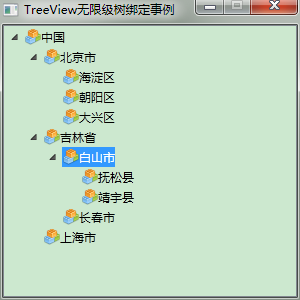
1.如图所示:绑定树效果图
2.前台Xaml代码:
<Window x:Class="WpfTest.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:mode="clr-namespace:WpfTest" Title="TreeView无限级树绑定事例" Height="300" Width="300" WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen" ResizeMode="CanMinimize"> <Grid> <Grid.Resources> <HierarchicalDataTemplate DataType="{x:Type mode:Node}" ItemsSource="{Binding Nodes}"> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,2,0,2"> <!--<Image Source="pack://application:,,,/WpfTest;Component/Resources/KnowDot.png" Width="16" Height="16" />--> <!--<Image Source="Resources/KnowDot.png" Width="16" Height="16" />--> <Image Source="/WpfTest;Component/Resources/KnowDot.png" Width="16" Height="16" /> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" ToolTip="{Binding Name}" Tag="{Binding}"/> </StackPanel> </HierarchicalDataTemplate> </Grid.Resources> <TreeView Name="TreeView"/> </Grid> </Window>
2.后台cs代码:采用递归无限极向下查询
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Data; using System.Windows.Documents; using System.Windows.Input; using System.Windows.Media; using System.Windows.Media.Imaging; using System.Windows.Navigation; using System.Windows.Shapes; using System.Threading; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Windows.Markup; namespace WpfTest { /// <summary> /// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// </summary> public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); List<Node> nodes = new List<Node>() { new Node { ID = 1, Name = "中国" }, new Node { ID = 2, Name = "北京市", ParentID = 1 }, new Node { ID = 3, Name = "吉林省", ParentID = 1 }, new Node { ID = 4, Name = "上海市", ParentID = 1 }, new Node { ID = 5, Name = "海淀区", ParentID = 2 }, new Node { ID = 6, Name = "朝阳区", ParentID = 2 }, new Node { ID = 7, Name = "大兴区", ParentID = 2 }, new Node { ID = 8, Name = "白山市", ParentID = 3 }, new Node { ID = 9, Name = "长春市", ParentID = 3 }, new Node { ID = 10, Name = "抚松县", ParentID = 8 }, new Node { ID = 11, Name = "靖宇县", ParentID = 8 } }; // 绑定树 List<Node> outputList = Bind(nodes); //(TreeView.SelectedItem as Node).ID this.TreeView.ItemsSource = outputList; //TreeViewItem item = new TreeViewItem(); //item.Header = ""; } /// <summary> /// 绑定树 /// </summary> List<Node> Bind(List<Node> nodes) { List<Node> outputList = new List<Node>(); for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Count; i++) { if (nodes[i].ParentID == -1) { outputList.Add(nodes[i]); } else { FindDownward(nodes, nodes[i].ParentID).Nodes.Add(nodes[i]); } } return outputList; } /// <summary> /// 递归向下查找 /// </summary> Node FindDownward(List<Node> nodes, int id) { if (nodes == null) return null; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.Count; i++) { if (nodes[i].ID == id) { return nodes[i]; } Node node = FindDownward(nodes[i].Nodes, id); if (node != null) { return node; } } return null; } } public class Node { public Node() { this.Nodes = new List<Node>(); this.ParentID = -1; } public int ID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int ParentID { get; set; } public List<Node> Nodes { get; set; } } }