一、AOP的概念
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),是面向切面编程的技术。AOP基于IoC基础,是对OOP的有益补充,流行的AOP框架有Sping AOP、AspectJ
AOP技术它利用一种称为“横切”的技术,剖解开封装的对象内部,并将那些影响了多个类的公共行为封装到一个可重用模块,并将其命名为”Aspect”,即切面。所谓”切面”,简单说就是那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑或责任封装起来,便于减少系统的重复代码,降低模块之间的耦合度,并有利于未来的可操作性和可维护性
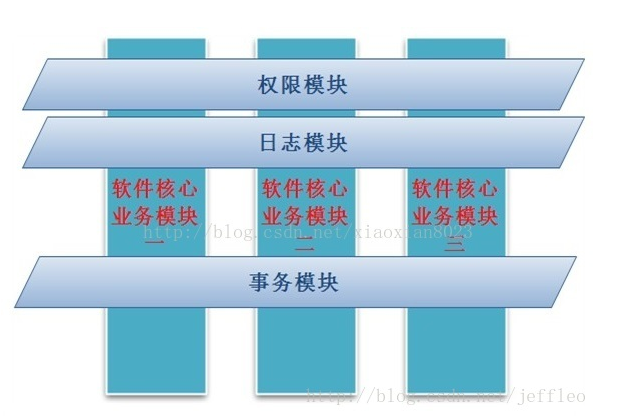
二、相关概念:
1、切面(aspect)
散落在系统各处的通用的业务逻辑代码,如上图中的日志模块,权限模块,事务模块等,切面用来装载pointcut和advice
2、通知(advice)
所谓通知指的就是指拦截到连接点之后要执行的代码,通知分为前置、后置、异常、最终、环绕通知五类
3、连接点(joinpoint)
被拦截到的点,因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点指的就是被拦截到的方法,实际上连接点还可以是字段或者构造器
4、切入点(pointcut)
拦截的方法,连接点拦截后变成切入点
6、目标对象(Target Object)
代理的目标对象,指要织入的对象模块,如上图的模块一、二、三
7、织入(weave)
通过切入点切入,将切面应用到目标对象并导致代理对象创建的过程
8、AOP代理(AOP Proxy)
AOP框架创建的对象,包含通知。在Spring中,AOP代理可以是JDK动态代理或CGLIB代理
三、五种类型的通知
-
Before advice:在某连接点(JoinPoint)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。
< aop:before> -
After advice:当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
< aop:after> -
After returnadvice:在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知,不包括抛出异常的情况。
< aop:after-returning> -
Around advice:包围一个连接点的通知,类似Web中Servlet规范中的Filter的doFilter方法。可以在方法执行的前后实现逻辑,也可以选择不执行方法
< aop:around> -
Afterthrowing advice:在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
< aop:after-throwing>
四、Spring AOP的3种实现方式
配置之前注意配置文件要加上命名空间:xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
1.基于xml配置的实现
spring-mvc.xml
1 <!-- 使用xml配置aop --> 2 <!-- 强制使用cglib代理,如果不设置,将默认使用jdk的代理,但是jdk的代理是基于接口的 --> 3 <aop:config proxy-target-class="true" /> 4 <aop:config> 5 <!--定义切面--> 6 <aop:aspect id="logAspect" ref="logInterceptor"> 7 <!-- 定义切入点 (配置在com.gray.user.controller下所有的类在调用之前都会被拦截)--> 8 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.gray.user.controller.*.*(..))" id="logPointCut"/> 9 <!--方法执行之前被调用执行的--> 10 <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="logPointCut"/><!--一个切入点的引用--> 11 <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="logPointCut"/><!--一个切入点的引用--> 12 </aop:aspect> 13 </aop:config>
LogInterceptor.java
1 package com.gray.interceptor; 2 3 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 4 import org.slf4j.Logger; 5 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 6 7 @Component 8 public class LogInterceptor { 9 private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogInterceptor.class); 10 public void before(){ 11 logger.info("login start!"); 12 } 13 14 public void after(){ 15 logger.info("login end!"); 16 } 17 }
在这里我没有配bean是因为我在之前的配置文件里面写了自动扫描组件的配置了
要加入日志管理逻辑的地方
1 @RequestMapping("/dologin.do") //url 2 public String dologin(User user, Model model){ 3 logger.info("login ...."); 4 String info = loginUser(user); 5 if (!"SUCC".equals(info)) { 6 model.addAttribute("failMsg", "用户不存在或密码错误!"); 7 return "/jsp/fail"; 8 }else{ 9 model.addAttribute("successMsg", "登陆成功!");//返回到页面说夹带的参数 10 model.addAttribute("name", user.getUsername()); 11 return "/jsp/success";//返回的页面 12 } 13 }
结果截图:

2.基于注解的实现
spring-mvc.xml
1 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"> 2 </aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
LogInterceptor.java
1 @Aspect 2 @Component 3 public class LogInterceptor { 4 private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogInterceptor.class); 5 @Before(value = "execution(* com.gray.user.controller.*.*(..))") 6 public void before(){ 7 logger.info("login start!"); 8 } 9 @After(value = "execution(* com.gray.user.controller.*.*(..))") 10 public void after(){ 11 logger.info("login end!"); 12 } 13 }
要加入逻辑的地方同上。
结果截图:

3.基于自定义注解的实现
基于注解,所以spring-mvc.xml也是和上面的一样的。
LogInterceptor.java(这里我只加入前置日志)
1 package com.gray.interceptor; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 4 5 import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; 6 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; 7 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; 8 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; 9 import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; 10 import org.slf4j.Logger; 11 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 12 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 13 14 import com.gray.annotation.Log; 15 16 @Aspect 17 @Component 18 public class LogInterceptor { 19 private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogInterceptor.class); 20 21 @Pointcut("@annotation(com.gray.annotation.Log)") 22 public void controllerAspect() { 23 24 } 25 @Before("controllerAspect()") 26 public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){ 27 logger.info(getOper(joinPoint)); 28 } 29 private String getOper(JoinPoint joinPoint) { 30 MethodSignature methodName = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature(); 31 Method method = methodName.getMethod(); 32 return method.getAnnotation(Log.class).oper(); 33 } 34 }
同时,加入逻辑的地方需要加入Log注解
1 @RequestMapping("/dologin.do") //url 2 @Log(oper="user login") 3 public String dologin(User user, Model model){ 4 logger.info("login ...."); 5 String info = loginUser(user); 6 if (!"SUCC".equals(info)) { 7 model.addAttribute("failMsg", "用户不存在或密码错误!"); 8 return "/jsp/fail"; 9 }else{ 10 model.addAttribute("successMsg", "登陆成功!");//返回到页面说夹带的参数 11 model.addAttribute("name", user.getUsername()); 12 return "/jsp/success";//返回的页面 13 } 14 }
结果截图:

五、基于Schema的Spring AOP实例
1、定义具体业务逻辑模块(目标对象)
两个业务逻辑模块都是基于接口
TestAOPDaoImpl .java
1 public class TestAOPDaoImpl implements TestAOPDao{ 2 3 @Override 4 public void addUser() { 5 System.out.println("添加成功"); 6 } 7 8 }
TestAOPServiceImpl.java
1 public class TestAOPServiceImpl implements TestAOPService{ 2 3 @Autowired 4 private TestAOPDao testAOPDao; 5 6 @Override 7 public void addUser() { 8 testAOPDao.addUser(); 9 } 10 11 }
2、 定义切面(即实现通知逻辑)
JointPoint是连接点,aop创建代理后会返回一个连接点,然后在通知中可以通过该连接点实现我们的切面逻辑
日志切面
1 public class LogAdivice{ 2 3 public void myBeforeAdivice(JoinPoint joinPoint){ 4 String classname = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(); 5 String methodname = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 6 System.out.println(classname + " ——前置通知——" + methodname); 7 } 8 9 public void myAfterAdivice(JoinPoint joinPoint){ 10 String classname = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(); 11 String methodname = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 12 System.out.println(classname + " ——后置通知——" + methodname); 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * 环绕通知将决定要不要执行连接点 17 * @throws Throwable 18 */ 19 public void myAroundAdivice(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable{ 20 System.out.println("环绕通知,执行代码前"); 21 //选择执行 22 point.proceed(); 23 System.out.println("环绕通知,执行代码后"); 24 } 25 }
时间切面:
1 public class TimeAdvice { 2 3 public void timeBefore(){ 4 System.out.println("beforeTime = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 5 } 6 7 public void timeAfter(){ 8 System.out.println("afterTime = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); 9 } 10 }
在applicationContext中配置切面:
1 <context:annotation-config/> 2 <bean id="testAOPDao" class="com.ssh.dao.impl.TestAOPDaoImpl"/> 3 <bean id="testAOPService" class="com.ssh.service.impl.TestAOPServiceImpl"/> 4 <bean id="logAdivice" class="com.ssh.adivice.LogAdivice"/> 5 <bean id="timeAdvice" class="com.ssh.adivice.TimeAdvice"/> 6 7 <aop:config> 8 <!-- 配置一个切面 --> 9 <aop:aspect id="logaop" ref="logAdivice" order="2"> 10 <!-- 定义切入点,表示对service的所有方法都进行拦截 --> 11 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ssh.service.TestAOPService.*(..))" id="testpointcut"/> 12 <!-- 定义前置通知 --> 13 <aop:before method="myBeforeAdivice" pointcut-ref="testpointcut"/> 14 <!-- 定义后置通知 --> 15 <aop:after-returning method="myAfterAdivice" pointcut-ref="testpointcut"/> 16 <!-- 定义环绕通知 --> 17 <aop:around method="myAroundAdivice" pointcut-ref="testpointcut"/> 18 </aop:aspect> 19 20 <!-- 定义另一个切面 --> 21 <aop:aspect id="timeaop" ref="timeAdvice" order="1"> 22 <!-- 定义切入点,表示对service的所有方法都进行拦截 --> 23 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ssh.service.TestAOPService.*(..))" id="testpointcut"/> 24 <!-- 定义前置通知 --> 25 <aop:before method="timeBefore" pointcut-ref="testpointcut"/> 26 <!-- 定义后置通知 --> 27 <aop:after-returning method="timeAfter" pointcut-ref="testpointcut"/> 28 </aop:aspect> 29 </aop:config>
当有多个切面时,Spring默认是按照切面定义的顺序来执行,也可以通过order属性来配置切面的执行属性,order=1 早于 order=2执行
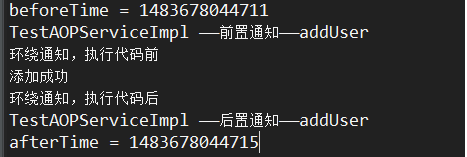
测试结果
1 public class AOPTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 5 TestAOPService service = (TestAOPService) context.getBean("testAOPService"); 6 service.addUser(); 7 } 8 9 }
六、基于@AspectJ注解的AOP实现
1、定义具体业务逻辑模块(目标对象)-----同上
2、定义切面(即实现通知逻辑)
重点是定义切入点
1 @Aspect 2 public class LogAdivice{ 3 4 //定义一个方法作为切入点id 5 @Pointcut("execution(* com.ssh.service.TestAOPService.*(..))") 6 private void allMethod(){} 7 8 @Before("allMethod()") 9 public void myBeforeAdivice(JoinPoint joinPoint){ 10 String classname = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(); 11 String methodname = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 12 System.out.println(classname + " ——前置通知——" + methodname); 13 } 14 15 @AfterReturning("allMethod()") 16 public void myAfterAdivice(JoinPoint joinPoint){ 17 String classname = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(); 18 String methodname = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); 19 System.out.println(classname + " ——后置通知——" + methodname); 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 环绕通知将决定要不要执行连接点 24 * @throws Throwable 25 */ 26 @Around("allMethod()") 27 public void myAroundAdivice(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable{ 28 System.out.println("环绕通知,执行代码前"); 29 //执行 30 point.proceed(); 31 System.out.println("环绕通知,执行代码后"); 32 } 33 }
在applicationContext的配置:
1 <!-- 打开自动扫描(隐式打开注解管理器) --> 2 <!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.ssh"/> --> 3 <context:annotation-config/> 4 <bean id="testAOPDao" class="com.ssh.dao.impl.TestAOPDaoImpl"/> 5 <bean id="testAOPService" class="com.ssh.service.impl.TestAOPServiceImpl"/> 6 <bean id="logAdivice" class="com.ssh.adivice.LogAdivice"/> 7 <bean id="timeAdvice" class="com.ssh.adivice.TimeAdvice"/> 8 9 <!-- 打开aop注解管理器 --> 10 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
七、Java代码使用AOP
1 public class TestControlFlowPointcut { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //只有TargetCaller中的方法才会被拦截 5 ControlFlowPointcut pointcut = new ControlFlowPointcut(TargetCaller.class); 6 BeforeAdvice beforeAdvice = new MethodBeforeAdvice() { 7 public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable { 8 System.out.println(method.getClass().getSimpleName() + ":" + 9 method.getName() + " - before logic "); 10 } 11 }; 12 13 // Spring 中的 Aspect,装载pointcut和advice 14 PointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, beforeAdvice); 15 16 // Spring 基本织入器weaver 17 ProxyFactory weaver = new ProxyFactory(); 18 weaver.setTarget(new TargetObject()); //指定代理目标对象 19 weaver.addAdvisor(advisor); //指定方面 20 21 Object proxy = weaver.getProxy(); 22 23 //直接调用Targetobject的方法不会被拦截 24 ((TargetObject)proxy).targetMethod(); 25 26 //使用ControlFlowPointcut指定的类中的方法才会被拦截 27 TargetCaller caller = new TargetCaller(); 28 caller.setTarget((TargetObject)proxy); 29 caller.callMethod(); 30 } 31 }