下载地址:https://github.com/dmajkic/redis/downloads 下载下来的包里有两个,
一个是32位的,一个是64位的。根据自己的实情情况选择,我的是64bit,
把这个文件夹复制到其它地方,比如E:TRS
edis目录下。
打开一个cmd窗口 使用cd命令切换目录到E:TRS
edis 运行 redis-server.exe redis.conf
如果想方便的话,可以把redis的路径加到系统的环境变量里,这样就省得再输路径了,后面的那个redis.conf可以省略,如果省略,会启用默认的。输入之后,会显示如下界面:
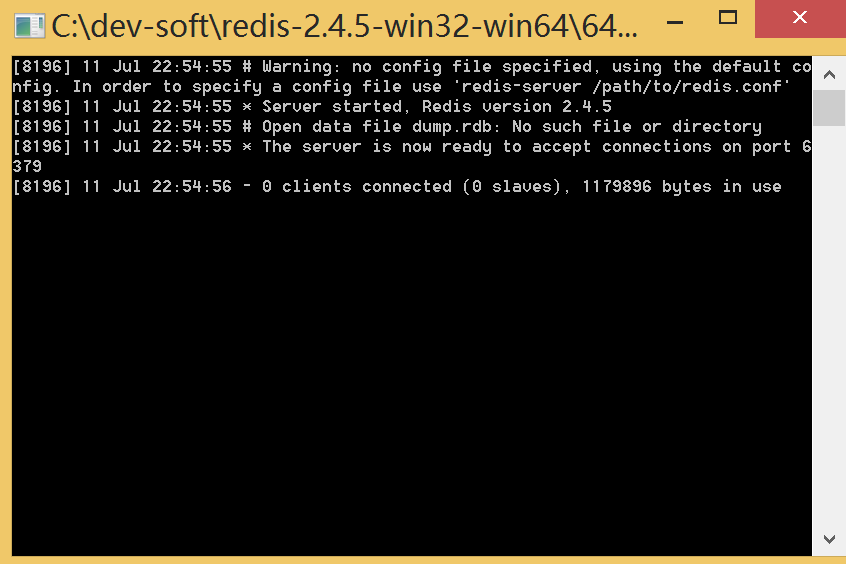
这时候别启一个cmd窗口,原来的不要关闭,不然就无法访问服务端了
切换到redis目录下运行 redis-cli.exe -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379 出现下图:

这时候,就已经完成配置了,现在说下它的的redis.conf配置文件。下面是相关项的说明,

1 # Redis configuration file example 2 3 4 5 # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specifiy 6 7 # it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth: 8 9 # 10 11 # 1k => 1000 bytes 12 13 # 1kb => 1024 bytes 14 15 # 1m => 1000000 bytes 16 17 # 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes 18 19 # 1g => 1000000000 bytes 20 21 # 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes 22 23 # 24 25 # units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same. 26 27 28 29 # By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. 30 31 # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized. 32 33 daemonize no 34 35 Redis默认不是以守护进程的方式运行,可以通过该配置项修改,使用yes启用守护进程 36 37 38 39 # When running daemonized, Redis writes a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid by 40 41 # default. You can specify a custom pid file location here. 42 43 pidfile /var/run/redis.pid 44 45 当Redis以守护进程方式运行时,Redis默认会把pid写入/var/run/redis.pid文件,可以通过pidfile指定 46 47 # Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379. 48 49 # If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket. 50 51 port 6379 52 53 指定Redis监听端口,默认端口为6379 54 55 # If you want you can bind a single interface, if the bind option is not 56 57 # specified all the interfaces will listen for incoming connections. 58 59 # 60 61 # bind 127.0.0.1 62 63 绑定的主机地址 64 65 # Specify the path for the unix socket that will be used to listen for 66 67 # incoming connections. There is no default, so Redis will not listen 68 69 # on a unix socket when not specified. 70 71 # 72 73 # unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock 74 75 # unixsocketperm 755 76 77 78 79 # Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds (0 to disable) 80 81 timeout 0 82 83 当 客户端闲置多长时间后关闭连接,如果指定为0,表示关闭该功能 84 85 # Set server verbosity to 'debug' 86 87 # it can be one of: 88 89 # debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing) 90 91 # verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level) 92 93 # notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably) 94 95 # warning (only very important / critical messages are logged) 96 97 loglevel verbose 98 99 指定日志记录级别,Redis总共支持四个级别:debug、verbose、notice、warning,默认为verbose 100 101 # Specify the log file name. Also 'stdout' can be used to force 102 103 # Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard 104 105 # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null 106 107 logfile stdout 108 109 日志记录方式,默认为标准输出,如果配置Redis为守护进程方式运行,而这里又配置为日志记录方式为标准输出,则日志将会发送给/dev/null 110 111 # To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes, 112 113 # and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs. 114 115 # syslog-enabled no 116 117 118 119 # Specify the syslog identity. 120 121 # syslog-ident redis 122 123 124 125 # Specify the syslog facility. Must be USER or between LOCAL0-LOCAL7. 126 127 # syslog-facility local0 128 129 130 131 # Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select 132 133 # a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where 134 135 # dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1 136 137 databases 16 138 139 设置数据库的数量,默认数据库为0,可以使用SELECT <dbid>命令在连接上指定数据库id 140 141 ################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################# 142 143 # 144 145 # Save the DB on disk: 146 147 # 148 149 # save <seconds> <changes> 150 151 # 152 153 # Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given 154 155 # number of write operations against the DB occurred. 156 157 # 158 159 # In the example below the behaviour will be to save: 160 161 # after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed 162 163 # after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed 164 165 # after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed 166 167 # 168 169 # Note: you can disable saving at all commenting all the "save" lines. 170 171 172 173 save 900 1 174 175 save 300 10 176 177 save 60 10000 178 179 分别表示900秒(15分钟)内有1个更改,300秒(5分钟)内有10个更改以及60秒内有10000个更改。 180 181 指定在多长时间内,有多少次更新操作,就将数据同步到数据文件,可以多个条件配合 182 183 # Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases? 184 185 # For default that's set to 'yes' as it's almost always a win. 186 187 # If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but 188 189 # the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys. 190 191 rdbcompression yes 192 193 指定存储至本地数据库时是否压缩数据,默认为yes,Redis采用LZF压缩,如果为了节省CPU时间,可以关闭该选项,但会导致数据库文件变的巨大 194 195 # The filename where to dump the DB 196 197 dbfilename dump.rdb 198 199 指定本地数据库文件名,默认值为dump.rdb 200 201 # The working directory. 202 203 # 204 205 # The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified 206 207 # above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive. 208 209 # 210 211 # Also the Append Only File will be created inside this directory. 212 213 # 214 215 # Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name. 216 217 dir ./ 218 219 指定本地数据库存放目录 220 221 ################################# REPLICATION ################################# 222 223 224 225 # Master-Slave replication. Use slaveof to make a Redis instance a copy of 226 227 # another Redis server. Note that the configuration is local to the slave 228 229 # so for example it is possible to configure the slave to save the DB with a 230 231 # different interval, or to listen to another port, and so on. 232 233 # 234 235 # slaveof <masterip> <masterport> 236 237 slaveof <masterip> <masterport> 设置当本机为slav服务时,设置master服务的IP地址及端口,在Redis启动时,它会自动从master进行数据同步 238 239 # If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration 240 241 # directive below) it is possible to tell the slave to authenticate before 242 243 # starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will 244 245 # refuse the slave request. 246 247 # 248 249 # masterauth <master-password> 250 251 masterauth <master-password> 当master服务设置了密码保护时,slav服务连接master的密码 252 253 # When a slave lost the connection with the master, or when the replication 254 255 # is still in progress, the slave can act in two different ways: 256 257 # 258 259 # 1) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'yes' (the default) the slave will 260 261 # still reply to client requests, possibly with out of data data, or the 262 263 # data set may just be empty if this is the first synchronization. 264 265 # 266 267 # 2) if slave-serve-stale data is set to 'no' the slave will reply with 268 269 # an error "SYNC with master in progress" to all the kind of commands 270 271 # but to INFO and SLAVEOF. 272 273 # 274 275 slave-serve-stale-data yes 276 277 278 279 # Slaves send PINGs to server in a predefined interval. It's possible to change 280 281 # this interval with the repl_ping_slave_period option. The default value is 10 282 283 # seconds. 284 285 # 286 287 # repl-ping-slave-period 10 288 289 290 291 # The following option sets a timeout for both Bulk transfer I/O timeout and 292 293 # master data or ping response timeout. The default value is 60 seconds. 294 295 # 296 297 # It is important to make sure that this value is greater than the value 298 299 # specified for repl-ping-slave-period otherwise a timeout will be detected 300 301 # every time there is low traffic between the master and the slave. 302 303 # 304 305 # repl-timeout 60 306 307 308 309 ################################## SECURITY ################################### 310 311 312 313 # Require clients to issue AUTH <PASSWORD> before processing any other 314 315 # commands. This might be useful in environments in which you do not trust 316 317 # others with access to the host running redis-server. 318 319 # 320 321 # This should stay commented out for backward compatibility and because most 322 323 # people do not need auth (e.g. they run their own servers). 324 325 # 326 327 # Warning: since Redis is pretty fast an outside user can try up to 328 329 # 150k passwords per second against a good box. This means that you should 330 331 # use a very strong password otherwise it will be very easy to break. 332 333 # 334 335 # requirepass foobared 336 337 requirepass foobared 设置Redis连接密码,如果配置了连接密码,客户端在连接Redis时需要通过AUTH <password>命令提供密码,默认关闭 338 339 # Command renaming. 340 341 # 342 343 # It is possilbe to change the name of dangerous commands in a shared 344 345 # environment. For instance the CONFIG command may be renamed into something 346 347 # of hard to guess so that it will be still available for internal-use 348 349 # tools but not available for general clients. 350 351 # 352 353 # Example: 354 355 # 356 357 # rename-command CONFIG b840fc02d524045429941cc15f59e41cb7be6c52 358 359 # 360 361 # It is also possilbe to completely kill a command renaming it into 362 363 # an empty string: 364 365 # 366 367 # rename-command CONFIG "" 368 369 370 371 ################################### LIMITS #################################### 372 373 374 375 # Set the max number of connected clients at the same time. By default there 376 377 # is no limit, and it's up to the number of file descriptors the Redis process 378 379 # is able to open. The special value '0' means no limits. 380 381 # Once the limit is reached Redis will close all the new connections sending 382 383 # an error 'max number of clients reached'. 384 385 # 386 387 # maxclients 128 388 389 maxclients 128 设置同一时间最大客户端连接数,默认无限制,Redis可以同时打开的客户端连接数为Redis进程可以打开的最大文件描述符数,如果设置 maxclients 0,表示不作限制。当客户端连接数到达限制时,Redis会关闭新的连接并向客户端返回max number of clients reached错误信息 390 391 # Don't use more memory than the specified amount of bytes. 392 393 # When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys with an 394 395 # EXPIRE set. It will try to start freeing keys that are going to expire 396 397 # in little time and preserve keys with a longer time to live. 398 399 # Redis will also try to remove objects from free lists if possible. 400 401 # 402 403 # If all this fails, Redis will start to reply with errors to commands 404 405 # that will use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue 406 407 # to reply to most read-only commands like GET. 408 409 # 410 411 # WARNING: maxmemory can be a good idea mainly if you want to use Redis as a 412 413 # 'state' server or cache, not as a real DB. When Redis is used as a real 414 415 # database the memory usage will grow over the weeks, it will be obvious if 416 417 # it is going to use too much memory in the long run, and you'll have the time 418 419 # to upgrade. With maxmemory after the limit is reached you'll start to get 420 421 # errors for write operations, and this may even lead to DB inconsistency. 422 423 # 424 425 # maxmemory <bytes> 426 427 maxmemory <bytes>指定Redis最大内存限制,Redis在启动时会把数据加载到内存中,达到最大内存后,Redis会先尝试清除已到期或即将到期的Key,当此方法处理 后,仍然到达最大内存设置,将无法再进行写入操作,但仍然可以进行读取操作。Redis新的vm机制,会把Key存放内存,Value会存放在swap区 428 429 # MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory 430 431 # is reached? You can select among five behavior: 432 433 # 434 435 # volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm 436 437 # allkeys-lru -> remove any key accordingly to the LRU algorithm 438 439 # volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set 440 441 # allkeys->random -> remove a random key, any key 442 443 # volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL) 444 445 # noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations 446 447 # 448 449 # Note: with all the kind of policies, Redis will return an error on write 450 451 # operations, when there are not suitable keys for eviction. 452 453 # 454 455 # At the date of writing this commands are: set setnx setex append 456 457 # incr decr rpush lpush rpushx lpushx linsert lset rpoplpush sadd 458 459 # sinter sinterstore sunion sunionstore sdiff sdiffstore zadd zincrby 460 461 # zunionstore zinterstore hset hsetnx hmset hincrby incrby decrby 462 463 # getset mset msetnx exec sort 464 465 # 466 467 # The default is: 468 469 # 470 471 # maxmemory-policy volatile-lru 472 473 474 475 # LRU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated 476 477 # algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can select as well the sample 478 479 # size to check. For instance for default Redis will check three keys and 480 481 # pick the one that was used less recently, you can change the sample size 482 483 # using the following configuration directive. 484 485 # 486 487 # maxmemory-samples 3 488 489 490 491 ############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ############################### 492 493 494 495 # By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. If you can live 496 497 # with the idea that the latest records will be lost if something like a crash 498 499 # happens this is the preferred way to run Redis. If instead you care a lot 500 501 # about your data and don't want to that a single record can get lost you should 502 503 # enable the append only mode: when this mode is enabled Redis will append 504 505 # every write operation received in the file appendonly.aof. This file will 506 507 # be read on startup in order to rebuild the full dataset in memory. 508 509 # 510 511 # Note that you can have both the async dumps and the append only file if you 512 513 # like (you have to comment the "save" statements above to disable the dumps). 514 515 # Still if append only mode is enabled Redis will load the data from the 516 517 # log file at startup ignoring the dump.rdb file. 518 519 # 520 521 # IMPORTANT: Check the BGREWRITEAOF to check how to rewrite the append 522 523 # log file in background when it gets too big. 524 525 526 527 appendonly no 528 529 appendonly no指定是否在每次更新操作后进行日志记录,Redis在默认情况下是异步的把数据写入磁盘,如果不开启,可能会在断电时导致一段时间内的数据丢失。因为 redis本身同步数据文件是按上面save条件来同步的,所以有的数据会在一段时间内只存在于内存中。默认为no 530 531 # The name of the append only file (default: "appendonly.aof") 532 533 # appendfilename appendonly.aof 534 535 appendfilename appendonly.aof指定更新日志文件名,默认为appendonly.aof 536 537 # The fsync() call tells the Operating System to actually write data on disk 538 539 # instead to wait for more data in the output buffer. Some OS will really flush 540 541 # data on disk, some other OS will just try to do it ASAP. 542 543 # 544 545 # Redis supports three different modes: 546 547 # 548 549 # no: don't fsync, just let the OS flush the data when it wants. Faster. 550 551 # always: fsync after every write to the append only log . Slow, Safest. 552 553 # everysec: fsync only if one second passed since the last fsync. Compromise. 554 555 # 556 557 # The default is "everysec" that's usually the right compromise between 558 559 # speed and data safety. It's up to you to understand if you can relax this to 560 561 # "no" that will will let the operating system flush the output buffer when 562 563 # it wants, for better performances (but if you can live with the idea of 564 565 # some data loss consider the default persistence mode that's snapshotting), 566 567 # or on the contrary, use "always" that's very slow but a bit safer than 568 569 # everysec. 570 571 # 572 573 # If unsure, use "everysec". 574 575 576 577 # appendfsync always 578 579 appendfsync everysec 580 581 # appendfsync no 582 583 指定更新日志条件,共有3个可选值: 584 585 no:表示等操作系统进行数据缓存同步到磁盘(快) 586 587 always:表示每次更新操作后手动调用fsync()将数据写到磁盘(慢,安全) 588 589 everysec:表示每秒同步一次(折衷,默认值) 590 591 # When the AOF fsync policy is set to always or everysec, and a background 592 593 # saving process (a background save or AOF log background rewriting) is 594 595 # performing a lot of I/O against the disk, in some Linux configurations 596 597 # Redis may block too long on the fsync() call. Note that there is no fix for 598 599 # this currently, as even performing fsync in a different thread will block 600 601 # our synchronous write(2) call. 602 603 # 604 605 # In order to mitigate this problem it's possible to use the following option 606 607 # that will prevent fsync() from being called in the main process while a 608 609 # BGSAVE or BGREWRITEAOF is in progress. 610 611 # 612 613 # This means that while another child is saving the durability of Redis is 614 615 # the same as "appendfsync none", that in pratical terms means that it is 616 617 # possible to lost up to 30 seconds of log in the worst scenario (with the 618 619 # default Linux settings). 620 621 # 622 623 # If you have latency problems turn this to "yes". Otherwise leave it as 624 625 # "no" that is the safest pick from the point of view of durability. 626 627 no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no 628 629 630 631 # Automatic rewrite of the append only file. 632 633 # Redis is able to automatically rewrite the log file implicitly calling 634 635 # BGREWRITEAOF when the AOF log size will growth by the specified percentage. 636 637 # 638 639 # This is how it works: Redis remembers the size of the AOF file after the 640 641 # latest rewrite (or if no rewrite happened since the restart, the size of 642 643 # the AOF at startup is used). 644 645 # 646 647 # This base size is compared to the current size. If the current size is 648 649 # bigger than the specified percentage, the rewrite is triggered. Also 650 651 # you need to specify a minimal size for the AOF file to be rewritten, this 652 653 # is useful to avoid rewriting the AOF file even if the percentage increase 654 655 # is reached but it is still pretty small. 656 657 # 658 659 # Specify a precentage of zero in order to disable the automatic AOF 660 661 # rewrite feature. 662 663 664 665 auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100 666 667 auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb 668 669 670 671 ################################## SLOW LOG ################################### 672 673 674 675 # The Redis Slow Log is a system to log queries that exceeded a specified 676 677 # execution time. The execution time does not include the I/O operations 678 679 # like talking with the client, sending the reply and so forth, 680 681 # but just the time needed to actually execute the command (this is the only 682 683 # stage of command execution where the thread is blocked and can not serve 684 685 # other requests in the meantime). 686 687 # 688 689 # You can configure the slow log with two parameters: one tells Redis 690 691 # what is the execution time, in microseconds, to exceed in order for the 692 693 # command to get logged, and the other parameter is the length of the 694 695 # slow log. When a new command is logged the oldest one is removed from the 696 697 # queue of logged commands. 698 699 700 701 # The following time is expressed in microseconds, so 1000000 is equivalent 702 703 # to one second. Note that a negative number disables the slow log, while 704 705 # a value of zero forces the logging of every command. 706 707 slowlog-log-slower-than 10000 708 709 710 711 # There is no limit to this length. Just be aware that it will consume memory. 712 713 # You can reclaim memory used by the slow log with SLOWLOG RESET. 714 715 slowlog-max-len 1024 716 717 718 719 ################################ VIRTUAL MEMORY ############################### 720 721 722 723 ### WARNING! Virtual Memory is deprecated in Redis 2.4 724 725 ### The use of Virtual Memory is strongly discouraged. 726 727 728 729 ### WARNING! Virtual Memory is deprecated in Redis 2.4 730 731 ### The use of Virtual Memory is strongly discouraged. 732 733 734 735 # Virtual Memory allows Redis to work with datasets bigger than the actual 736 737 # amount of RAM needed to hold the whole dataset in memory. 738 739 # In order to do so very used keys are taken in memory while the other keys 740 741 # are swapped into a swap file, similarly to what operating systems do 742 743 # with memory pages. 744 745 # 746 747 # To enable VM just set 'vm-enabled' to yes, and set the following three 748 749 # VM parameters accordingly to your needs. 750 751 752 753 vm-enabled no 754 755 指定是否启用虚拟内存机制,默认值为no,简单的介绍一下,VM机制将数据分页存放,由Redis将访问量较少的页即冷数据swap到磁盘上,访问多的页面由磁盘自动换出到内存中(在后面的文章我会仔细分析Redis的VM机制) 756 757 # vm-enabled yes 758 759 760 761 # This is the path of the Redis swap file. As you can guess, swap files 762 763 # can't be shared by different Redis instances, so make sure to use a swap 764 765 # file for every redis process you are running. Redis will complain if the 766 767 # swap file is already in use. 768 769 # 770 771 # The best kind of storage for the Redis swap file (that's accessed at random) 772 773 # is a Solid State Disk (SSD). 774 775 # 776 777 # *** WARNING *** if you are using a shared hosting the default of putting 778 779 # the swap file under /tmp is not secure. Create a dir with access granted 780 781 # only to Redis user and configure Redis to create the swap file there. 782 783 vm-swap-file /tmp/redis.swap 784 785 虚拟内存文件路径,默认值为/tmp/redis.swap,不可多个Redis实例共享 786 787 # vm-max-memory configures the VM to use at max the specified amount of 788 789 # RAM. Everything that deos not fit will be swapped on disk *if* possible, that 790 791 # is, if there is still enough contiguous space in the swap file. 792 793 # 794 795 # With vm-max-memory 0 the system will swap everything it can. Not a good 796 797 # default, just specify the max amount of RAM you can in bytes, but it's 798 799 # better to leave some margin. For instance specify an amount of RAM 800 801 # that's more or less between 60 and 80% of your free RAM. 802 803 vm-max-memory 0 804 805 将所有大于vm-max-memory的数据存入虚拟内存,无论vm-max-memory设置多小,所有索引数据都是内存存储的(Redis的索引数据 就是keys),也就是说,当vm-max-memory设置为0的时候,其实是所有value都存在于磁盘。默认值为0 806 807 # Redis swap files is split into pages. An object can be saved using multiple 808 809 # contiguous pages, but pages can't be shared between different objects. 810 811 # So if your page is too big, small objects swapped out on disk will waste 812 813 # a lot of space. If you page is too small, there is less space in the swap 814 815 # file (assuming you configured the same number of total swap file pages). 816 817 # 818 819 # If you use a lot of small objects, use a page size of 64 or 32 bytes. 820 821 # If you use a lot of big objects, use a bigger page size. 822 823 # If unsure, use the default :) 824 825 vm-page-size 32 826 827 Redis swap文件分成了很多的page,一个对象可以保存在多个page上面,但一个page上不能被多个对象共享,vm-page-size是要根据存储的 数据大小来设定的,作者建议如果存储很多小对象,page大小最好设置为32或者64bytes;如果存储很大大对象,则可以使用更大的page,如果不 确定,就使用默认值 828 829 # Number of total memory pages in the swap file. 830 831 # Given that the page table (a bitmap of free/used pages) is taken in memory, 832 833 # every 8 pages on disk will consume 1 byte of RAM. 834 835 # 836 837 # The total swap size is vm-page-size * vm-pages 838 839 # 840 841 # With the default of 32-bytes memory pages and 134217728 pages Redis will 842 843 # use a 4 GB swap file, that will use 16 MB of RAM for the page table. 844 845 # 846 847 # It's better to use the smallest acceptable value for your application, 848 849 # but the default is large in order to work in most conditions. 850 851 vm-pages 134217728 852 853 设置swap文件中的page数量,由于页表(一种表示页面空闲或使用的bitmap)是在放在内存中的,,在磁盘上每8个pages将消耗1byte的内存。 854 855 # Max number of VM I/O threads running at the same time. 856 857 # This threads are used to read/write data from/to swap file, since they 858 859 # also encode and decode objects from disk to memory or the reverse, a bigger 860 861 # number of threads can help with big objects even if they can't help with 862 863 # I/O itself as the physical device may not be able to couple with many 864 865 # reads/writes operations at the same time. 866 867 # 868 869 # The special value of 0 turn off threaded I/O and enables the blocking 870 871 # Virtual Memory implementation. 872 873 vm-max-threads 4 874 875 设置访问swap文件的线程数,最好不要超过机器的核数,如果设置为0,那么所有对swap文件的操作都是串行的,可能会造成比较长时间的延迟。默认值为4 876 877 ############################### ADVANCED CONFIG ############################### 878 879 880 881 # Hashes are encoded in a special way (much more memory efficient) when they 882 883 # have at max a given numer of elements, and the biggest element does not 884 885 # exceed a given threshold. You can configure this limits with the following 886 887 # configuration directives. 888 889 hash-max-zipmap-entries 512 890 891 hash-max-zipmap-value 64 892 893 指定在超过一定的数量或者最大的元素超过某一临界值时,采用一种特殊的哈希算法 894 895 # Similarly to hashes, small lists are also encoded in a special way in order 896 897 # to save a lot of space. The special representation is only used when 898 899 # you are under the following limits: 900 901 list-max-ziplist-entries 512 902 903 list-max-ziplist-value 64 904 905 906 907 # Sets have a special encoding in just one case: when a set is composed 908 909 # of just strings that happens to be integers in radix 10 in the range 910 911 # of 64 bit signed integers. 912 913 # The following configuration setting sets the limit in the size of the 914 915 # set in order to use this special memory saving encoding. 916 917 set-max-intset-entries 512 918 919 920 921 # Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded in 922 923 # order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the length and 924 925 # elements of a sorted set are below the following limits: 926 927 zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 928 929 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 930 931 932 933 # Active rehashing uses 1 millisecond every 100 milliseconds of CPU time in 934 935 # order to help rehashing the main Redis hash table (the one mapping top-level 936 937 # keys to values). The hash table implementation redis uses (see dict.c) 938 939 # performs a lazy rehashing: the more operation you run into an hash table 940 941 # that is rhashing, the more rehashing "steps" are performed, so if the 942 943 # server is idle the rehashing is never complete and some more memory is used 944 945 # by the hash table. 946 947 # 948 949 # The default is to use this millisecond 10 times every second in order to 950 951 # active rehashing the main dictionaries, freeing memory when possible. 952 953 # 954 955 # If unsure: 956 957 # use "activerehashing no" if you have hard latency requirements and it is 958 959 # not a good thing in your environment that Redis can reply form time to time 960 961 # to queries with 2 milliseconds delay. 962 963 # 964 965 # use "activerehashing yes" if you don't have such hard requirements but 966 967 # want to free memory asap when possible. 968 969 activerehashing yes 970 971 972 973 ################################## INCLUDES ################################### 974 975 976 977 # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you 978 979 # have a standard template that goes to all redis server but also need 980 981 # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include 982 983 # other files, so use this wisely. 984 985 # 986 987 # include /path/to/local.conf 988 989 # include /path/to/other.conf
