使用vuex前后的对比
使用vuex前
//BookRecommend.vue
<script>
import * as API from '../api/index'
export default{
name:'bookrecommend',
data () {
return {
oBRData:{}
}
},
methods: {
getBookRecommendData(){
API.getBookRecommend()
.then((response)=>{
this.oBRData = response.data;
console.log(response)
})
.catch((err)=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
},
mounted () {
this.getBookRecommendData();
}
}
</script>
使用vuex后
//BookRecommend.vue
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default{
name:'bookrecommend',
computed: mapState([
'index'
]),
methods: {
},
mounted () {
this.$store.dispatch('getBookRecommend');
}
}
</script>
变化
- 剥离了state的管理
- 剥离了异步请求
- .vue文件变得更加"纯粹"了
下面我们就从几个方面来描述一下vuex带给我们的变化。
剥离了state的管理
这个当然是vuex最主要的任务了。
将组件模块的state放到了module中,这里是放在了module/index.js中。
//module/index.js
import * as API from '../../api/index'
import * as types from '../mutation-types'
//BookRecommend.vue单文件的state管理
const state = {
oBRData: {}
}
const actions = {
...
}
const mutations = {
...
}
export default {
state,
...
}
剥离了异步请求
上一篇从交互到状态变化的Vuex中说了actions的作用。
将异步处理也放在了module中的module/index.js中。
import * as API from '../../api/index'
import * as types from '../mutation-types'
const state = {
oBRData: {}
}
//actions方便做异步操作,这里是获取数据
const actions = {
getBookRecommend({ commit }, playload) {
API.getBookRecommend()
.then((response) => {
commit(types.GET_BOOKRECOMMEND_DATA, {
obr: response.data
})
console.log(response);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err)
})
}
}
const mutations = {
...
}
export default {
state,
actions
...
}
Modules
这个也是上篇文章没说的一个点,具体的见:http://vuex.vuejs.org/zh-cn/modules.html
最后通过new Vuex.Store将分散的module合并在一起
//组装module和跟级别的模块并导出 store 的地方
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import * as actions from './actions'
import * as mutations from './mutations'
import index from './modules/index'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
where: '发现'
},
actions,
//将modules中的合并
modules: {
index
},
mutations
})
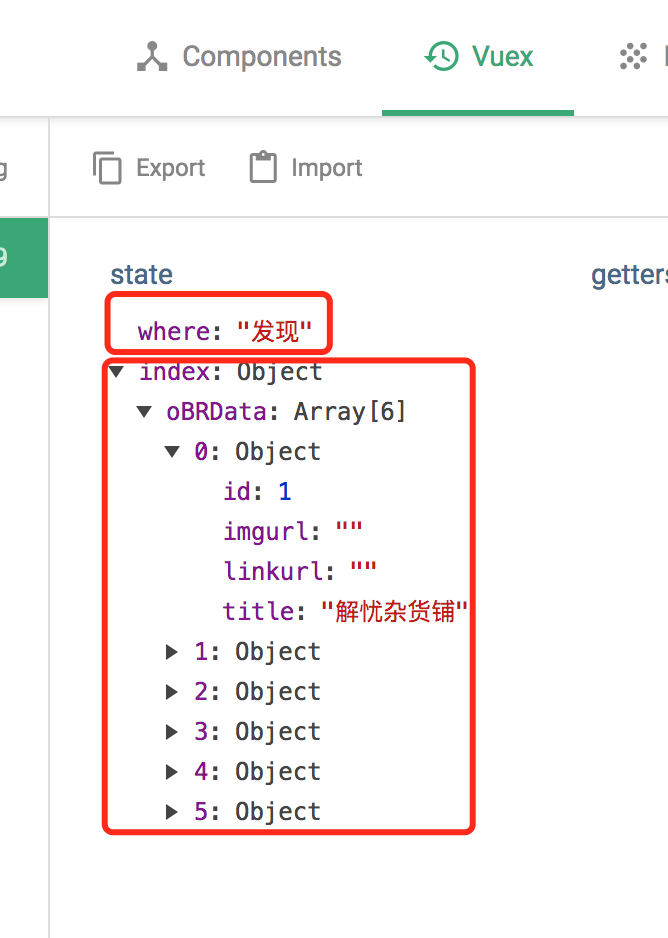
结果
这就是完整的state树,应该很清晰。
首发于我的segmentfault:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008721043