对于一个CS程序, 可以直接连接数据库(方式一);
为了安全起见,可能会通过web service来获取数据(方式二),此时客户端程序在一台机器上, Web Service在另外一台机器上。
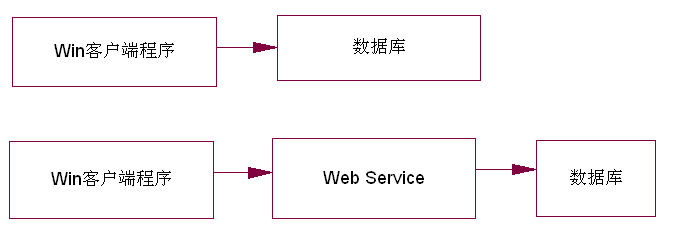
两者在代码实现上也是不一样的 。
方式一:只需要实现核心代码,然后客户端直接引用就可以了
方式二:除了实现核心代码外,web服务器上需要添加相应的web service, 同时客户端需要引用相应的web service, 客户端使用生成的代理去发送请求。
现在使用Spring.net后, 可以按方式一来编写代码, 但是部署时却可以支持两种布署方式。
现在使用为什么要使用AOP?中的例子来说明这个功能。
1.在IAccount类中加入一个新的接口DataSource, 用来表示数据的来源,其它不变。
{
string DataSource { get; }
}
2. Account类实现此接口
{
public string DataSource { get; private set; }
}
3.客户端实现代码
{
IApplicationContext ctx = ContextRegistry.GetContext();
IAccount account = (IAccount)ctx.GetObject("MyAccount");
Console.WriteLine(account.DataSource);
Console.ReadKey();
}
下面就来通过配置来支持上面两种布署方式。
App.config的配置如下:
<configSections>
<sectionGroup name="spring">
<section name="context" type="Spring.Context.Support.ContextHandler, Spring.Core"/>
<section name="objects" type="Spring.Context.Support.DefaultSectionHandler, Spring.Core"/>
</sectionGroup>
</configSections>
<spring>
<context>
<!--User Local -->
<resource uri="file://config/Local.config" />
<!--User Web Service -->
<!--<resource uri="file://config/WebService.config" />-->
</context>
</spring>
</configuration>
方式一的配置如上面, 如果要用方式二, 则注释掉方式一的配置,启用方式二的配置。
Local.config的配置如下:
<object id="ConsoleLogAspect" type="Spring.Aop.Support.NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor, Spring.Aop">
<property name="Advice">
<object type="Aspects.ConsoleLogAspect, Aspects" />
</property>
<property name="MappedNames">
<list>
<value>Deposit</value>
<value>Withdraw</value>
</list>
</property>
</object>
<object id="MyAccount" type="Spring.Aop.Framework.ProxyFactoryObject">
<property name="Target">
<object type="Business.Account, Business" >
<property name="DataSource" value="Data Source from Local"></property>
</object>
</property>
<property name="InterceptorNames">
<list>
<value>ConsoleLogAspect</value>
</list>
</property>
</object>
</objects>
在Local.config中,调用方法时会输入日志。
WebService.config 中的配置如下:
<object id="MyAccount" type="Spring.Web.Services.WebServiceProxyFactory, Spring.Services">
<property name="ServiceUri" value="http://localhost:1376/AopWeb/AccountService.asmx"/>
<property name="ServiceInterface" value="Business.IAccount, Business"/>
<property name="ProductTemplate">
<object>
<property name="Timeout" value="10000"/>
<!--10s-->
</object>
</property>
</object>
</objects>
ServiceUri定义了请求的web service url
4.为了支持方式二布署, 我们需要一个web site来发布web service。新建一个web site项目,只需要引用相应的dll, 然后配置一下就OK了, 为了简单,配置直接写到web.config中(配置可以写到单独的文件中的),web.config中的配置如下:
<configSections>
<sectionGroup name="spring">
<section name="context" type="Spring.Context.Support.WebContextHandler, Spring.Web"/>
<section name="objects" type="Spring.Context.Support.DefaultSectionHandler, Spring.Core" />
</sectionGroup>
</configSections>
<spring>
<context>
<resource uri="config://spring/objects"/>
</context>
<objects xmlns="http://www.springframework.net">
<object id="MyAccount" type="Business.Account, Business">
<property name="DataSource" value="Data Source from Remote Web Service"></property>
</object>
<object id="AccountService" type="Spring.Web.Services.WebServiceExporter, Spring.Web">
<property name="TargetName" value="MyAccount" />
<property name="Namespace" value="http://AccountService/WebServices" />
</object>
</objects>
</spring>
<system.web>
<compilation debug="false"></compilation>
<authentication mode="Windows"/>
<httpHandlers>
<add verb="*" path="*.asmx" type="Spring.Web.Services.WebServiceHandlerFactory, Spring.Web"/>
</httpHandlers>
<httpModules>
<add name="Spring" type="Spring.Context.Support.WebSupportModule, Spring.Web"/>
</httpModules>
</system.web>
</configuration>
现在不用添加AccountService.asmx文件,就可以访问http://localhost:1376/WebSite/AccountService.asmx web服务了。
到这里所有的工作都做完了, 下面来看一下运行的效果。
方式一运行时:
运行时会有相应的日志输出, 这里显示的是加载本地数据
方式二运行时:
运行时无日志输出, 这里显示的是从Web服务加载数据
结论:通过引用AOP框架, 可以在布署时决定布署方式, 只需要修改配置文件就可以实现不同的布署。
虽然CSLA.Net 也有相似的功能, 但是和Spring.net相比, CSLA.net对类具有侵入性,需要业务类继承它的泛型基类, 但Spring.net没有这方面的要求,只需要实现自己的接口就可以了,基于接口编程在这时就显得特别重要了。
一直以来,业务类都没有采用接口的方式编写, 因为觉得业务类是不会替换的, 但业务类面向接口编程在这里显示出了优势, 只要实现了接口, 就可以直接配置成web服务。
示例文件下载:AOPSample1.1
