# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base1{
public:
Base1(int m,int n):a(m),b(n){
cout<<a<<"+"<<b<<"="<<a+b<<endl;
}
private:
int a;
int b;
};
class chipA: virtual public Base1{
public:
chipA(int m,int n):Base1(m,n),x(m),y(n){};
void cal1(){
cout<<x<<"-"<<y<<"="<<x-y<<endl;
}
private:
int x,y;
};
class chipB:virtual public Base1{
public:
chipB(int m,int n):Base1(m,n),x(m),y(n){};
void cal2(){
cout<<x<<"*"<<y<<"="<<x*y<<endl;
}
private:
int x,y;
};
class chipC:virtual public Base1{
public:
chipC(int m,int n):Base1(m,n),x(m),y(n){};
void cal3(){
cout<<x<<"/"<<y<<"="<<x/y<<endl;
}
private:
int x,y;
};
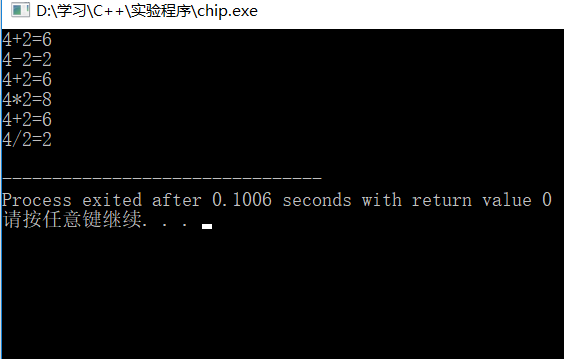
int main (){
chipA a(4,2);
a.cal1();
chipB b(4,2);
b.cal2();
chipC c(4,2);
c.cal3();
return 0;
}
- 一开始在基类Base里面定义了一个cal函数,用于计算m+n,但是这样子运行后发现,并没有每一个芯片都输出m+n,后来就改在了构造函数里面,就解决了。
- 舍友告诉我Virtual 虚基类可以节约空间,书上也有,看了后改进了一下自己的。
- 自己一开始做的时候,在派生类的定义初值上出现了问题,没有把基类写进去,结果就一直报错没有匹配的函数。
- 主函数里面调用的时候,一开始没有赋初值,直接调用函数,结果也是报错。
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class vehicle{
public:
vehicle(int m,int w):maxspeed(m),weight(w){};
void run(){
cout<<"vehicle is running"<<endl;
}
void stop(){
cout<<"vehicle has stopped"<<endl;
}
protected:
int maxspeed,weight;
};
class bicycle:virtual public vehicle{
public:
bicycle(int m,int w,double h):vehicle(m,w),height(h){};
void run(){
cout<<"bicycle is running"<<endl;
cout<<"height is "<<height<<endl;
}
void stop(){
cout<<"bicycle has stopped"<<endl;
}
protected:
double height;
};
class motorcar:virtual public vehicle{
public:
motorcar(int m,int w,int s):vehicle(m,w),seatnum(s){};
void run(){
cout<<"motorcar is running"<<endl;
cout<<"seatnum is "<<seatnum<<endl;
}
void stop(){
cout<<"motorcar has stopped";
}
protected:
int seatnum;
};
class motorcycle:public bicycle,public motorcar{
public:
motorcycle(int m,int w,double h,int s):vehicle(m,w),bicycle(m,w,h),motorcar(m,w,s){};
void run(){
cout<<"motorcycle is running"<<endl;
cout<<"maxspeed is "<<maxspeed<<endl;
cout<<"weight is "<<weight<<endl;
cout<<"height is "<<height<<endl;
cout<<"seatnum is "<<seatnum<<endl;
}
void stop(){
cout<<"motorcycle has stopped"<<endl;
}
};
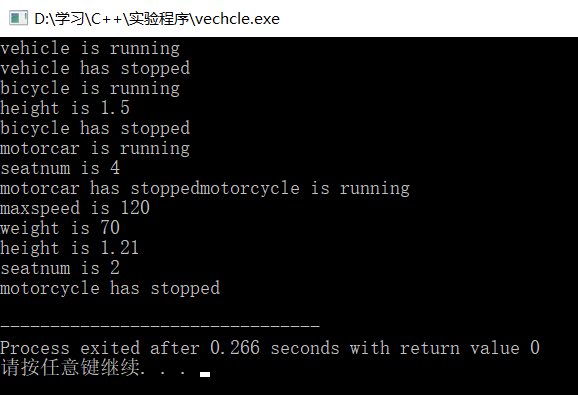
int main(){
vehicle a(200,100);
a.run();
a.stop();
bicycle b(15,5,1.50);
b.run();
b.stop();
motorcar c(120,80,4);
c.run();
c.stop();
motorcycle d(120,70,1.21,2);
d.run();
d.stop();
return 0;
}
- 私有成员是不能用的,后来借鉴了舍友的,改成了保护型(这点书上也有说明),格式上也对比她的进行了一些修改,感觉自己写的就乱乱的,其实并没有把一些细节理的很清楚,细节真的挺重要的。
- 好不容易没有bug了,一运行,出来一连串,要注意输出的格式美观。
#ifndef FRACTION_H
#define FRACTION_H
class Fraction{
public:
Fraction(int t=0,int b=1);
Fraction();
Fraction(int t);
~Fraction();
Fraction(Fraction &f);
void fenshu();
void add(int c1,int c2);
friend Fraction operator+(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 );
friend Fraction operator-(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 );
void refenshu();
private:
int top;
int botton;
};
#endif
# include <iostream>
# include "fraction.h"
using namespace std;
Fraction::Fraction(int t,int b):top(t),botton(b){
}
Fraction::Fraction(){ //函数的重载
top=0;
botton=1;
}
Fraction::Fraction(int t):top(t){ //函数的重载
botton=1;
}
Fraction::~Fraction()
{}
void Fraction::fenshu(){
if(top/botton==0){
cout<<top % botton<<endl;
cout<<"-"<<endl;
cout<<botton<<endl;
}
else {
cout<<" "<<top % botton<<endl;
cout<<top/botton<<"-"<<endl;
cout<<" "<<botton<<endl;
}
}
Fraction operator+(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 ){
return Fraction (c1.top+c2.top,c1.botton+c2.botton);
}
Fraction operator-(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 ){
return Fraction (c1.top-c2.top,c1.botton-c2.botton);
}
Fraction operator*(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 ){
return Fraction (c1.top*c2.top,c1.botton*c2.botton);
}
Fraction operator/(const Fraction &c1, const Fraction &c2 ){
return Fraction (c1.top/c2.top,c1.botton/c2.botton);
}
# include <iostream>
# include "fraction.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
Fraction a;
Fraction b(3,4);
Fraction c(5);
return 0;
}
这个还没有做出来,晚点再看看第八章试试。