原创博客:转载请标明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zxouxuewei/
1.首先确保你的kinect驱动或者uvc相机驱动能正常启动:(如果你使用的是kinect,请运行openni驱动)
roslaunch openni_launch openni.launch
如果你没有安装kinect深度相机驱动,请看我前面的博文。
2.确保安装深度相机NITE。
首先下载NITE-Bin-Dev-Linux-x64-v1.5.2.23,链接如下:
a. 32-bit: http://www.openni.ru/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/NITE-Bin-Linux-x86-v1.5.2.23.tar.zip
b. 64-bit: http://www.openni. ru /wp-content/uploads/2013/10/NITE-Bin-Linux-x64-v1.5.2.23.tar.zip
2.然后安装,
root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:cd /root/kinect-install-driver-ubuntu/NITE-Bin-Dev-Linux-x64-v1.5.2.23/
root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:sudo ./uninstall.sh
root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:sudo ./install.sh
3.安装skeleton_markers功能包。
root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:cd ~/catkin_ws/src root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:git clone -b https://github.com/pirobot/skeleton_markers.git root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:cd skeleton_markers root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:git checkout indigo-devel root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:cd ~/catkin_ws root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:catkin_make root@zxwubuntu-Aspire-V3-572G:rospack profile
4.运行启动文件
roslaunch skeleton_markers markers_from_tf.launch
5,运行rviz 查看骨架图。
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find skeleton_markers`/markers_from_tf.rviz
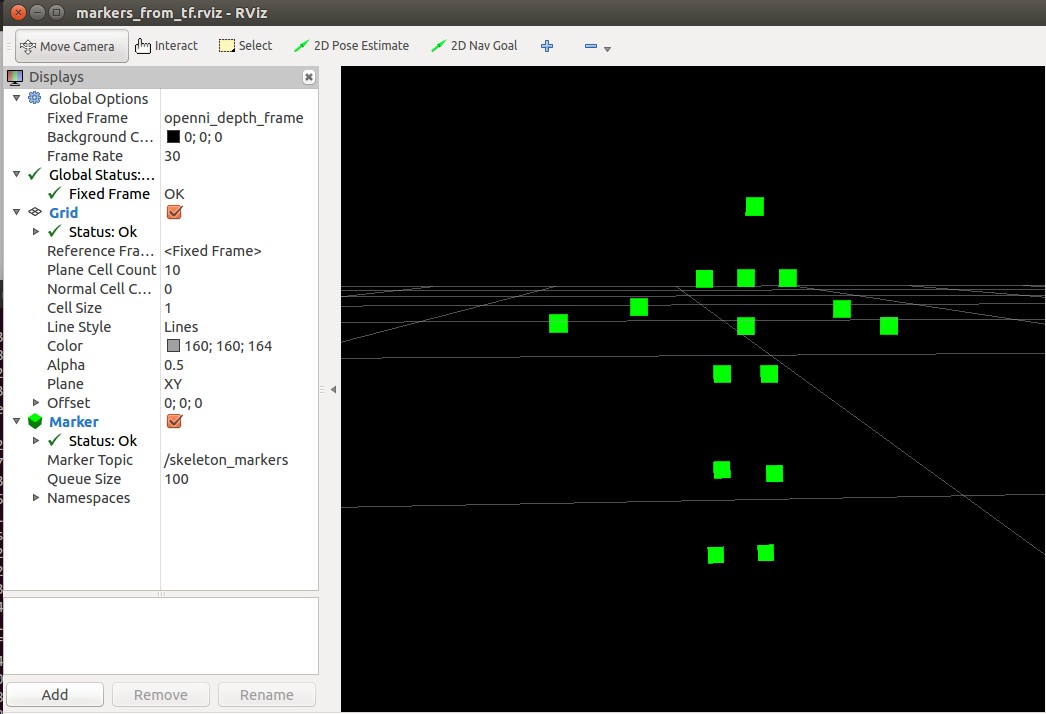
6,运行结果如下:
7.markers_from_tf.launch文件内容如下:
<launch> <node pkg="openni_tracker" name="openni_tracker" type="openni_tracker"output="screen"> <param name="fixed_frame" value="openni_depth_frame" /> </node> <node pkg="skeleton_markers" name="markers_from_tf" type="markers_from_tf.py"output="screen"> <rosparam file="$(find skeleton_markers)/params/marker_params.yaml"command="load" /> </node> </launch>
8.skeleton_markers/nodes/markers_from_tf.py节点代码如下
#!/usr/bin/env python """ Convert a skeleton transform tree to a list of visualization markers for RViz. Created for the Pi Robot Project: http://www.pirobot.org Copyright (c) 2011 Patrick Goebel. All rights reserved. This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details at: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html """ import rospy from visualization_msgs.msg import Marker from geometry_msgs.msg import Point import tf class SkeletonMarkers(): def __init__(self): rospy.init_node('markers_from_tf') rospy.loginfo("Initializing Skeleton Markers Node...") rate = rospy.get_param('~rate', 20) r = rospy.Rate(rate) # There is usually no need to change the fixed frame from the default self.fixed_frame = rospy.get_param('~fixed_frame', 'openni_depth_frame') # Get the list of skeleton frames we want to track self.skeleton_frames = rospy.get_param('~skeleton_frames', '') # Initialize the tf listener tf_listener = tf.TransformListener() # Define a marker publisher marker_pub = rospy.Publisher('skeleton_markers', Marker, queue_size=5) # Intialize the markers self.initialize_markers() # Make sure we see the openni_depth_frame tf_listener.waitForTransform(self.fixed_frame, self.fixed_frame, rospy.Time(), rospy.Duration(60.0)) # A flag to track when we have detected a skeleton skeleton_detected = False # Begin the main loop while not rospy.is_shutdown(): # Set the markers header self.markers.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now() # Clear the markers point list self.markers.points = list() # Check to see if a skeleton is detected while not skeleton_detected: # Assume we can at least see the head frame frames = [f for f in tf_listener.getFrameStrings() if f.startswith('head_')] try: # If the head frame is visible, pluck off the # user index from the name head_frame = frames[0] user_index = head_frame.replace('head_', '') # Make sure we have a transform between the head # and the fixed frame try: (trans, rot) = tf_listener.lookupTransform(self.fixed_frame, head_frame, rospy.Time(0)) skeleton_detected = True except (tf.Exception, tf.ConnectivityException, tf.LookupException): skeleton_detected = False rospy.loginfo("User index: " + str(user_index)) r.sleep() except: skeleton_detected = False # Loop through the skeleton frames for frame in self.skeleton_frames: # Append the user_index to the frame name skel_frame = frame + "_" + str(user_index) # We only need the origin of each skeleton frame # relative to the fixed frame position = Point() # Get the transformation from the fixed frame # to the skeleton frame try: (trans, rot) = tf_listener.lookupTransform(self.fixed_frame, skel_frame, rospy.Time(0)) position.x = trans[0] position.y = trans[1] position.z = trans[2] # Set a marker at the origin of this frame self.markers.points.append(position) except: pass # Publish the set of markers marker_pub.publish(self.markers) r.sleep() def initialize_markers(self): # Set various parameters scale = rospy.get_param('~scale', 0.07) lifetime = rospy.get_param('~lifetime', 0) # 0 is forever ns = rospy.get_param('~ns', 'skeleton_markers') id = rospy.get_param('~id', 0) color = rospy.get_param('~color', {'r': 0.0, 'g': 1.0, 'b': 0.0, 'a': 1.0}) # Initialize the marker points list self.markers = Marker() self.markers.header.frame_id = self.fixed_frame self.markers.ns = ns self.markers.id = id self.markers.type = Marker.POINTS self.markers.action = Marker.ADD self.markers.lifetime = rospy.Duration(lifetime) self.markers.scale.x = scale self.markers.scale.y = scale self.markers.color.r = color['r'] self.markers.color.g = color['g'] self.markers.color.b = color['b'] self.markers.color.a = color['a'] if __name__ == '__main__': try: SkeletonMarkers() except rospy.ROSInterruptException: pass