字节流主要操作byte类型数据,以byte数组为准,主要操作类有InputStream(字节输入流)、OutputSteam(字节输出流)由于IputStream和OutputStream都是抽象类,所要要用这两个类的话,则首先要通过子类实例化对象。下面就是这两个类的一些子类结构图
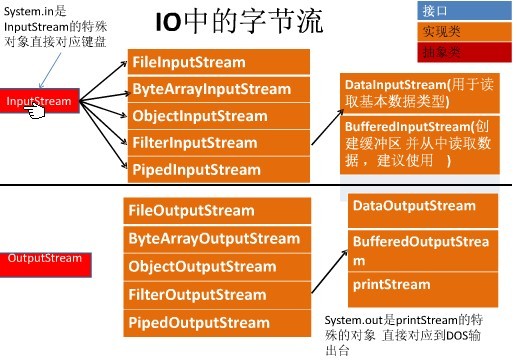
一、InputStream中的读取数据的方法如下:
1 、int read()
功能:读取一个字节的数据,并且返回读到得数据,如果返回-1,则表示读到输入流的末尾。
2、int read(byte[] b)
功能:从输入流中读取一定量的字节,并将其存储在字节数组b中,返回实际读取的字节数,如果返回-1,则表示读到输入流的末尾。
3、int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
功能:将数据读入一个字节数组,同时返回读取的实际字节数,如果返回-1,则表示读到输入流的末尾。off指定在数组b中存放数据的起始偏移位置,len指定读取的最大字节数。
4、available()
功能:返回此输入流下一个方法调用可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取或跳过的估计字节数。
5、close()
功能:关闭输入流,释放这个流的相关资源。
二、OutputStream中写入数据的方法如下:
1 、int write(int b)
功能:将b的最低的一个字节写入此输入流,其他三个字节丢弃。
2、int write(byte[] b)
功能:将指定的字节数组b写入此输入流。
3、int write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
功能:将指定byte数组中从偏移量off开始的len个字节写入输入流。
4、flush()
功能:刷新此输入流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节数。
5、close()
功能:关闭输出流,释放这个流的相关资源。
一、字节流演示:复制媒体文件
字符流中有FileWriter、FileReader用于对文本文件的字符读写操作,在字节流中,有FileInputStream、FileOutputStream用于对文件的字节读写操作。
(1)使用read()方法复制mp3文件
【1】不使用缓冲流
public int read()
throws IOException
|
该方法为堵塞式方法,即如果流中没有数据,则会等到流中有数据再读取。

private static void function1() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("music.mp3"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("1.mp3"); int ch; while((ch=fis.read())!=-1) { fos.write(ch); } fis.close(); fos.close(); }
【2】使用缓冲流BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream。

private static void function1() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("music.mp3"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("1.mp3"); BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); int ch; while((ch=bis.read())!=-1) { bos.write(ch); bos.flush(); } bis.close(); bos.close(); }
使用缓冲流和不使用缓冲流程序执行效率差别很大(只针对读取单个字节的这种特殊情况),这是因为不使用缓冲流的时候是从文件直接读取单个字节,而使用缓冲流的时候是从内存读取单个字节,所以速度要快一些。
(2)使用read(byte[]buf)方法复制文本文件
【1】不使用缓冲流的情况
public int read(byte[] b)
throws IOException
|
注意,该方法也是堵塞式方法。

private static void function2() throws IOException { byte buf[]=new byte[1024]; FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("music.mp3"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("2.mp3"); int length; while((length=fis.read(buf))!=-1) { fos.write(buf,0,length); } fis.close(); fos.close(); }
【2】使用缓冲流的情况

private static void function2() throws IOException { byte buf[]=new byte[1024]; FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("music.mp3"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("2.mp3"); BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); int length; while((length=bis.read(buf))!=-1) { bos.write(buf,0,length); bos.flush(); } bis.close(); bos.close(); }
着这种情况下两者的程序执行效率相差不多,原因是两者都使用了数组。因此很多情况下不需要使用此缓冲流。
二、键盘录入
System.in为标准输入流(对应的设备为键盘),System.out为标准输出流(对应的设备为显示器)
System.in:
public static final InputStream in
|
System.out:
|
注意:默认的输入流和默认的输出流是不需要关闭的,因为一旦关闭,就用不了了,这和其他的流有很大的不相同之处。
1.从键盘输入单个字符
(1)只输入一个字符的标准形式(非中文)
int ch=System.in.read();
System.out.println(ch);
使用System.in.read()方法由于读取的只有一个字节,所以不能表示一个中文字符(至少两个字节)
(2)读入3个字符
使用for循环控制:

private static void singleCharacterInputDemo02() throws IOException { int ch; System.out.println("请输入:"); for(int i=1;i<=3;i++) { ch=System.in.read(); System.out.println(ch); } System.out.println("程序结束!"); }
运行结果:

很明显,程序运行的结果有问题,明明需要输入三个字符,但是却值输入了一个字符就结束了循环。原因就是系统默认在回车的时候添加上' '、' '两个字符。
验证:
private static void CheckRN() {
System.out.println((int)'
');
System.out.println((int)'
');
}
可以发现输出的两个数字分别是13、10,这样就验证了我们的猜想。
2.需求:获取用户键盘录入的数据并将数据变成大写显示在控制台上,如果用户输入的数据是over,则结束键盘录入
分析:输入的字符长度不确定,所以使用可变长的容器:StringBuilder或者StringBuffer

private static void function1() throws IOException { //1.获取流对象。 InputStream is=System.in; //2.创建容器StringBuilder StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); //3.获取键盘录入,转变并判断、显示 int ch; while((ch=is.read())!=-1) { if(ch==' ') continue; if(ch==' ') { if(sb.toString().equals("over")) { break; } else { System.out.println(sb.toString().toUpperCase()); sb.delete(0, sb.length()); continue; } } sb.append((char)ch); } }
观察代码可以发现这和之前写的MyBufferedReader的readLine方法的实现很相似,我们可以考虑是否能使用字符缓冲流将此流对象封装起来,使用readLine方法读取一行数据。
分析:BufferedReader只能接受字符流对象,但是System.in,即InputStream对象为字节流对象,所以不能直接操作。因此如果有一个转换流,将字节流转换为字符流的话,将会省去比较多的麻烦。
3.转换流简介
之前提到了能将字节流转换为字符流的流,思考,如果该类存在,它应当在字符流的体系中还是字节流的体系中?
分析:字节流很简单,正因为出现了字符流,因此才需要转换,因此该流应当在Reader体系中。相应的,如果有能将字符流转换为字节流的类,该类应当在Writer体系中。
Java中提供了能将字节流转换为字符流的类InputStreamReader,与之相应的,java也提供了将字符流转换为字节流的类OutputStreamWriter。
(1)InputStreamReader:
public class InputStreamReaderextends Reader InputStreamReader 是字节流通向字符流的桥梁:它使用指定的 每次调用 InputStreamReader 中的一个 read() 方法都会导致从底层输入流读取一个或多个字节。要启用从字节到字符的有效转换,可以提前从底层流读取更多的字节,使其超过满足当前读取操作所需的字节。 为了达到最高效率,可要考虑在 BufferedReader 内包装 InputStreamReader。例如: BufferedReader in= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); |
可以看到,该类有个很大的特点,那就是能够按照指定方式的编码读取字节流中的数据。事实上InputStreamReader就是字节流+编码的体现,而其子类FileReader封装的也正是InputStream的字节流+编码,只不过编码方式是平台上的默认编码而已。
(2)OutputStream:
public class OutputStreamWriterextends Writer OutputStreamWriter 是字符流通向字节流的桥梁:可使用指定的 每次调用 write() 方法都会导致在给定字符(或字符集)上调用编码转换器。在写入底层输出流之前,得到的这些字节将在缓冲区中累积。可以指定此缓冲区的大小,不过,默认的缓冲区对多数用途来说已足够大。注意,传递给 write() 方法的字符没有缓冲。 为了获得最高效率,可考虑将 OutputStreamWriter 包装到 BufferedWriter 中,以避免频繁调用转换器。例如: Writer out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)); |
(3)指定编码的方式:使用构造方法。
两种方式指定编码的方式都是在生成对象的时候就已经制定好了的。即不仅仅指定要接受的流对象,还要指定读取或者写入的编码方式。
4.使用转换流将字节流转换为字符流并反其道而行之将从键盘读到的数据写入到屏幕上显示
(1)不使用缓冲流也不使用字符到字节的转换流。

private static void function01() throws IOException { InputStream is=System.in;//该流为字节流 InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is);//该流是字符流 // int ch=isr.read();//读取一个字符 // System.out.println(ch); char buf[]=new char[1024]; int length=isr.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length)); System.out.println(length); }
运行结果:

虽然输入了10个字符,但是却显示字符长度为12,这是因为默认添加了' '与' '两个字符。很明显,需要手动判去除这两字个字符。

private static void function01() throws IOException { InputStream is=System.in;//该流为字节流 InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is);//该流是字符流 // int ch=isr.read();//读取一个字符 // System.out.println(ch); char buf[]=new char[1024]; int length=isr.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length-2)); System.out.println(length-2); }
运行结果:

很明显,每次这么做的话就很麻烦了,所以可以考虑使用缓冲流提高效率。
(2)使用字符缓冲流提高输入效率。

private static void function02() throws IOException { InputStream is=System.in; InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); String str=br.readLine(); System.out.println(str); System.out.println(str.length()); }
运行结果和上面的第二个示例完全相同,除此之外,BufferedReader类还提供了其它方法如newLine方法简化了我们的书写。因此,如果需要提高效率的话,使

private static void function03() throws IOException { InputStream is=System.in; InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(is); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); OutputStream os=System.out; OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(os); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); String str=br.readLine(); bw.write(str); bw.flush();//不能忘了刷新操作,否则无法显示。 }
用BufferedReader是很好地选择。
(3)使用字符转字节的转换流和缓冲流。
注意,使用字符缓冲刘输出数据之后要刷新流,否则无法显示出内容(除非缓冲区已满)。
简写形式:
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
5.转换流的强大功能
(1)转换流和FileWriter与FileReader的关系
FileReader的继承体系:
java.io.Reader
|--java.io.InputStreamReader
|--java.io.FileReader
FileWriter的继承体系:
java.io.Writer
|--java.io.OutputStreamWriter
|--java.io.FileWriter
由此可见,FileReader和FileWriter的父类就是转换流。但是我们知道,FileReader和FileWriter并没有转换流的功能,这是因为它的构造方法中明确了要处理的参数是文件,并且使用默认的编码集(系统平台上使用的编码),因此,我们可以想象的出来,当操作文件的时候,
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("date.txt"));
等价于
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("date.txt")));
即FileReader默认使用系统平台的编码将字节流转变成了字符流。
同样的,
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("date.txt"));
等价于
BufferedWriter bw1=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("date.txt")));
说明:等价指的是转换的动作相同,即使用默认系统平台的编码将字符流转变为字节流或者将字节流转换为字符流。很明显使用FileWriter和FileReader操作文件要比使用转换流操作文件方便的多,但是因为方便,所以就有了缺点,那就是使用FileWriter和FileReader不能够指定编码方式。因此,如果要以指定的编码方式读或者写就需要使用转换流
(2)转换流的编码解码
转换流通过构造方法确认使用的编码解码方式。
首先明确
编码:由已知到未知,由字符到字节,为OutputStreamWriter。
解码:由未知到已知,由字节到字符,为InputStreamReader
【1】InputStreamReader的构造方法:
常用的有两个:
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in)创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader。 |
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException
|
可以看到,如果要指定编码,必须使用正确的编码名称,否则会抛出不支持的编码异常。
【2】OutputStreamWriter的构造方法。
|
|
创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。 |
【3】使用指定的编码方式将键盘上输入的文字保存入硬盘上的data.txt文件中。
注意!!!!如果想要验证某种方式下的读写,在Eclipse环境下必须设置文件的编码方式,设置默认的编码方式之后,java程序标准输入的编码方式(键盘等)将会变成这种编码方式,比如,一个中文字符将会表示成3个字节分别输入。
方式一:读入写出都是用utf-8编码(Eclipse环境下设置源文件的编码类型为utf-8)。

private static void encodeAndeDecodeDemo() throws IOException { InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System.in,"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("date2.txt"),"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+osw.getEncoding()); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); String str=null; while(!(str=br.readLine()).equals("over")) { System.out.println(str); bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("date2.txt"),"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); br=new BufferedReader(isr); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); }
写入你好两个中文,结果:无乱码
方式二:读入写出都是使用gbk编码(Eclipse环境下设置文件的编码类型为gbk)。

private static void encodeAndeDecodeDemo() throws IOException { InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System.in,"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("date2.txt"),"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+osw.getEncoding()); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); String str=null; while(!(str=br.readLine()).equals("over")) { System.out.println(str); bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("date2.txt"),"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); br=new BufferedReader(isr); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); }
显示结果:无乱码
【4】使用指定的编码输入文件
例:使用utf-8编码写入文件,使用gbk编码读出(Eclipse环境下将源文件设置成utf-8编码方式)。

private static void encodeAndeDecodeDemo() throws IOException { InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System.in,"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("date2.txt"),"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+osw.getEncoding()); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); String str=null; while(!(str=br.readLine()).equals("over")) { System.out.println(str); bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("date2.txt"),"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); br=new BufferedReader(isr); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); }
结果:出现乱码。
例:使用gbk编码写入文件,使用utf-8编码读出(Eclipse环境下将源文件设置成gbk编码方式)

private static void encodeAndeDecodeDemo() throws IOException { InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System.in,"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("date2.txt"),"gbk"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+osw.getEncoding()); BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); String str=null; while(!(str=br.readLine()).equals("over")) { System.out.println(str); bw.write(str); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); isr=new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("date2.txt"),"utf-8"); System.out.println("kind of encode :"+isr.getEncoding()); br=new BufferedReader(isr); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); }
结果:出现乱码。
