Description
Background
Regardless of the fact, that Vologda could not get rights to hold the Winter Olympic games of 20**, it is well-known, that the city will conduct one of the Formula 1 events. Surely, for such an important thing a new race circuit should be built as well as hotels, restaurants, international airport - everything for Formula 1 fans, who will flood the city soon. But when all the hotels and a half of the restaurants were built, it appeared, that at the site for the future circuit a lot of gophers lived in their holes. Since we like animals very much, ecologists will never allow to build the race circuit over the holes. So now the mayor is sitting sadly in his office and looking at the map of the circuit with all the holes plotted on it.
Problem
Who will be smart enough to draw a plan of the circuit and keep the city from inevitable disgrace? Of course, only true professionals - battle-hardened programmers from the first team of local technical university!.. But our heroes were not looking for easy life and set much more difficult problem: "Certainly, our mayor will be glad, if we find how many ways of building the circuit are there!" - they said.
It should be said, that the circuit in Vologda is going to be rather simple. It will be a rectangle N* Mcells in size with a single circuit segment built through each cell. Each segment should be parallel to one of rectangle's sides, so only right-angled bends may be on the circuit. At the picture below two samples are given for N = M = 4 (gray squares mean gopher holes, and the bold black line means the race circuit). There are no other ways to build the circuit here.
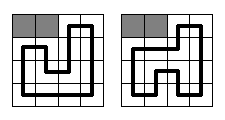
Input
The first line contains the integer numbers N and M (2 ≤ N, M ≤ 12). Each of the next N lines contains M characters, which are the corresponding cells of the rectangle. Character "." (full stop) means a cell, where a segment of the race circuit should be built, and character "*" (asterisk) - a cell, where a gopher hole is located.
Output
You should output the desired number of ways. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 2 63-1.
Sample Input
| input | output |
|---|---|
4 4 **.. .... .... .... |
2 |
4 4 .... .... .... .... |
6 |
Source
Problem Author: Nikita Rybak, Ilya Grebnov, Dmitry Kovalioff
Problem Source: Timus Top Coders: Third Challenge
Problem Source: Timus Top Coders: Third Challenge
注意long long...回路的题貌似还是比较简单的。。

1 #include<queue> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 using namespace std; 8 const int N = 531450; 9 const int Hash = 10007; 10 #define nxt (cur^1) 11 #define For(i,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 12 #define Rep(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) 13 #define Down(i,r,l) for(int i=r;i>=l;i--) 14 struct statedp{ 15 int size,head[Hash],next[N],st[N]; 16 long long f[N]; 17 void clear(){size=0;memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));} 18 void push(int state,long long ans){ 19 int Key = state % Hash; 20 for(int p=head[Key];p!=-1;p=next[p]) 21 if(st[p]==state) {f[p]+=ans;return;} 22 f[size]=ans;st[size]=state; 23 next[size]=head[Key];head[Key]=size++; 24 } 25 }dp[2]; 26 char ch; 27 int n,m,code[15],maze[15][15],Sx,Sy; 28 long long ans; 29 30 void init(){ 31 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 32 For(i,n){ 33 scanf(" "); 34 For(j,m){ 35 scanf("%c",&ch); 36 if(ch=='.') {maze[i][j] = 0;Sx=i;Sy=j;} 37 else maze[i][j] = 1; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 void decode(int st){ 43 Down(i,m,0) code[i]=st&3,st>>=2; 44 } 45 46 int encode(){ 47 int ret = 0; 48 Rep(i,0,m) ret = ret << 2 | code[i]; 49 return ret; 50 } 51 52 void shift(){ 53 Down(j,m,1) code[j] = code[j-1];code[0]=0; 54 } 55 56 void dpblock(int i,int j,int cur){ 57 int Lim = (j==m)?(2):(0); 58 int quick = (1<<(2*m+2-Lim))-1; 59 Rep(k,0,dp[cur].size-1) 60 dp[nxt].push((dp[cur].st[k]>>Lim)%quick,dp[cur].f[k]); 61 } 62 63 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cur){ 64 Rep(k,0,dp[cur].size-1){ 65 decode(dp[cur].st[k]); 66 int Left = code[j-1] , Up = code[j]; 67 if(Left && Up){ 68 if(Left==2&&Up==1){ 69 if(i!=Sx || j!=Sy) continue; 70 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 71 ans+=dp[cur].f[k]; 72 continue; 73 } 74 else if(Left==2&&Up==2){ 75 code[j-1] = code[j] = 0;int KH = 1; 76 Rep(kh,j+1,m){ 77 if(code[kh]==2) KH++; 78 if(code[kh]==1) KH--; 79 if(!KH){code[kh]=3-code[kh];break;} 80 } 81 } 82 else if(Left==1&&Up==1){ 83 code[j-1] = code[j] = 0; int KH = 1; 84 Down(kh,j-2,0){ 85 if(code[kh]==2) KH--; 86 if(code[kh]==1) KH++; 87 if(!KH) {code[kh]=3-code[kh];break;} 88 } 89 } 90 else code[j-1] = code[j] = 0; 91 if(j==m) shift(); 92 dp[nxt].push(encode(),dp[cur].f[k]); 93 } 94 else if(Left || Up){ 95 int CODE = Left | Up; 96 if( (i<n) && (!maze[i+1][j])){ 97 code[j-1] = CODE; code[j] = 0; 98 if(j==m) shift(); 99 dp[nxt].push(encode(),dp[cur].f[k]); 100 } 101 if( (j<m) && (!maze[i][j+1])){ 102 code[j] = CODE; code[j-1] = 0; 103 dp[nxt].push(encode(),dp[cur].f[k]); 104 } 105 } 106 else { 107 if((i<n) && (j<m) && (!maze[i+1][j]) && (!maze[i][j+1])){ 108 code[j-1] = 2; code[j] = 1; 109 dp[nxt].push(encode(),dp[cur].f[k]); 110 } 111 } 112 } 113 } 114 115 void DP(){ 116 int cur = 0;dp[cur].clear(); 117 dp[cur].push(0,1); 118 For(i,n) 119 For(j,m){ 120 dp[nxt].clear(); 121 if(maze[i][j]) dpblock(i,j,cur); 122 else dpblank(i,j,cur); 123 cur^=1; 124 } 125 printf("%I64d ",ans); 126 } 127 128 int main(){ 129 init(); 130 DP(); 131 return 0; 132 }
