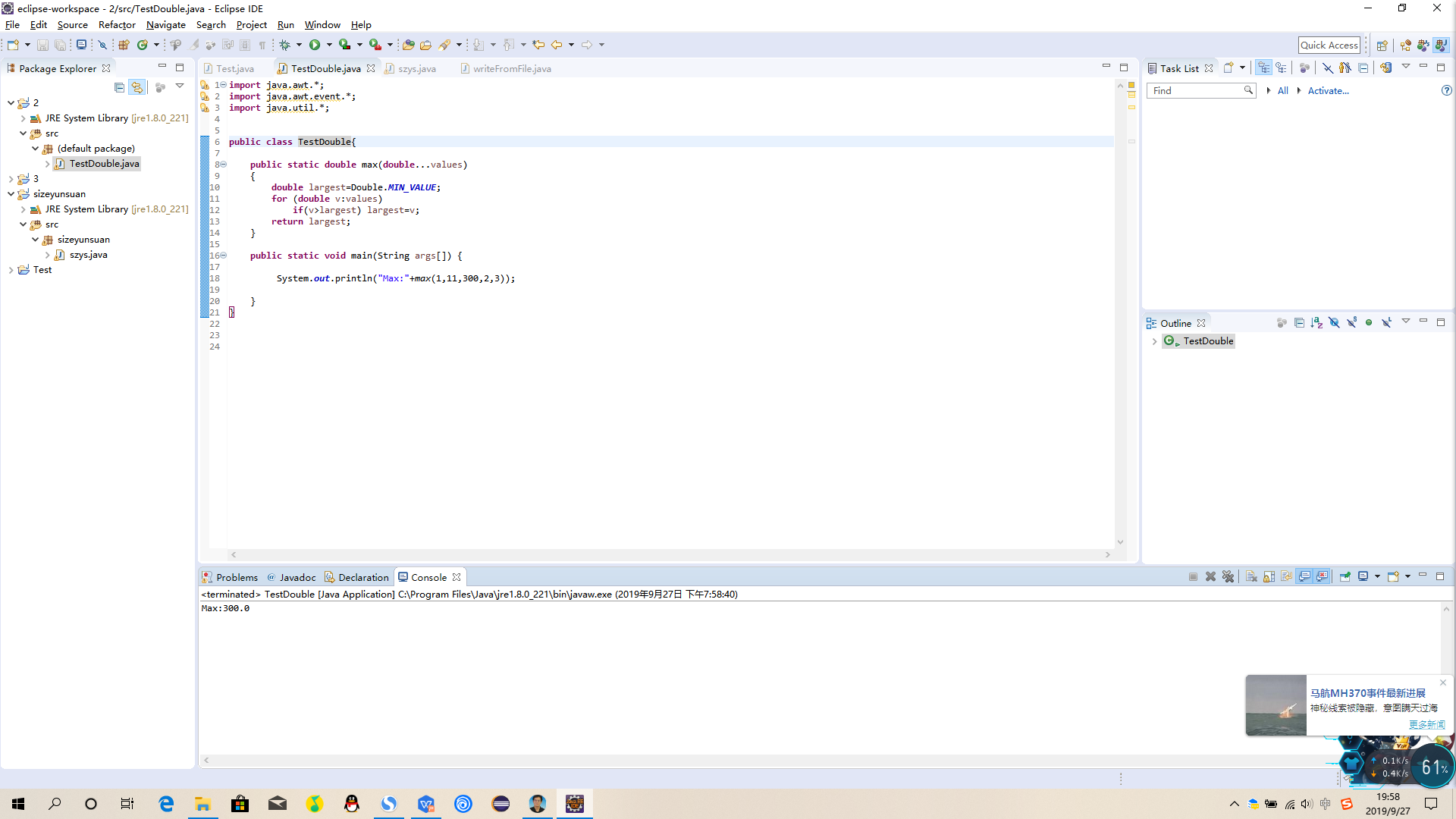
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalculateN {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("请输入N:");
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
int number=scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(number+"!="+calculateN2(number));
}
public static long calculateN(int n) {
if(n==1 || n==0){
return 1;
}
return n*calculateN(n-1);
}
public static BigInteger calculateN2(int n) {
if(n==1 || n==0){
return BigInteger.valueOf(1);
}
return BigInteger.valueOf(n).multiply(calculateN2((n-1)));
}
}
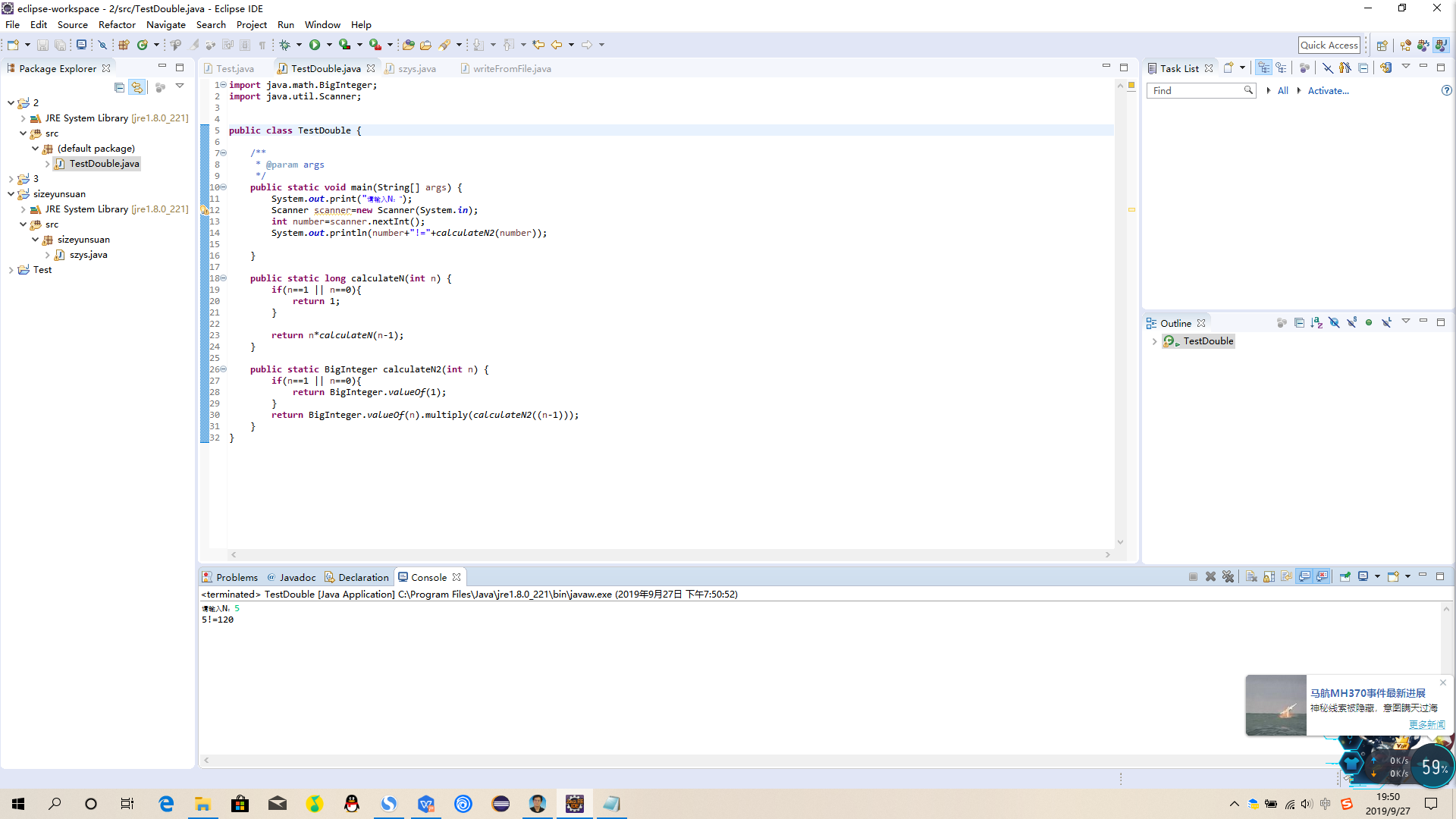
public class CompareFloatNumber {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//compare();
compare2();
}
private static void compare() {
double i = 0.0001;
double j = 0.00010000000000000001;
System.out.println(i==j); //输出:true
}
private static void compare2() {
double i = 0.0001;
double j = 0.00010000000000000001;
if(Math.abs(i-j)<1e-10){
System.out.println("true");
}
else
{
System.out.println("false");
}
}
}
// MethodOverload.java
// Using overloaded methods
public class MethodOverload {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("The square of integer 7 is " + square(7));
System.out.println("
The square of double 7.5 is " + square(7.5));
}
public static int square(int x) {
return x * x;
}
public static double square(double y) {
return y * y;
}
}

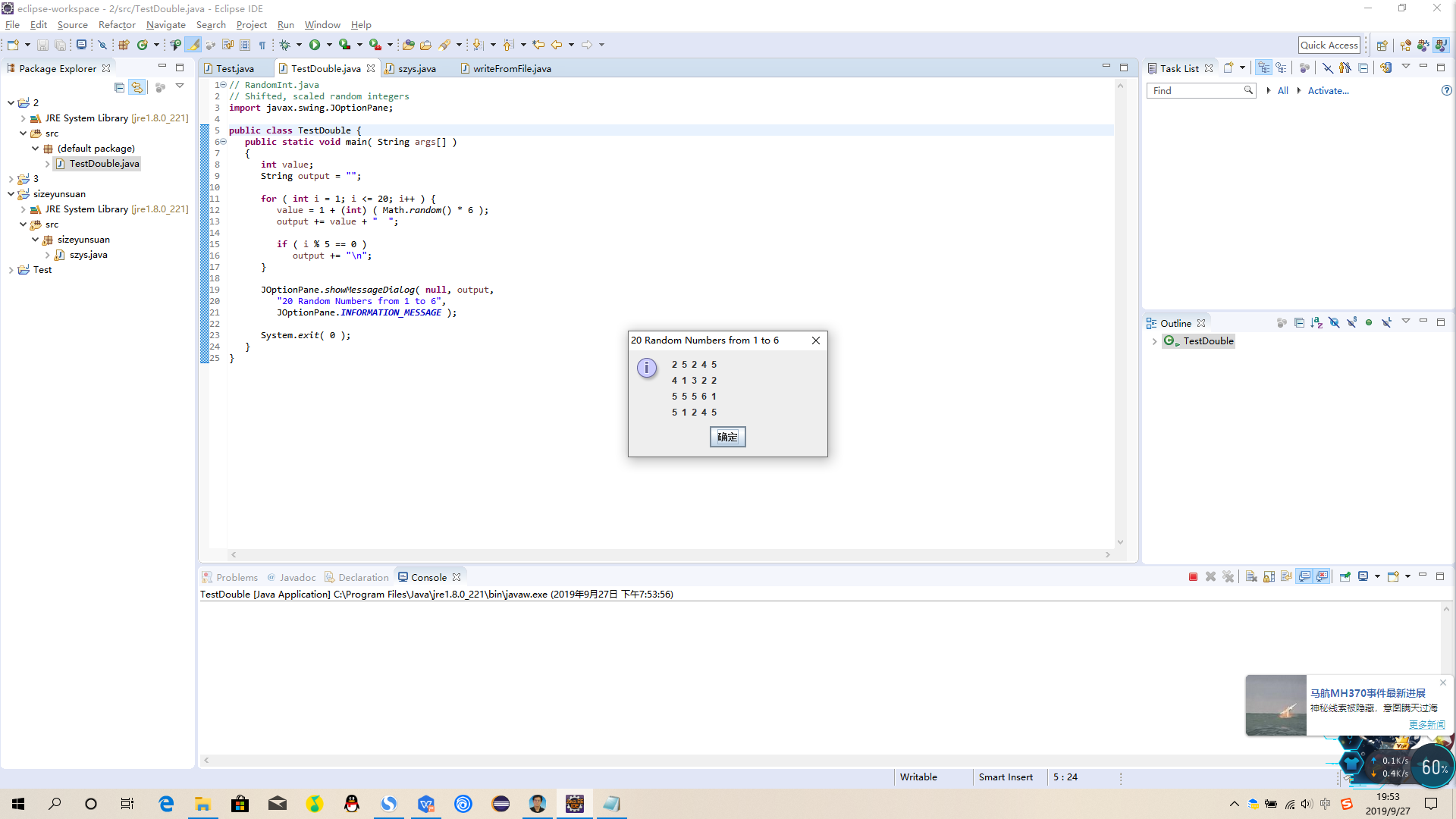
// RandomInt.java
// Shifted, scaled random integers
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class RandomInt {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int value;
String output = "";
for ( int i = 1; i <= 20; i++ ) {
value = 1 + (int) ( Math.random() * 6 );
output += value + " ";
if ( i % 5 == 0 )
output += "
";
}
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, output,
"20 Random Numbers from 1 to 6",
JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
System.exit( 0 );
}
}
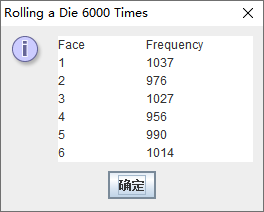
// RollDie.java
// Roll a six-sided die 6000 times
import javax.swing.*;
public class RollDie {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
int frequency1 = 0, frequency2 = 0,
frequency3 = 0, frequency4 = 0,
frequency5 = 0, frequency6 = 0, face;
// summarize results
for ( int roll = 1; roll <= 6000; roll++ ) {
face = 1 + (int) ( Math.random() * 6 );
switch ( face ) {
case 1:
++frequency1;
break;
case 2:
++frequency2;
break;
case 3:
++frequency3;
break;
case 4:
++frequency4;
break;
case 5:
++frequency5;
break;
case 6:
++frequency6;
break;
}
}
JTextArea outputArea = new JTextArea( 7, 10 );
outputArea.setText(
"Face Frequency" +
"
1 " + frequency1 +
"
2 " + frequency2 +
"
3 " + frequency3 +
"
4 " + frequency4 +
"
5 " + frequency5 +
"
6 " + frequency6 );
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null, outputArea,
"Rolling a Die 6000 Times",
JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE );
System.exit( 0 );
}
}
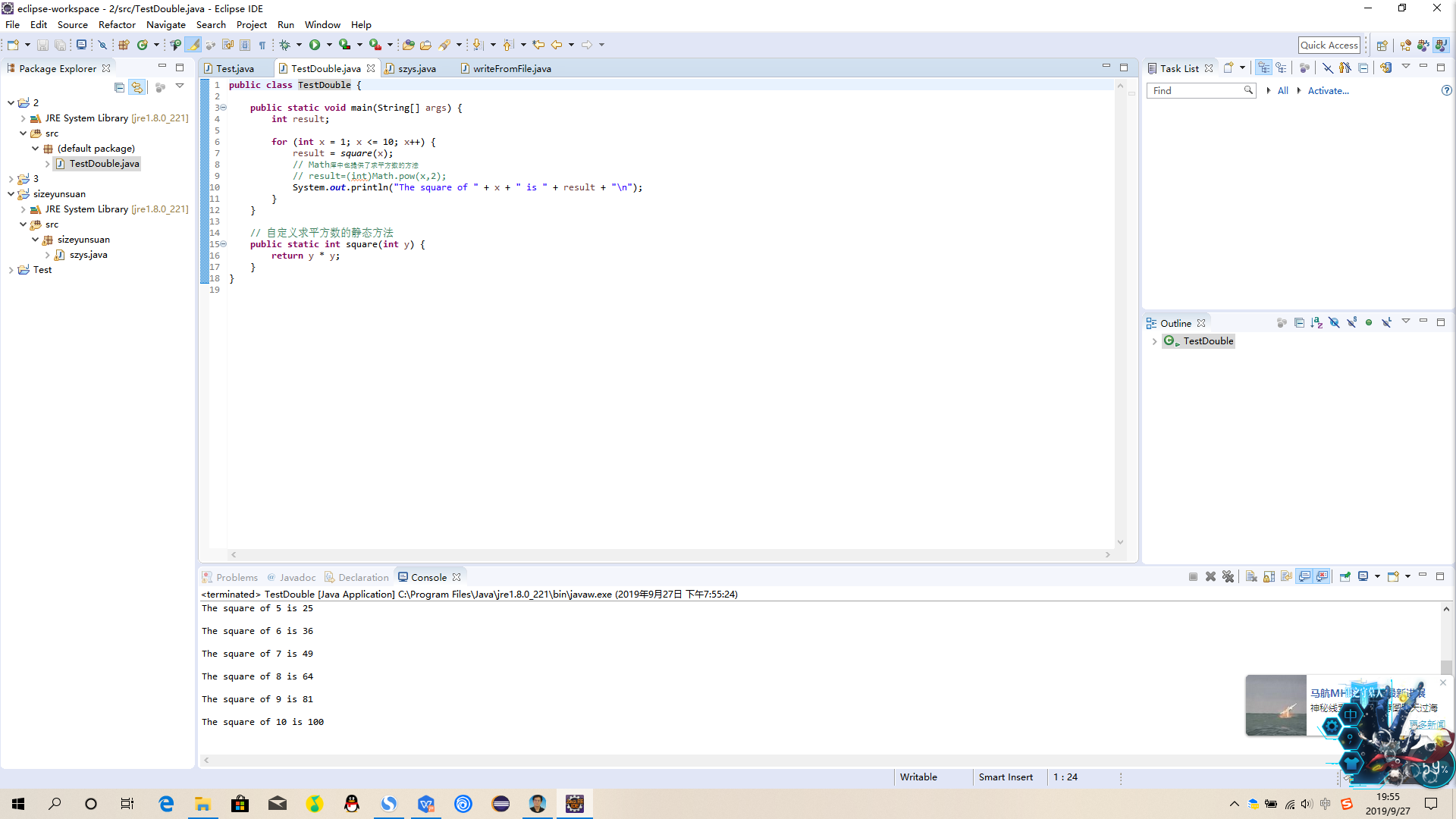
public class SquareInt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result;
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
result = square(x);
// Math库中也提供了求平方数的方法
// result=(int)Math.pow(x,2);
System.out.println("The square of " + x + " is " + result + "
");
}
}
// 自定义求平方数的静态方法
public static int square(int y) {
return y * y;
}
}
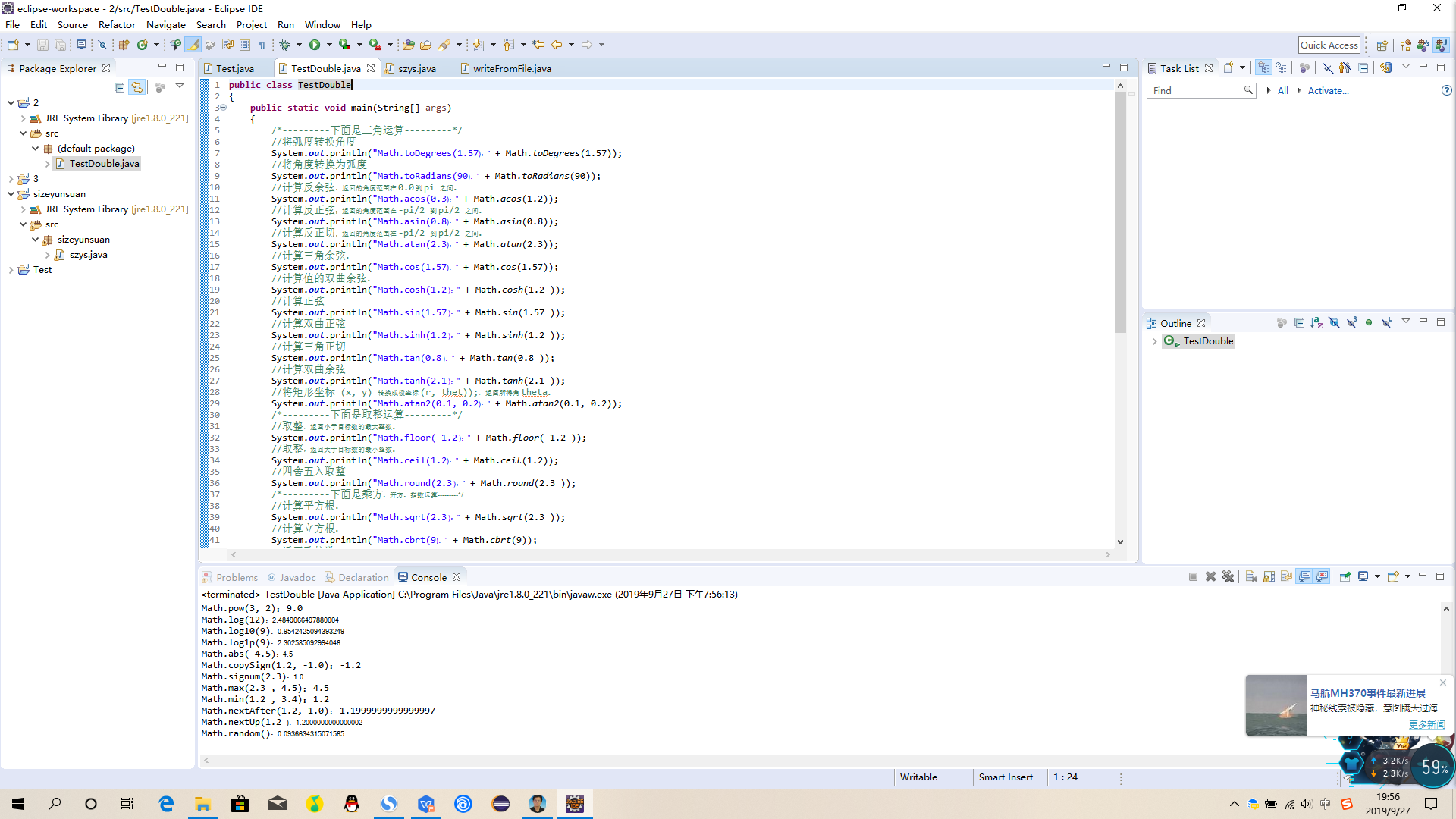
public class TestDouble
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*---------下面是三角运算---------*/
//将弧度转换角度
System.out.println("Math.toDegrees(1.57):" + Math.toDegrees(1.57));
//将角度转换为弧度
System.out.println("Math.toRadians(90):" + Math.toRadians(90));
//计算反余弦,返回的角度范围在 0.0 到 pi 之间。
System.out.println("Math.acos(0.3):" + Math.acos(1.2));
//计算反正弦;返回的角度范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
System.out.println("Math.asin(0.8):" + Math.asin(0.8));
//计算反正切;返回的角度范围在 -pi/2 到 pi/2 之间。
System.out.println("Math.atan(2.3):" + Math.atan(2.3));
//计算三角余弦。
System.out.println("Math.cos(1.57):" + Math.cos(1.57));
//计算值的双曲余弦。
System.out.println("Math.cosh(1.2 ):" + Math.cosh(1.2 ));
//计算正弦
System.out.println("Math.sin(1.57 ):" + Math.sin(1.57 ));
//计算双曲正弦
System.out.println("Math.sinh(1.2 ):" + Math.sinh(1.2 ));
//计算三角正切
System.out.println("Math.tan(0.8 ):" + Math.tan(0.8 ));
//计算双曲余弦
System.out.println("Math.tanh(2.1 ):" + Math.tanh(2.1 ));
//将矩形坐标 (x, y) 转换成极坐标 (r, thet));,返回所得角 theta。
System.out.println("Math.atan2(0.1, 0.2):" + Math.atan2(0.1, 0.2));
/*---------下面是取整运算---------*/
//取整,返回小于目标数的最大整数。
System.out.println("Math.floor(-1.2 ):" + Math.floor(-1.2 ));
//取整,返回大于目标数的最小整数。
System.out.println("Math.ceil(1.2):" + Math.ceil(1.2));
//四舍五入取整
System.out.println("Math.round(2.3 ):" + Math.round(2.3 ));
/*---------下面是乘方、开方、指数运算---------*/
//计算平方根。
System.out.println("Math.sqrt(2.3 ):" + Math.sqrt(2.3 ));
//计算立方根。
System.out.println("Math.cbrt(9):" + Math.cbrt(9));
//返回欧拉数 e 的n次幂。
System.out.println("Math.exp(2):" + Math.exp(2));
//返回 sqrt(x2:" +y2),没有中间溢出或下溢。
System.out.println("Math.hypot(4 , 4):" + Math.hypot(4 , 4));
// 按照 IEEE 754 标准的规定,对两个参数进行余数运算。
System.out.println("Math.IEEEremainder(5 , 2):" + Math.IEEEremainder(5 , 2));
//计算乘方
System.out.println("Math.pow(3, 2):" + Math.pow(3, 2));
//计算自然对数
System.out.println("Math.log(12):" + Math.log(12));
//计算底数为 10 的对数。
System.out.println("Math.log10(9):" + Math.log10(9));
// 回参数与 1 之和的自然对数。
System.out.println("Math.log1p(9):" + Math.log1p(9));
/*---------下面是符号相关的运算---------*/
//计算绝对值。
System.out.println("Math.abs(-4.5):" + Math.abs(-4.5));
//符号赋值,返回带有第二个浮点数符号的第一个浮点参数。
System.out.println("Math.copySign(1.2, -1.0):" + Math.copySign(1.2, -1.0));
//符号函数;如果参数为 0,则返回 0;如果参数大于 0,则返回 1.0;如果参数小于 0,则返回 -1.0。
System.out.println("Math.signum(2.3):" + Math.signum(2.3));
/*---------下面是大小相关的运算运算---------*/
//找出最大值
System.out.println("Math.max(2.3 , 4.5):" + Math.max(2.3 , 4.5));
//计算最小值
System.out.println("Math.min(1.2 , 3.4):" + Math.min(1.2 , 3.4));
//返回第一个参数和第二个参数之间与第一个参数相邻的浮点数。
System.out.println("Math.nextAfter(1.2, 1.0):" + Math.nextAfter(1.2, 1.0));
//返回比目标数略大的浮点数
System.out.println("Math.nextUp(1.2 ):" + Math.nextUp(1.2 ));
//返回一个伪随机数,该值大于等于 0.0 且小于 1.0。
System.out.println("Math.random():" + Math.random());
}
}
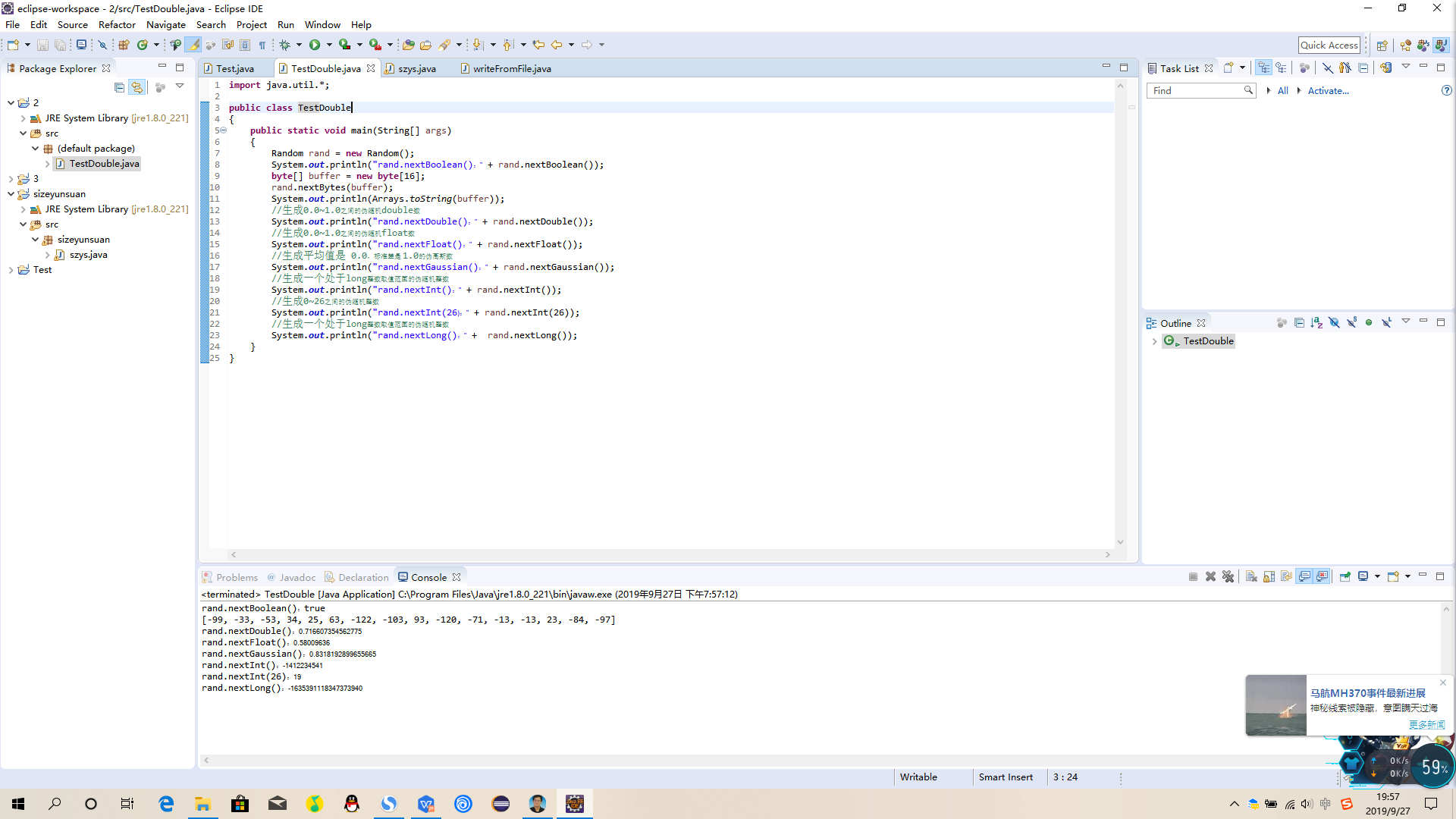
import java.util.*;
public class TestRandom
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Random rand = new Random();
System.out.println("rand.nextBoolean():" + rand.nextBoolean());
byte[] buffer = new byte[16];
rand.nextBytes(buffer);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
//生成0.0~1.0之间的伪随机double数
System.out.println("rand.nextDouble():" + rand.nextDouble());
//生成0.0~1.0之间的伪随机float数
System.out.println("rand.nextFloat():" + rand.nextFloat());
//生成平均值是 0.0,标准差是 1.0的伪高斯数
System.out.println("rand.nextGaussian():" + rand.nextGaussian());
//生成一个处于long整数取值范围的伪随机整数
System.out.println("rand.nextInt():" + rand.nextInt());
//生成0~26之间的伪随机整数
System.out.println("rand.nextInt(26):" + rand.nextInt(26));
//生成一个处于long整数取值范围的伪随机整数
System.out.println("rand.nextLong():" + rand.nextLong());
}
}
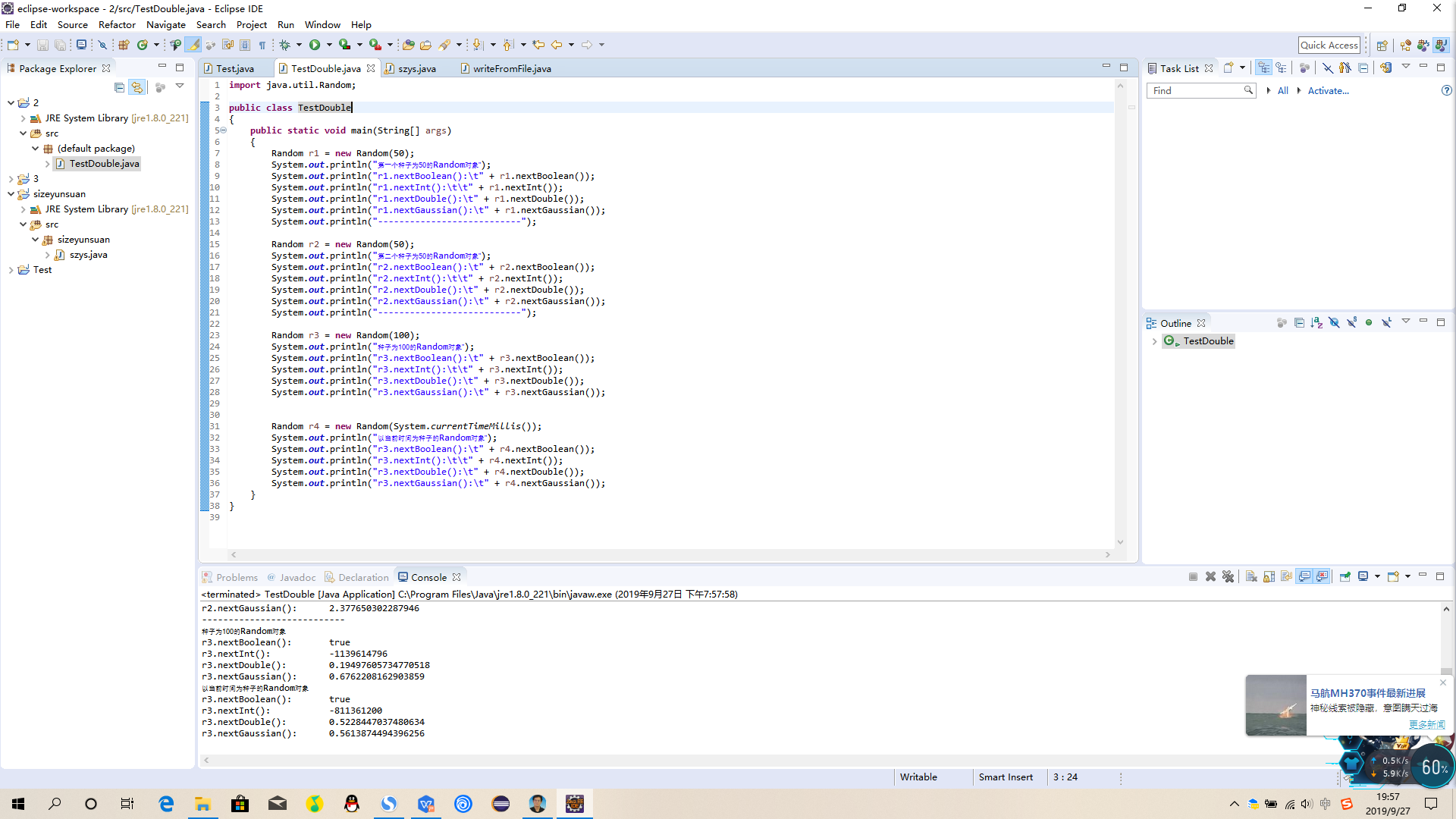
import java.util.Random;
public class TestSeed
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Random r1 = new Random(50);
System.out.println("第一个种子为50的Random对象");
System.out.println("r1.nextBoolean(): " + r1.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("r1.nextInt(): " + r1.nextInt());
System.out.println("r1.nextDouble(): " + r1.nextDouble());
System.out.println("r1.nextGaussian(): " + r1.nextGaussian());
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Random r2 = new Random(50);
System.out.println("第二个种子为50的Random对象");
System.out.println("r2.nextBoolean(): " + r2.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("r2.nextInt(): " + r2.nextInt());
System.out.println("r2.nextDouble(): " + r2.nextDouble());
System.out.println("r2.nextGaussian(): " + r2.nextGaussian());
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Random r3 = new Random(100);
System.out.println("种子为100的Random对象");
System.out.println("r3.nextBoolean(): " + r3.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("r3.nextInt(): " + r3.nextInt());
System.out.println("r3.nextDouble(): " + r3.nextDouble());
System.out.println("r3.nextGaussian(): " + r3.nextGaussian());
Random r4 = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("以当前时间为种子的Random对象");
System.out.println("r3.nextBoolean(): " + r4.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("r3.nextInt(): " + r4.nextInt());
System.out.println("r3.nextDouble(): " + r4.nextDouble());
System.out.println("r3.nextGaussian(): " + r4.nextGaussian());
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
public class VariableArgumentsTest{
public static double max(double...values)
{
double largest=Double.MIN_VALUE;
for (double v:values)
if(v>largest) largest=v;
return largest;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Max:"+max(1,11,300,2,3));
}
}