
二 . Object : 所有类的超类
1. equals : 用于测试某个对象是否同另一个对象相等。
定义子类的equals 方法时,可调用超类的 equals 方法。 super.equals (otherObject)
2. hashCode方法 : 用于导出某个对象的散列码 ----表示对象的存储地址。两个相等对象的散列码相等。
3. toString 方法 : 用于返回一个代表该对象域值的字符串。 定义子类的toString方法时,可先调用超类的toString方法. super.toString()
三. 泛型数组列表
1. Java中 利用ArrayList类,可允许程序在运行时确定数组的大小。
2. ArrayList 是一个采用类型参数的泛型类,为指定数组列表保存元素的对象类型,需要用一对<>将数组元素的对象名括起来加在后面; ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<Employee>();
3. 数组列表的操作
a) ArrayList 定义 ArrayList <T> staff = new ArrayList<T>(); ArrayList<T>()构造一个空的数组列表
b) 添加新元素 API : boolean add(T obj) 把元素obj 追加到数组列表的结尾
c) 统计个数 API : int size() 返回数组列表中当前元素的个数
d) 调整大小 API :void trimToSize() 把数组列表的存储空间调整到当前大小
e) 访问 API : void set(int index, T obj) 将obj放入数组列表index位置,将覆盖这个位置的原有内容。
API : T get (int index) 获得指定位置index 的元素值
f) 增加与删除 API : boolean add(int index , T obj) 向后移动元素,在第n个位置插入 obj
API : T remove (int index) ; 将第n个位置存放的对象删除,并将后面的元素向前移动
四. 对象包装器与自动打包
1. 所有基本数据类型都有着与之对应的预定义类,它们被称为对象包装器。
2. Integer Long Float Double Short Byte Character Void Boolean (前六个包装器类都是从公共包装器累Number继承而来
3. 对象包装器类是不可变的。对象包装器类还是final , 因此不能定义它们的子类。
4. 可以自动将基本数据类型转换为包装器类对象, 将这种变换称为自动打包。
5. 当对一个包装器类的对象进行赋值或算法运算时,将会自动拆包。
6. 打包和拆包是编译器认可的。
五. 枚举类
1. 声明枚举类 public enum Grade {A , B , C , D , E }
a) 枚举类是一个类,它的隐含超类是 java. lang. Enum.
b) 枚举类并不是整数或其他类型,是被声明的枚举类的自身实例。
c) 枚举类不能有 public 修饰的构造函数,构造函数都是隐含private,编译器自动处理。
d) 枚举值隐含都是由 public , static, final 修饰的,无需自己添加这些修饰。
e) 比较两个枚举类型的值时,永远不要调用 equals 方法,直接使用“==”进行相等比较。
六. 继承设计的技巧
a) 将公共操作和域放在超类。
b) 不要使用受保护的域。
c) 使用继承实现"is-a"关系。
d) 除非所有继承的方法都有意义, 否则就不要使用继承。
e) 在覆盖方法时, 不要改变预期的行为。
f) 使用多态,而非类型信息。
第二部分:实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解继承的定义;
(2) 掌握子类的定义要求
(3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法;
(4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第5章示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
Ÿ 在elipse IDE中编辑、调试、运行程序5-1 —5-3(教材152页-153页) ;
Ÿ 掌握子类的定义及用法;
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解并总结OO风格程序构造特点,理解Employee和Manager类的关系子类的用途,并在代码中添加注释;
Ÿ 删除程序中Manager类、ManagerTest类,背录删除类的程序代码,在代码录入中理解父类与子类的关系和使用特点。
5-1 ManagerTest.java
程序代码如下:
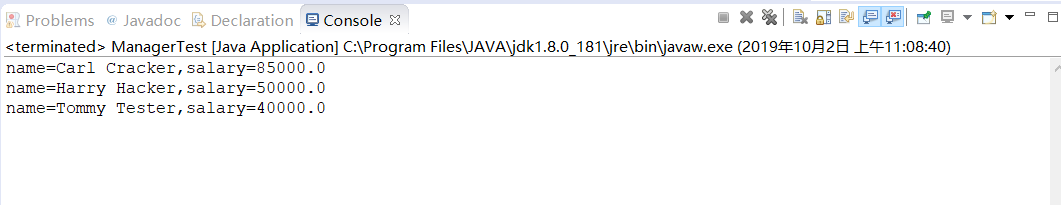
1 /** 2 * This program demonstrates inheritance. 3 * @version 1.21 2004-02-21 4 * @author Cay Horstmann 5 */ 6 public class ManagerTest 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 // construct a Manager object 11 Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); //创建了一个Manager类 12 boss.setBonus(5000); 13 14 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; //定义了一个三个雇员的数组staff 15 16 // fill the staff array with Manager and Employee objects 17 //用Manager和Employee对象对数组进行初始化 18 staff[0] = boss; 19 staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 20 staff[2] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); 21 22 // print out information about all Employee objects 23 for (Employee e : staff) //利用了for each 循环语句,打印出关于Employee类的所有信息 24 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); 25 } 26 }
运行结果如下:
5-2 Employee.java
程序代码如下:
1 import java.time.*; 2 3 public class Employee 4 { 5 private String name; 6 private double salary; 7 private LocalDate hireDay; 8 9 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 10 { 11 this.name = name; 12 this.salary = salary; 13 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 14 } 15 16 public String getName() 17 { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public double getSalary() 22 { 23 return salary; 24 } 25 26 public LocalDate getHireDay() 27 { 28 return hireDay; 29 } 30 31 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 32 { 33 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 34 salary += raise; 35 } 36 }
运行结果如下:
5-3 Manager.java
程序代码如下:
1 public class Manager extends Employee //利用extends关键字,用Employee类派生出Manager 2 { 3 private double bonus; 4 5 /** 6 * @param name the employee's name 7 * @param salary the salary 8 * @param year the hire year 9 * @param month the hire month 10 * @param day the hire day 11 */ 12 public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 13 { 14 super(name, salary, year, month, day); //利用super关键字,调用超类的构造器 15 bonus = 0; 16 } 17 18 public double getSalary() 19 { 20 double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); //利用super关键字,调用超类的方法 21 return baseSalary + bonus; 22 } 23 24 public void setBonus(double b) 25 { 26 bonus = b; 27 } 28 }
运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材PersonTest程序(教材163页-165页);
Ÿ 掌握超类的定义及其使用要求;
Ÿ 掌握利用超类扩展子类的要求;
Ÿ 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
Ÿ 删除程序中Person类、PersonTest类,背录删除类的程序代码,在代码录入中理解抽象类与子类的关系和使用特点。
5-4 PersonTest.java
程序代码如下:
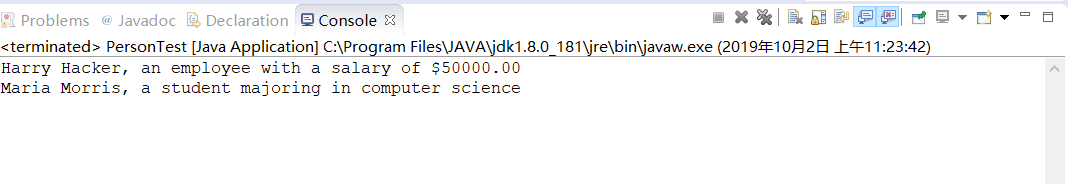
1 /** 2 * This program demonstrates abstract classes. 3 * @version 1.01 2004-02-21 4 * @author Cay Horstmann 5 */ 6 public class PersonTest 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 Person[] people = new Person[2]; 11 12 //用Student和Employee类填充people这个数组 13 people[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 14 people[1] = new Student("Maria Morris", "computer science"); 15 16 //打印出所有Person类的姓名和描述 17 for (Person p : people) 18 System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getDescription()); 19 } 20 }
运行结果如下:
5-5 Person.java
程序代码如下:
1 public abstract class Person //定义抽象类型Person 2 { 3 public abstract String getDescription(); //定义抽象描述 4 private String name; 5 6 public Person(String name) 7 { 8 this.name = name; 9 } 10 11 public String getName() 12 { 13 return name; 14 } 15 }
运行结果如下:

5-6 Employee.java
程序代码如下:
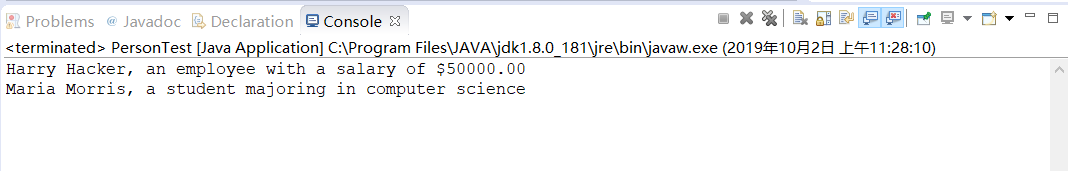
1 import java.time.*; 2 3 public class Employee extends Person //子类Employee继承父类Person 4 { 5 private double salary; 6 private LocalDate hireDay; 7 8 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 9 { 10 super(name);//调用父类构造器 11 this.salary = salary; 12 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); //hireDay使用LocalDate的方法 13 } 14 15 public double getSalary() 16 { 17 return salary; 18 } 19 20 public LocalDate getHireDay() 21 { 22 return hireDay; 23 } 24 25 public String getDescription() 26 { 27 return String.format("an employee with a salary of $%.2f", salary); 28 } 29 30 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 31 { 32 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 33 salary += raise; 34 } 35 }
运行结果如下:
5-7 Student.java
程序代码如下:
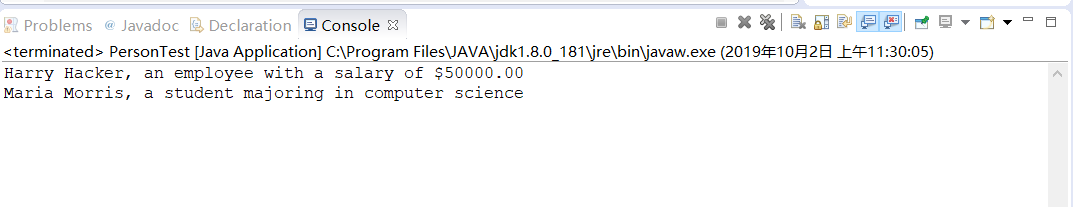
1 public class Student extends Person //子类Student继承父类Person 2 { 3 private String major; 4 5 /** 6 * @param name the student's name 7 * @param major the student's major 8 */ 9 public Student(String name, String major) 10 { 11 // pass name to superclass constructor 12 super(name); //将name传递给父类的构造函数 13 this.major = major; 14 } 15 16 public String getDescription() 17 { 18 return "a student majoring in " + major; 19 } 20 }
运行结果如下:
测试程序3:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
Ÿ 掌握Object类的定义及用法;
Ÿ 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
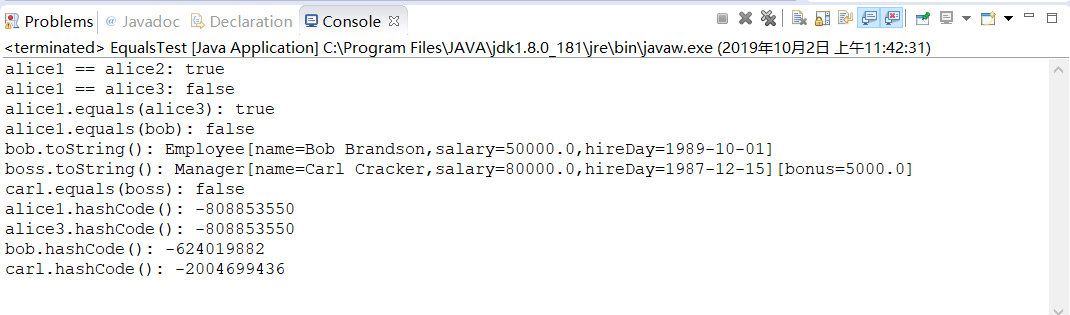
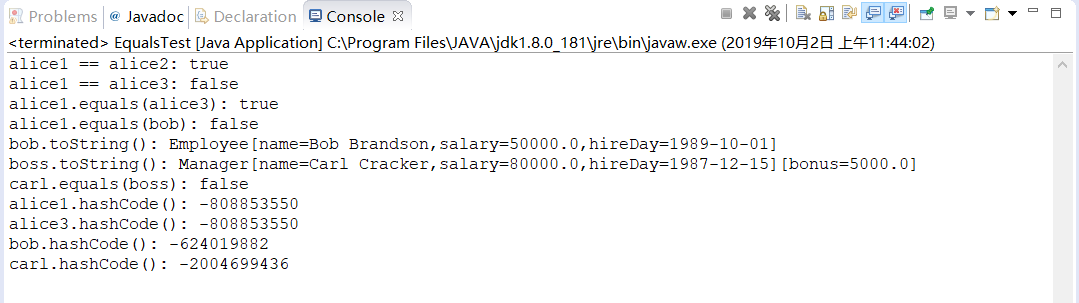
5-8 Equals Test.java
程序代码如下:
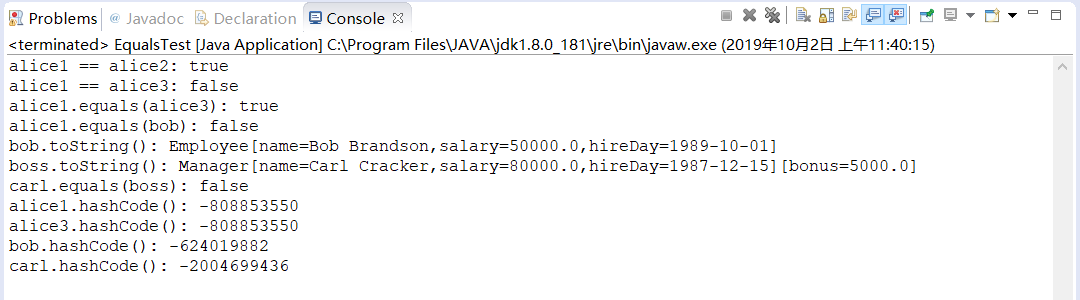
1 /** 2 * This program demonstrates the equals method. 3 * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 4 * @author Cay Horstmann 5 */ 6 public class EqualsTest 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); 11 Employee alice2 = alice1; 12 Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); 13 Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 14 15 System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); 16 17 System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); 18 19 System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); 20 21 System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); 22 23 System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); 24 25 Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); 26 Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); 27 boss.setBonus(5000); 28 System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); 29 System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); 30 System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); 31 System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); 32 System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); 33 System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); 34 } 35 }
运行结果如下:
5-9 Employee.java
程序代码如下:
1 import java.time.*; 2 import java.util.Objects; 3 4 public class Employee 5 { 6 private String name; 7 private double salary; 8 private LocalDate hireDay; 9 10 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 11 { 12 this.name = name; 13 this.salary = salary; 14 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 15 } 16 17 public String getName() 18 { 19 return name; 20 } 21 22 public double getSalary() 23 { 24 return salary; 25 } 26 27 public LocalDate getHireDay() 28 { 29 return hireDay; 30 } 31 32 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 33 { 34 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 35 salary += raise; 36 } 37 38 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 39 { 40 //快速测试,看看这些对象是否相同 41 if (this == otherObject) return true; 42 43 // 如果显示参数为空,则必须返回false 44 if (otherObject == null) return false; 45 46 //如果类不匹配,它们就不能相等 47 if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; 48 49 // 现在我们知道 otherObject是一个非空雇员 50 Employee other = (Employee) otherObject; 51 52 // 测试字段是否具有相同的值 53 return Objects.equals(name, other.name) 54 && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); 55 } 56 57 public int hashCode() // 58 { 59 return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); 60 } 61 62 public String toString() 63 { 64 return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" 65 + hireDay + "]"; 66 } 67 }
运行结果如下:
5-10 Manager.java
程序代码如下:
1 public class Manager extends Employee //子类Employee继承父类Manager 2 { 3 private double bonus; 4 5 public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 6 { 7 super(name, salary, year, month, day); // //利用super关键字,调用超类的构造器 8 bonus = 0; 9 } 10 11 public double getSalary() 12 { 13 double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); 14 return baseSalary + bonus; 15 } 16 17 public void setBonus(double bonus) 18 { 19 this.bonus = bonus; 20 } 21 22 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 23 { 24 if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; 25 Manager other = (Manager) otherObject; 26 // super.equals 检查这个和其他属于同一类 27 return bonus == other.bonus; 28 } 29 30 public int hashCode() 31 { 32 return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); 33 } 34 35 public String toString() 36 { 37 return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; 38 } 39 }
运行结果如下:
实验2:编程练习
Ÿ 定义抽象类Shape:
属性:不可变常量double PI,值为3.14;
方法:public double getPerimeter();public double getArea())。
Ÿ 让Rectangle与Circle继承自Shape类。
Ÿ 编写double sumAllArea方法输出形状数组中的面积和和double sumAllPerimeter方法输出形状数组中的周长和。
Ÿ main方法中
1)输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则再输入长和宽。如果输入cir,则再输入半径。
2) 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。
3) 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型,使用类似shape.getClass()(获得类型),shape.getClass().getSuperclass()(获得父类型);
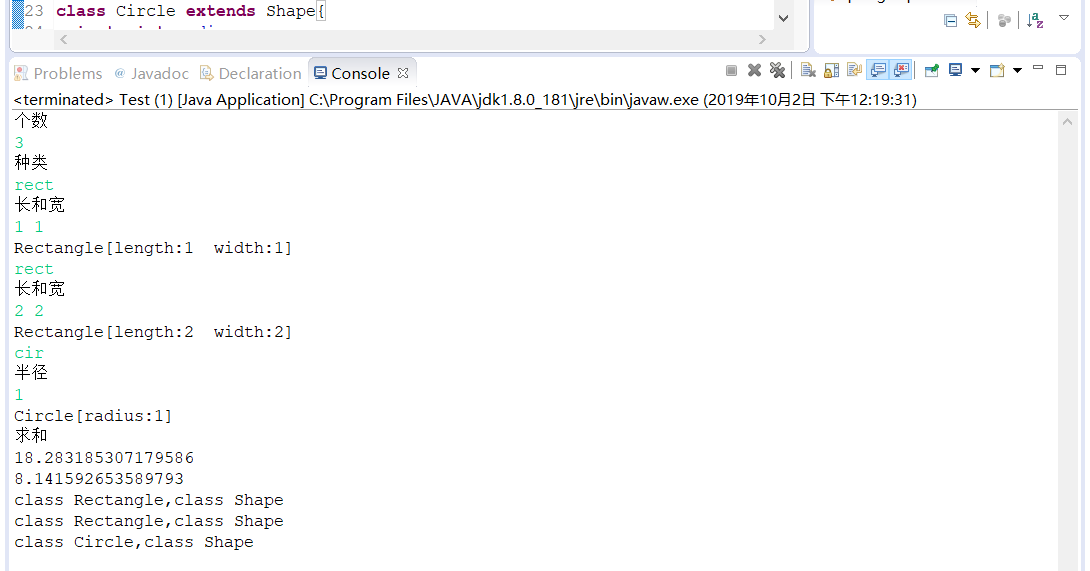
输入样例:
| 3 |
| rect |
| 1 1 |
| rect |
| 2 2 |
| cir |
| 1 |
输出样例:
| 18.28 |
| 8.14 |
|
[Rectangle [width=1, length=1], Rectangle [width=2, length=2], Circle [radius=1]] |
|
class Rectangle,class Shape |
|
class Rectangle,class Shape |
|
class Circle,class Shape |
程序代码:
Test.java:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Test { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 System.out.println("个数"); 6 int a = in.nextInt(); 7 System.out.println("种类"); 8 String rect="rect"; 9 String cir="cir"; 10 Shape[] num = new Shape[a]; 11 for(int i=0;i<a;i++){ 12 String input=in.next(); 13 if(input.equals(rect)) { 14 System.out.println("长和宽"); 15 int length = in.nextInt(); 16 int width = in.nextInt(); 17 num[i]=new Rectangle(width,length); 18 System.out.println("Rectangle["+"length:"+length+" "+width+"]"); 19 } 20 if(input.equals(cir)) { 21 System.out.println("半径"); 22 int radius = in.nextInt(); 23 num[i]=new Circle(radius); 24 System.out.println("Circle["+"radius:"+radius+"]"); 25 } 26 } 27 Test c=new Test(); 28 System.out.println("求和"); 29 System.out.println(c.sumAllPerimeter(num)); 30 System.out.println(c.sumAllArea(num)); 31 32 for(Shape s:num) { 33 System.out.println(s.getClass()+","+s.getClass().getSuperclass()); 34 } 35 } 36 37 public double sumAllArea(Shape score[]) 38 { 39 double sum=0; 40 for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++) 41 sum+= score[i].getArea(); 42 return sum; 43 } 44 public double sumAllPerimeter(Shape score[]) 45 { 46 double sum=0; 47 for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++) 48 sum+= score[i].getPerimeter(); 49 return sum; 50 } 51 }
shape.java:
1 abstract class Shape { //定义抽象父类Shape 2 abstract double getPerimeter(); //定义求解周长的方法 3 abstract double getArea(); //定义求解面积的方法 4 } 5 6 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 7 private int length; 8 private int width; 9 public Rectangle(int length, int width) { 10 this.length = length; 11 this.width = width; 12 } 13 //继承父类 14 double getPerimeter(){ //调用父类求周长的方法 15 return 2*(length+width); 16 } 17 double getArea(){ 18 return length*width; //调用父类求面积的方法 19 } 20 } 21 22 class Circle extends Shape{ 23 private int radius; 24 public Circle(int radius) { 25 this.radius = radius; 26 } 27 double getPerimeter(){ 28 return 2 * Math.PI * radius; 29 } 30 double getArea(){ 31 return Math.PI * radius * radius; 32 } 33 }
运行结果:
实验总结: 在这一章中,我学到了“继承”这一重要部分,在继承中,用到了extends关键字,子类继承了父类的域和方法,同时也添加新的域和方法以适应新情况。子类的构造器不能直接访问超类的私有域,必须调用超类构造器,super(); 子类不能直接访问超类的私有域,必须要用到,super.方法名();但是父类对象可以直接引用子类对象, 子类可以增加父类的域的方法或覆盖,但不可以删除父类的任何方法和域。Java只支持单继承,也就是只能有一个父类,但可以有多个子类。 Object类是所有类的超类,equals方法和toString方法比较重要,其中equals方法用于比较两个 对象是否相等。 在数组列表中,用到了ArrayList这个关键字,它是ArrayList <T> staff = new ArrayList<T>来定义的。 还有对象包装器与自动打包以及枚举类。
在实验中我遇到了很多困难,包括程序有些错误改不过来,有时候不知道错在了哪里,以及题目不太理解等情况。 在实验中有重复用到了extends关键字以及super的应用,所以因此也巩固了这一方面的理解, 通过向同学寻求帮助以及找资料搜索,解决了这些问题, 当然我自己也会在后期努力。