1、线程的并发工具类
Fork-Join
什么是分而治之?
规模为N的问题,N<阈值,直接解决,N>阈值,将N分解为K个小规模子问题,子问题互相对立,与原问题形式相同,将子问题的解合并得到原问题的解
动态规范
工作密取
workStealing
Fork/Join使用的标准范式
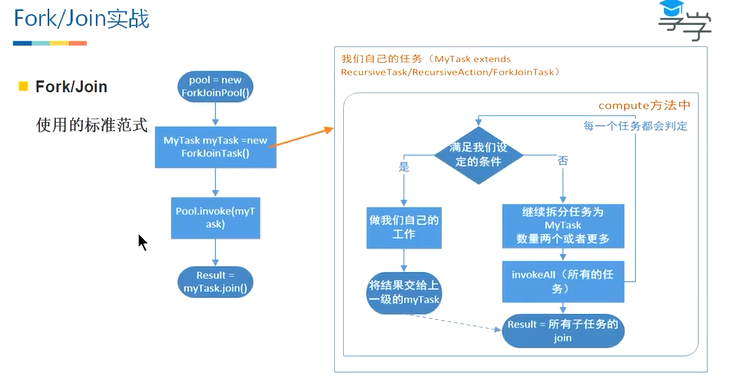

下面演示第一种用法:由于上下文切换的原因,所以性能上有可能不如单线程效果好。
package com.xiangxue.ch2.forkjoin.sum; import java.util.Random; /** * @author mark *产生整形数组 */ public class MakeArray { //数组长度 public static final int ARRAY_LENGTH = 100000000; public static int[] makeArray() { //new一个随机数发生器 Random r = new Random(); int[] result = new int[ARRAY_LENGTH]; for(int i=0;i<ARRAY_LENGTH;i++){ //用随机数填充数组 result[i] = r.nextInt(ARRAY_LENGTH*3); } return result; } }
package com.xiangxue.ch2.forkjoin.sum; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; public class SumNormal { public static void main(String[] args) { int count = 0; int[] src = MakeArray.makeArray(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i= 0;i<src.length;i++){ //SleepTools.ms(1); count = count + src[i]; } System.out.println("The count is "+count +" spend time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms"); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch2.forkjoin.sum; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; public class SumArray { private static class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{ private final static int THRESHOLD = MakeArray.ARRAY_LENGTH/10; private int[] src; //表示我们要实际统计的数组 private int fromIndex;//开始统计的下标 private int toIndex;//统计到哪里结束的下标 public SumTask(int[] src, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { this.src = src; this.fromIndex = fromIndex; this.toIndex = toIndex; } @Override protected Integer compute() { if(toIndex-fromIndex < THRESHOLD) { int count = 0; for(int i=fromIndex;i<=toIndex;i++) { //SleepTools.ms(1); count = count + src[i]; } return count; }else { //fromIndex....mid....toIndex //1...................70....100 int mid = (fromIndex+toIndex)/2; SumTask left = new SumTask(src,fromIndex,mid); SumTask right = new SumTask(src,mid+1,toIndex); invokeAll(left,right); return left.join()+right.join(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); int[] src = MakeArray.makeArray(); SumTask innerFind = new SumTask(src,0,src.length-1); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); pool.invoke(innerFind);//同步调用 System.out.println("Task is Running....."); System.out.println("The count is "+innerFind.join() +" spend time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms"); } }
IO密集型--》使用多线程
Fork--Join 异步用法:
package com.xiangxue.ch2.forkjoin; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction; /** *@author * *类说明:遍历指定目录(含子目录)找寻指定类型文件 */ public class FindDirsFiles extends RecursiveAction{ private File path;//当前任务需要搜寻的目录 public FindDirsFiles(File path) { this.path = path; } public static void main(String [] args){ try { // 用一个 ForkJoinPool 实例调度总任务 ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); FindDirsFiles task = new FindDirsFiles(new File("F:/")); pool.execute(task);//异步调用 System.out.println("Task is Running......"); Thread.sleep(1); int otherWork = 0; for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ otherWork = otherWork+i; } System.out.println("Main Thread done sth......,otherWork="+otherWork); task.join();//阻塞的方法 System.out.println("Task end"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override protected void compute() { List<FindDirsFiles> subTasks = new ArrayList<>(); File[] files = path.listFiles(); if(files!=null) { for(File file:files) { if(file.isDirectory()) { subTasks.add(new FindDirsFiles(file)); }else { //遇到文件,检查 if(file.getAbsolutePath().endsWith("txt")) { System.out.println("文件:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); } } } if(!subTasks.isEmpty()) { for(FindDirsFiles subTask:invokeAll(subTasks)) { subTask.join();//等待子任务执行完成 } } } } }
常用的并发工具类
CountDownLatch
作用:是指一组线程等待其他的线程完成工作以后在执行,加强版join
await用来等待,countDown负责计数器的减一
使用:
package com.xiangxue.tools; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * *@author * *类说明:线程休眠辅助工具类 */ public class SleepTools { /** * 按秒休眠 * @param seconds 秒数 */ public static final void second(int seconds) { try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } /** * 按毫秒数休眠 * @param seconds 毫秒数 */ public static final void ms(int seconds) { try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(seconds); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author * *类说明:演示CountDownLatch,有5个初始化的线程,6个扣除点, *扣除完毕以后,主线程和业务线程才能继续自己的工作 */ public class UseCountDownLatch { static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(6); //初始化线程(只有一步,有4个) private static class InitThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +" ready init work......"); latch.countDown();//初始化线程完成工作了,countDown方法只扣减一次; for(int i =0;i<2;i++) { System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +" ........continue do its work"); } } } //业务线程 private static class BusiThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i =0;i<3;i++) { System.out.println("BusiThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +" do business-----"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //单独的初始化线程,初始化分为2步,需要扣减两次 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { SleepTools.ms(1); System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +" ready init work step 1st......"); latch.countDown();//每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次 System.out.println("begin step 2nd......."); SleepTools.ms(1); System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +" ready init work step 2nd......"); latch.countDown();//每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次 } }).start(); new Thread(new BusiThread()).start(); for(int i=0;i<=3;i++){ Thread thread = new Thread(new InitThread()); thread.start(); } latch.await(); System.out.println("Main do ites work........"); } }
CyclicBarrier
让一组线程达到某个屏障,被阻塞,一直到组内最后一个线程达到屏障时,屏障开放,所有被阻塞的线程会继续运行CyclicBarrier(int parties)
CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction),屏障开放,barrierAction定义的任务会执行
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:CyclicBarrier的使用 */ public class UseCyclicBarrier { private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5,new CollectThread()); private static ConcurrentHashMap<String,Long> resultMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();//存放子线程工作结果的容器 public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<=4;i++){ Thread thread = new Thread(new SubThread()); thread.start(); } } //负责屏障开放以后的工作 private static class CollectThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); for(Map.Entry<String,Long> workResult:resultMap.entrySet()){ result.append("["+workResult.getValue()+"]"); } System.out.println(" the result = "+ result); System.out.println("do other business........"); } } //工作线程 private static class SubThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();//线程本身的处理结果 resultMap.put(Thread.currentThread().getId()+"",id); Random r = new Random();//随机决定工作线程的是否睡眠 try { if(r.nextBoolean()) { Thread.sleep(2000+id); System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" ....do something "); } System.out.println(id+"....is await"); barrier.await(); Thread.sleep(1000+id); System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" ....do its business "); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier辨析
1、countdownlatch放行由第三者控制,CyclicBarrier放行由一组线程本身控制
2、countdownlatch放行条件》=线程数,CyclicBarrier放行条件=线程数
Semaphore
控制同时访问某个特定资源的线程数量,用在流量控制
实现数据库连接:
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools.semaphore; import java.sql.Array; import java.sql.Blob; import java.sql.CallableStatement; import java.sql.Clob; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData; import java.sql.NClob; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLClientInfoException; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.SQLWarning; import java.sql.SQLXML; import java.sql.Savepoint; import java.sql.Statement; import java.sql.Struct; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:数据库连接的平庸实现 */ public class SqlConnectImpl implements Connection{ /*拿一个数据库连接*/ public static final Connection fetchConnection(){ return new SqlConnectImpl(); } @Override public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public void commit() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void rollback() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void close() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public String getCatalog() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public int getHoldability() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Clob createClob() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; } @Override public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public String getSchema() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } }
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools.semaphore; import java.sql.Connection; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:演示Semaphore用法,一个数据库连接池的实现 */ public class DBPoolSemaphore { private final static int POOL_SIZE = 10; private final Semaphore useful,useless;//useful表示可用的数据库连接,useless表示已用的数据库连接 public DBPoolSemaphore() { this.useful = new Semaphore(POOL_SIZE); this.useless = new Semaphore(0); } //存放数据库连接的容器 private static LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<Connection>(); //初始化池 static { for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) { pool.addLast(SqlConnectImpl.fetchConnection()); } } /*归还连接*/ public void returnConnect(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException { if(connection!=null) { System.out.println("当前有"+useful.getQueueLength()+"个线程等待数据库连接!!" +"可用连接数:"+useful.availablePermits()); useless.acquire(); synchronized (pool) { pool.addLast(connection); } useful.release(); } } /*从池子拿连接*/ public Connection takeConnect() throws InterruptedException { useful.acquire(); Connection conn; synchronized (pool) { conn = pool.removeFirst(); } useless.release(); return conn; } }
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools.semaphore; import java.sql.Connection; import java.util.Random; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:测试数据库连接池 */ public class AppTest { private static DBPoolSemaphore dbPool = new DBPoolSemaphore(); //业务线程 private static class BusiThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { Random r = new Random();//让每个线程持有连接的时间不一样 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { Connection connect = dbPool.takeConnect(); System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId() +"_获取数据库连接共耗时【"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"】ms."); SleepTools.ms(100+r.nextInt(100));//模拟业务操作,线程持有连接查询数据 System.out.println("查询数据完成,归还连接!"); dbPool.returnConnect(connect); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { Thread thread = new BusiThread(); thread.start(); } } }
Exchange
两个线程间的数据交换,
package com.xiangxue.ch2.tools; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:Exchange的使用 */ public class UseExchange { private static final Exchanger<Set<String>> exchange = new Exchanger<Set<String>>(); public static void main(String[] args) { //第一个线程 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Set<String> setA = new HashSet<String>();//存放数据的容器 try { /*添加数据 * set.add(.....) * */ setA = exchange.exchange(setA);//交换set /*处理交换后的数据*/ } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }).start(); //第二个线程 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Set<String> setB = new HashSet<String>();//存放数据的容器 try { /*添加数据 * set.add(.....) * set.add(.....) * */ setB = exchange.exchange(setB);//交换set /*处理交换后的数据*/ } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }).start(); } }
Callable、Future和FutureTask
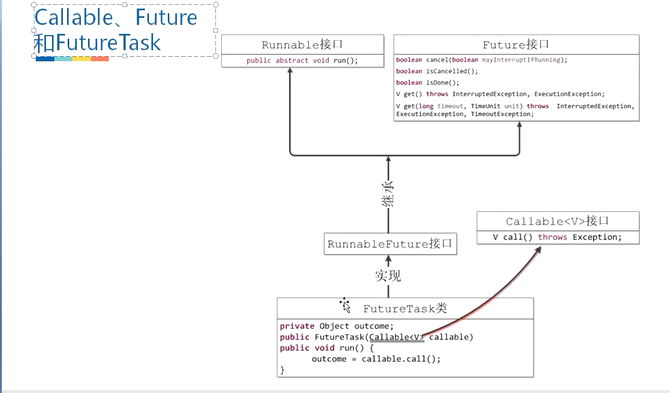
isDone,结束,正常还是异常结束,或者自己取消,返回true;
isCancelled 任务完成前被取消,返回true;
cancel(boolean):
1、 任务还没开始,返回false
2、 任务已经启动,cancel(true),中断正在运行的任务,中断成功,返回true,cancel(false),不会去中断已经运行的任务
3、 任务已经结束,返回false
package com.xiangxue.ch2.future; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 享学课堂 https://enjoy.ke.qq.com * *类说明:演示Future等的使用 */ public class UseFuture { /*实现Callable接口,允许有返回值*/ private static class UseCallable implements Callable<Integer>{ private int sum; @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { System.out.println("Callable子线程开始计算"); Thread.sleep(2000); for(int i=0;i<5000;i++) { sum = sum+i; } System.out.println("Callable子线程计算完成,结果="+sum); return sum; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { UseCallable useCallable = new UseCallable(); FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(useCallable); new Thread(futureTask).start(); Random r = new Random(); SleepTools.second(1); if(r.nextBoolean()) {//随机决定是获得结果还是终止任务 System.out.println("Get UseCallable result = "+futureTask.get()); }else { System.out.println("中断计算"); futureTask.cancel(true); } } }
包含图片和文字的文档的处理:图片(云上),可以用future去取图片,主线程继续解析文字。