简介
虚树,顾名思义就是不真实的树。
它往往出现在一类树形动态规划问题中。
换句话说,虚树实际就是为了解决一类树形动态规划问题而诞生的!
我们从一道经典的虚树题目入手
[SDOI2011]消耗战
链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P2495
题目大意
给出一棵树,每条边有边权。
有$m$次询问,每次询问给出$k$个点,问使得这$k$个点均不与$1$号点(根节点)相连的最小代价
$n<=250000, m>=1,sum k <= 500000$(m是smg..)
暴力dp
首先考虑$m=1$,也就是只有一次询问的情况。我们考虑暴力dp
设$f[x]$为处理完以$x$为根的树的最小代价
转移分为两种情况
1.断开自己与父亲的联系,代价为从根到该节点的最小值
2.不考虑该节点(前提是该节点不是询问点),把子树内的所有询问点都断开的代价
但是这样的复杂度是$O(nm)$的,显然无法AC
然而我们发现$sum k$是比较小的,我们可不可以对$k$下手呢?
于是,虚树诞生了
虚树
思想
虚树的主要思想是:对于一棵树,仅仅保留有用的点,重新构建一棵树
这里有用的点指的是询问点和它们的lca
煮个栗子
比如这样的一棵树(没错就是样例)

对于样例中的三次询问,
3
2 10 6
4 5 7 8 3
3 9 4 6
那么它的虚树分别长这样
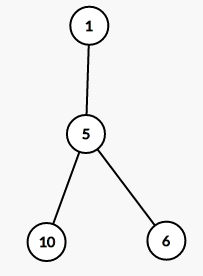
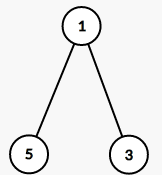
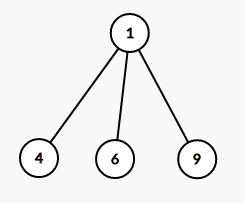
第二张比较鬼畜,因为在这道题中我们必须要断开$5$号点,因此$7,8$号点用不到
构建
考虑得到了询问点,如何构造出一棵虚树。
首先我们要先对整棵树dfs一遍,求出他们的dfs序,然后对每个节点以dfs序为关键字从小到大排序
同时维护一个栈,表示从根到栈顶元素这条链
假设当前要加入的节点为$p$,栈顶元素为$x = s[top]$,$lca$为他们的最近公共祖先
因为我们是按照dfs序遍历,因此$lca$不可能是$p$
那么现在会有两种情况
- $lca$是$x$,直接将$p$入栈。
- $x,p$分别位于$lca$的两棵子树中,此时$x$这棵子树已经遍历完毕,(如果没有,即x的子树中还有一个未加入的点y,但是dfn[y]<dfn[p],即应先访问y), 我们需要对其进行构建
设栈顶元素为$x$,第二个元素为$y$
- 若$dfn[y]>dfn[lca]$,可以连边$y->x$,将$x$出栈;
- 若$dfn[y]=dfn[lca]$,即$y=lca$,连边$lca->x$,此时子树构建完毕(break);
- 若$dfn[y]<dfn[lca]$,即$lca$在$y,x$之间,连边$lca->x$,$x$出栈,再将$lca$入栈。此时子树构建完毕(break)。
此处较为抽象,建议大家画图理解一下
不断重复这个过程,虚树就构建完成了,另外我们需要维护出链上的最小值,然后我们直接在虚树上dp就可以了
复杂度
虚树上除了要加入的询问点外,还有可能出现的$LCA$。
假设当前要加入$x$,它与之前加入的y产生一个新的$LCA$记作$lca1$,还与之前的$z$产生一个新的$LCA$记作$lca2$。
设$dep[lca1]<dep[lca2]$(否则交换$y,z$即可)
那么$LCA(y,z)=lca1$,所以假设不成立。
即每次加入点,最多会产生一个新的$LCA$。
那么虚树中的点数是$O(2*k)$的。
这样复杂度就只与k有关,$O(2*sum k_i)$。
代码
// luogu-judger-enable-o2 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++) #define LL long long char buf[(1 << 21) + 1], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf; using namespace std; const int MAXN = 250001; inline int read() { char c = getchar(); int x = 0, f = 1; while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); return x * f; } char obuf[1 << 24], *O=obuf; void print(LL x) { if(x > 9) print(x / 10); *O++= x % 10 + '0'; } int N, M; struct Edge { int u, v, w, nxt; }E[MAXN << 1]; int head[MAXN], num = 1; inline void AddEdge(int x, int y, int z) { E[num] = (Edge) {x, y, z, head[x]}; head[x] = num++; } vector<int> v[MAXN]; void add_edge(int x, int y) { v[x].push_back(y); } int a[MAXN], dfn[MAXN], topf[MAXN], siz[MAXN], son[MAXN], s[MAXN], top, deep[MAXN], fa[MAXN], ID = 0; LL mn[MAXN]; void dfs1(int x, int _fa) { siz[x] = 1; fa[x] = _fa; for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = E[i].nxt) { if(E[i].v == _fa) continue; deep[E[i].v] = deep[x] + 1; mn[E[i].v] = min(mn[x], (LL)E[i].w); dfs1(E[i].v, x); siz[x] += siz[E[i].v]; if(siz[E[i].v] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = E[i].v; } } void dfs2(int x, int topfa) { topf[x] = topfa; dfn[x] = ++ID; if(!son[x]) return ; dfs2(son[x], topfa); for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = E[i].nxt) if(!topf[E[i].v]) dfs2(E[i].v, E[i].v); } int LCA(int x, int y) { while(topf[x] != topf[y]) { if(deep[topf[x]] < deep[topf[y]]) swap(x, y); x = fa[topf[x]]; } if(deep[x] < deep[y]) swap(x, y); return y; } void insert(int x) { if(top == 1) {s[++top] = x; return ;} int lca = LCA(x, s[top]); if(lca == s[top]) return ; while(top > 1 && dfn[s[top - 1]] >= dfn[lca]) add_edge(s[top - 1], s[top]), top--; if(lca != s[top]) add_edge(lca, s[top]), s[top] = lca;// s[++top] = x; } LL DP(int x) { if(v[x].size() == 0) return mn[x]; LL sum = 0; for(int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i++) sum += DP(v[x][i]); v[x].clear(); return min(sum, (LL)mn[x]); } int comp(const int &a, const int &b) { return dfn[a] < dfn[b]; } int main() { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); //memset(mn, 0xff, sizeof(mn)); mn[1] = 1ll << 60; N = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= N - 1; i++) { int x = read(), y = read(), z = read(); AddEdge(x, y, z); AddEdge(y, x, z); } deep[1] = 1; dfs1(1, 0); dfs2(1, 1); M = read(); /*for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++) printf("%d %d %d ", i, j, LCA(i, j));*/ //for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) printf("%d ", mn[i]); puts(""); while(M--) { int K = read(); for(int i = 1; i <= K; i++) a[i] = read(); sort(a + 1, a + K + 1, comp); s[top = 1] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= K; i++) insert(a[i]); while(top > 0) add_edge(s[top - 1], s[top]), top--; print(DP(1)), *O++ = ' '; } fwrite(obuf, O-obuf, 1 , stdout); return 0; }